Method for generating biogas by fermenting pig excrement of pig farm and plants
A plant fermentation and pig manure technology, applied in fermentation, waste fuel, biological sludge treatment, etc., can solve the problems of long and uncontrollable process, and achieve the goal of improving the utilization rate of raw materials, rapid processing, and improving the efficiency of biogas production Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] A method for generating biogas by fermenting pig manure and plants in a pig farm, comprising the following steps:
[0025] Step S1, crush fresh sweet potato stalks to 0.6 cm, place the crushed sweet potato stalks in an airtight container, add catalyst A accounting for 10% of the dry weight of the crushed plant stalks and mix evenly, pretreat at a temperature of 40°C for 5 hours; then add Catalyst B which accounts for 10% of the dry weight of the crushed plant stalks and mix evenly, at a temperature of 45°C, use semi-closed pre-degradation for 5 days, after solid-liquid separation, to obtain the pretreated white sweet potato stalks, fresh The water content of the white sweet potato stalk is 67% by mass percentage,
[0026] Described catalyst A is the mixed solution of sodium dodecylsulfonate, sodium edetate, sodium chloride and hydrogen peroxide, and the concentration of sodium dodecylsulfonate in catalyst A is 0.8wt%, and B The concentration of sodium diamine tetraacet...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The method for generating biogas by fermenting pig manure from a pig farm with plants described in Example 1, the difference is that:
[0035] In step S1, take the naturally dried sweet potato stalks and crush them to 0.6 cm. After natural drying, the water content of the white sweet potato stalks is 17% by mass. The crushed white sweet potato stalks are placed in an airtight container, and added Catalyst A with 8% of the dry weight of the crushed plant stalks was mixed evenly, and pretreated at a temperature of 40° C. for 10 hours; Closed pre-degradation for 10 days, and solid-liquid separation to obtain pretreated sweet potato stalks.
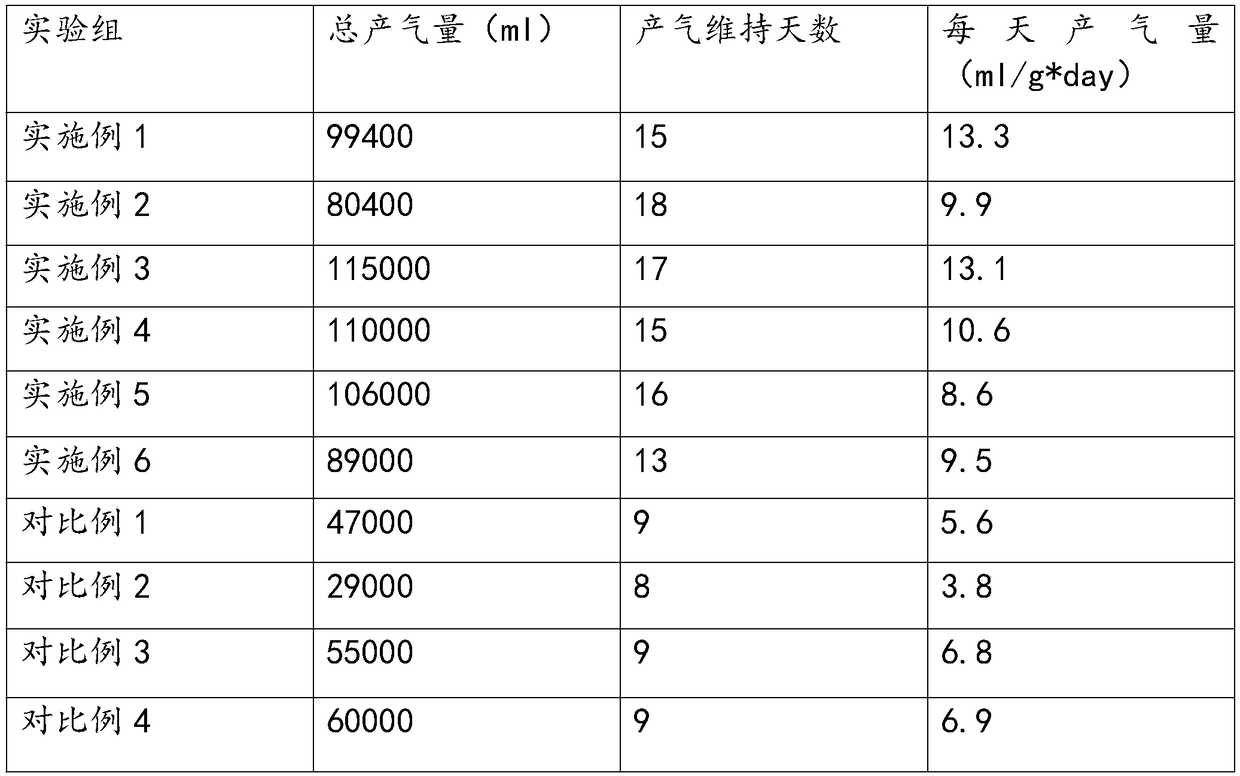
[0036] The biogas production and other indicators were measured every day. After 20 days of anaerobic fermentation, the total production in this example was 80400 mL, the gas production was 9.9 mL / g*day, and the methane content was 57%.
Embodiment 3
[0038] The method for generating biogas by fermenting pig manure from a pig farm with plants described in Example 1, the difference is that:
[0039] In step S1, crush fresh sweet potato stalks to 0.7 cm, the concentration of sodium dodecylsulfonate in catalyst A is 0.8 wt%, the concentration of sodium edetate is 0.5 wt%, and the concentration of hydrogen peroxide is 0.8 wt%.
[0040] The concentration of magnesium sulfate in catalyst B is 0.08wt%, the concentration of iron sulfate is 0.03wt%, and the concentration of lactic acid is 0.4wt%.
[0041] Step S2, taking 300 g of the pretreated white sweet potato stalks in step S1 and mixing them with 300 g of fresh pig manure, adding water and stirring evenly, adjusting the moisture content to 84%, and adjusting the C / N ratio to 28:1 to obtain a mixed solution;
[0042] Step S3, add 300g of activated sludge as an inoculum to the mixed solution in step S2, adjust the pH value to 7.8, place in a 10m3 fully mixed anaerobic reactor, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com