Preparation method of self-repair thermosetting epoxy resin based on disulfide bond exchange
A technology of epoxy resin and disulfide bond, which is applied in the field of preparation of self-healing thermosetting epoxy resin based on disulfide bond exchange, can solve the problem of harsh conditions and reconfigurable thermosetting resin system limited to laboratory stage and other problems , to achieve the effect of low cost, favorable for large-scale production and excellent mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030] The preparation method of thermosetting epoxy resin containing disulfide bonds is characterized in that it has the following classic steps:
[0031] Step 1: Synthesis of epoxy resin containing disulfide bonds:
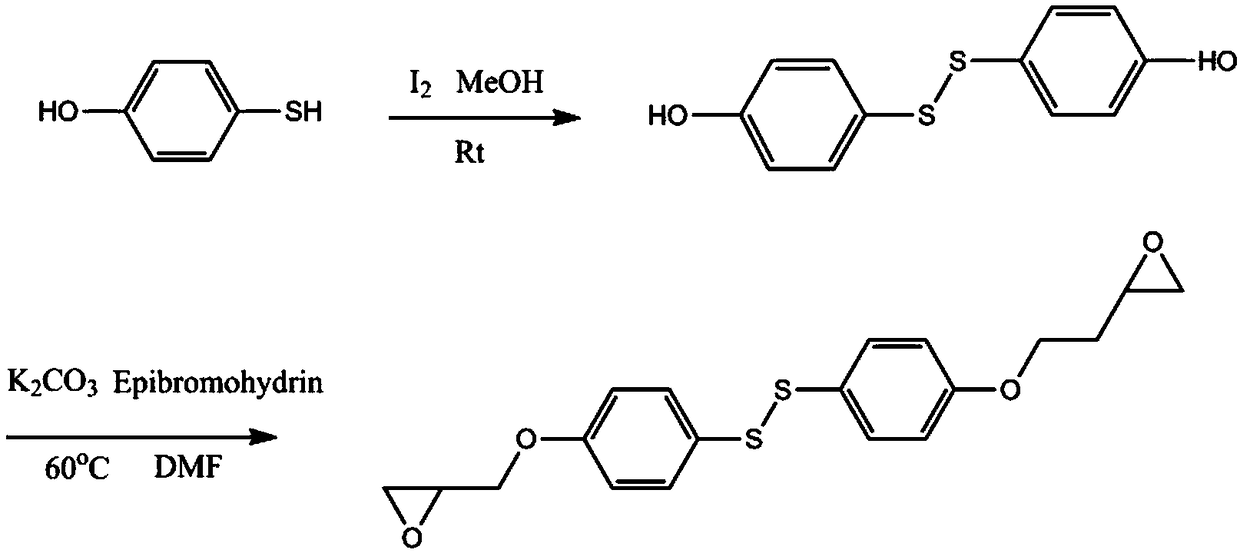
[0032] Step a1: Add 4-mercaptophenol and methyl alcohol successively in a container equipped with a magnetic stirrer, and slowly add iodine simple substance (I 2 ), react overnight at room temperature. 4-Mercaptophenol monomer and I 2 The molar ratio of methanol is 1:0.2-0.6, and the mass ratio of methanol to 4-mercaptophenol monomer is 6-10:1.
[0033] Step b1: After confirming the completion of the reaction by TLC, add anhydrous sodium sulfite to the system until the solution fades to pale yellow, then rotatively evaporate and control the temperature at 30-50°C. After the solvent was completely removed, 100-300 mL of deionized water was added to the system, and extracted three times with ethyl acetate. The organic phase was washed with saturated brine for ...
specific Embodiment
[0039] Step 1: Synthesis of epoxy resin monomer containing disulfide bonds:
[0040] First: add 30g of 4-mercaptophenol, 300ml methyl alcohol successively in the container that magnetic stirrer is housed and slowly add 30.5g iodine simple substance (I 2 ) element, and react overnight at room temperature. After the completion of the reaction was confirmed by TLC, 3 g of anhydrous sodium sulfite was added to the system until the solution faded to light yellow, and the rotary evaporation was performed with the temperature controlled at 30-50 ° C. After the solvent was completely removed, 200 mL of deionized water was added to the system, and the Ethyl ester extracted 3 times. The organic phase was washed with saturated brine for 3 times, dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate, filtered, and then the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain the product bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)disulfide.
Embodiment 1
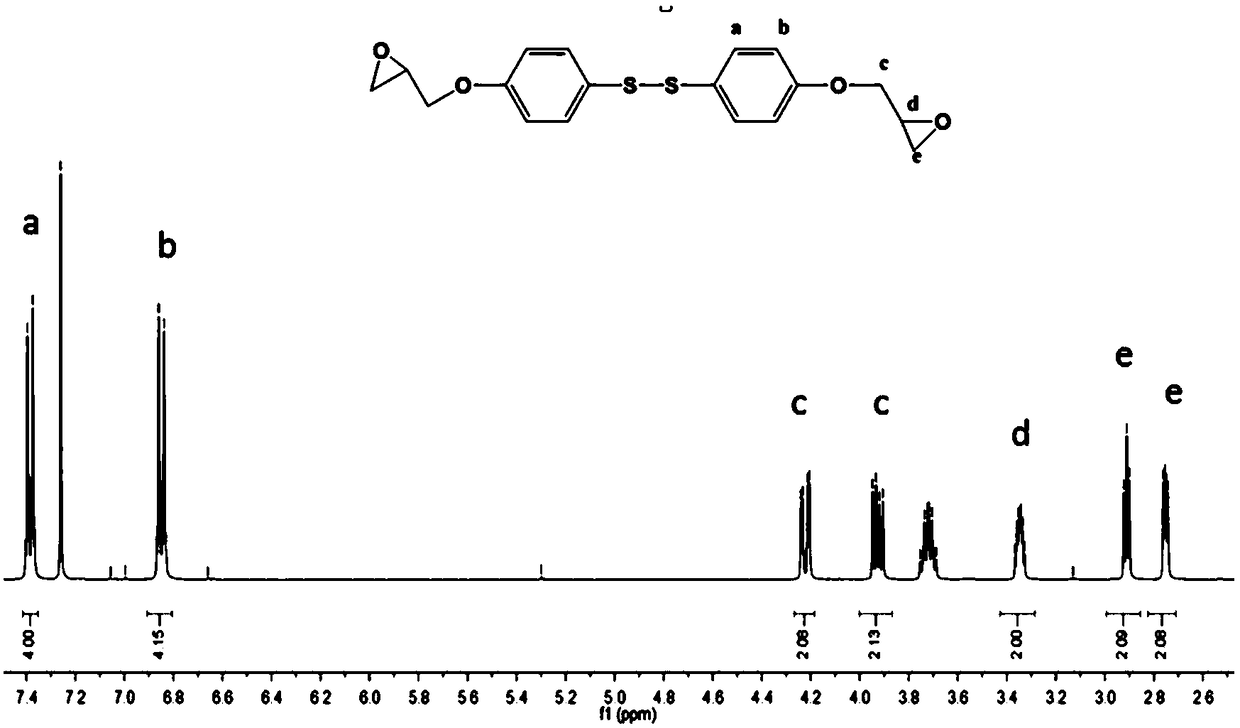
[0041] Embodiment 1: In the container that magnetic stirrer is housed, add the double (4-hydroxyphenyl) disulfide of 4.83g successively, 200mlDMF, 17.7ml epibromohydrin, 27.5g anhydrous potassium carbonate, ventilate After 3 times, at N 2 The reaction was carried out at 60°C under protection for 4h. After the completion of the reaction was confirmed by TLC, 300 mL of deionized water was added to the system, extracted three times with dichloromethane, the organic phase was washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and the dichloromethane was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain a crude product. The crude product was recrystallized in methanol, filtered and dried to obtain 5.7 g of bis(4-glycidyloxyphenyl) disulfide as a white solid.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com