Milbemycin synthetic positive-regulation gene kelR, encoding protein and genetically engineered bacterium and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of milbemycin and genetically engineered bacteria, which is applied in genetic engineering, botany equipment and methods, and methods based on microorganisms, can solve the problems of not finding regulatory genes, increase production, reduce production costs, and improve economic efficiency. benefit effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1. Research on the function of milbemycin synthesis positively regulating gene kelR.
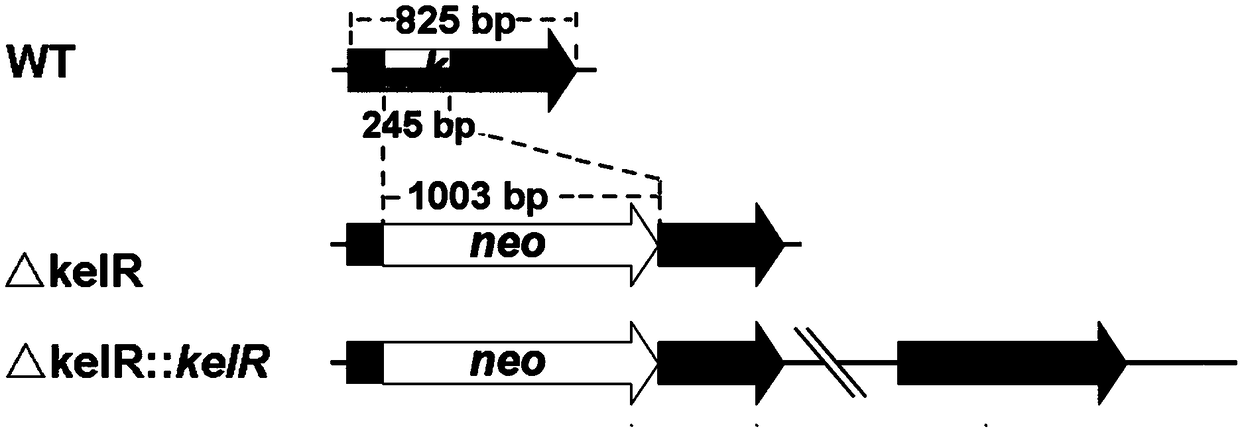
[0040] 1. Construction of milbemycin synthesis positive regulatory gene kelR blocking mutant strain
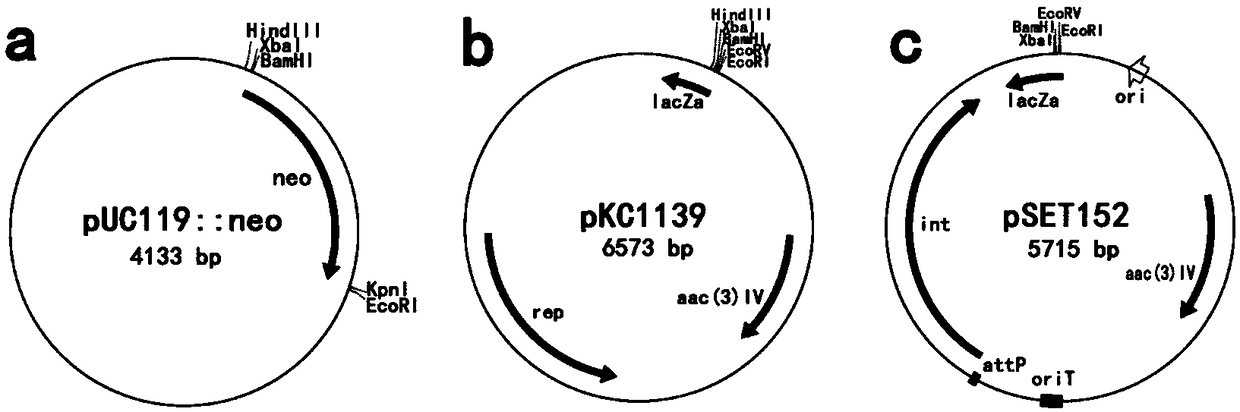
[0041] Using primers 6842up-f / 6842up-r from Streptomyces bingchenggensis BCWT (the Streptomyces bingchenggensis BCWT is recorded in Gao Aili, Wang Xiangjing, et al. (2007). "Screening and identification of new species of Streptomyces hygroscopicus." Northeast Agriculture University Journal 38(3):361-364.) PCR amplification on the genome obtained the homologous recombination left arm fragment of the kelR gene, ie the upstream fragment of kelR.
[0042] Using primers 6842down-f / 6842down-r, the right arm fragment of kelR gene homologous recombination, namely the downstream fragment of kelR, was obtained by PCR amplification from Streptomyces bingchenggensis BCWT genome.
[0043] The Streptomyces bingchenggensis BCWT genomic DNA was extracted according to the method described in ...
Embodiment 2
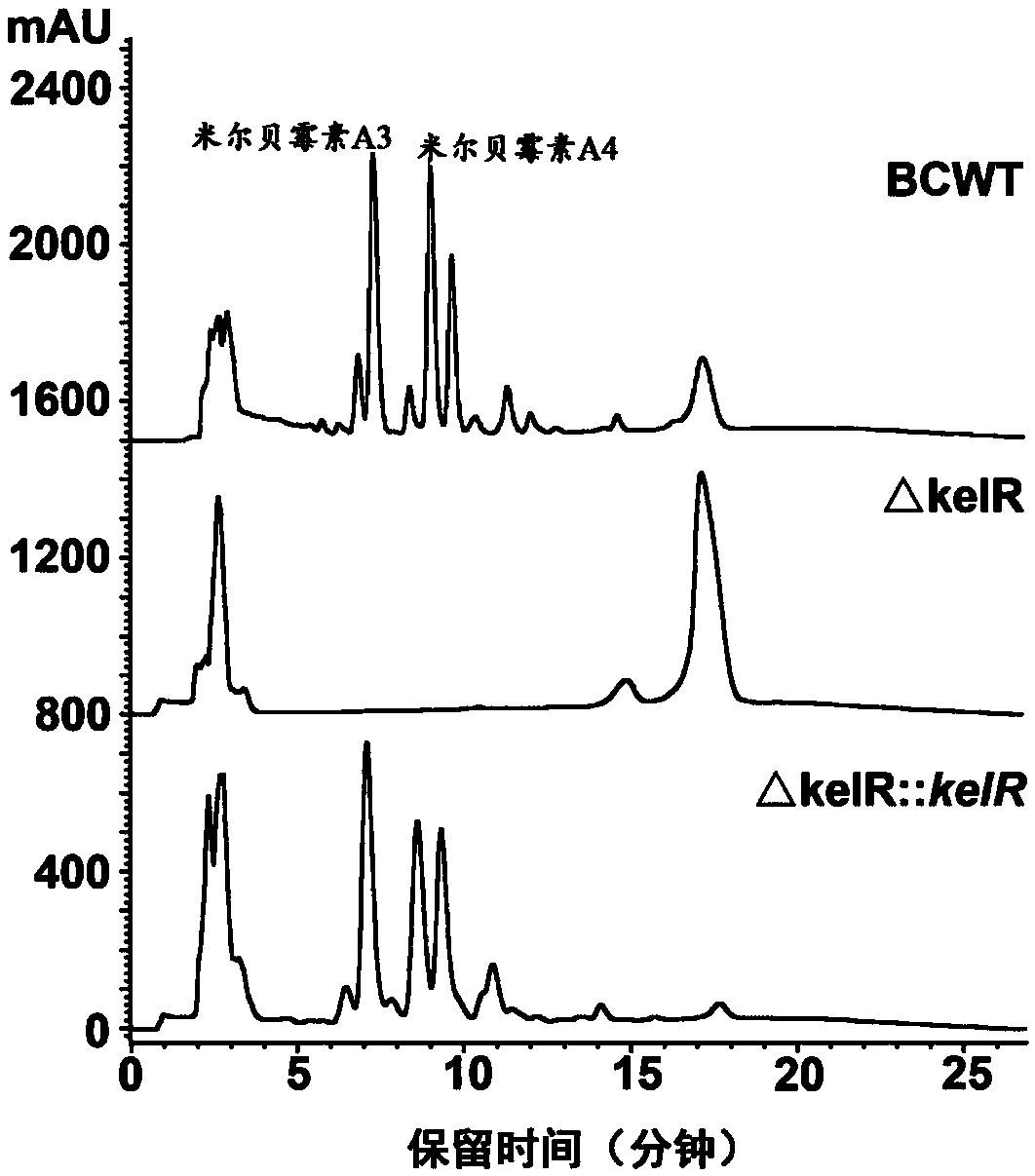
[0073] Example 2. Analysis of milbemycin synthesis of milbemycin synthesis positive regulatory gene kelR blocking mutant strain and anaplerotic mutant strain.
[0074] 1. Fermentation culture adopts the following medium
[0075] Seed medium (1L): sucrose 10g, skim milk powder 1g, peptone 3.5g, yeast extract powder 5g, K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O0.5g, distilled water 1L, pH 7.0. 121°C, 1.01×10 5 Pa sterilized for 20 minutes.
[0076] Fermentation medium (1L): 80g sucrose, 20g soybean cake powder, 1g skimmed milk powder, K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O 1g, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.1g, CaCO 3 3g, 1L distilled water, pH 7.0-7.2. 121℃, 1.01×10 5 Pa sterilized for 30 minutes.
[0077] 2. Fermentation process
[0078] The pre-prepared spores of Streptomyces bingchenggensis BCWT, the knockout mutant strain ΔkelR and the complementation mutant strain ΔkelR::kelR prepared above were activated by streaking on the MS plate, and scooped out about 2 cm 2 The mycelium block was inoculated into a Erlenmeyer fl...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Example 3. Construction of high-yielding milbemycin genetically engineered bacteria.
[0090] Transform the recombinant vector pSET152::kelR used in Example 1 into E.coli ET12567\pUZ8002 competent cells to obtain E.coli ET12567\pUZ8002 transformants containing pSET152::kelR, and transfer pSET152 :: kelR is transferred into Streptomyces bingchenggensis BC-120-4 bacterial strain (the BC-120-4 bacterial strain is recorded in Wang H et al. Combined application of plasma mutagenesis and gene engineering leads to 5-oxomilbemycins A3 / A4as main components fromStreptomyces bingchenggensis.Applied microbiology and biotechnology.2014;98:9703-9712), the specific process is:
[0091] The competent state of Escherichia coli ET12567\pUZ8002 was prepared, and the preparation method was described in the Streptomyces Genetic Operation Manual. The constructed plasmid was transformed into competent cells of ET12567\pUZ8002; spread on the LB medium plate containing Apr antibiotics, cultiva...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com