Method for extracting chitin by comprehensively treating and utilizing shrimp and crab shells
A technology for comprehensive treatment of shrimp and crab shells, applied in the field of comprehensive treatment and utilization of shrimp and crab shells to extract chitin, can solve problems such as pollution, resource waste, resource waste, and environmental pollution, and achieve high utilization value, controllable costs, and structural damage small effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
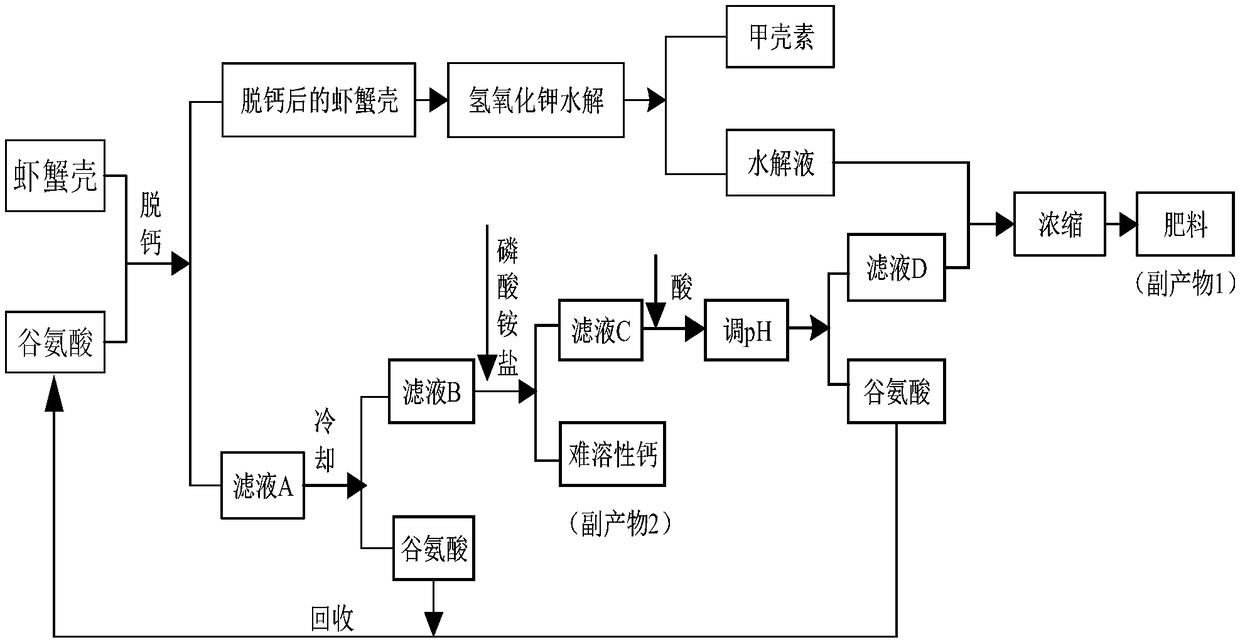
[0024] The comprehensive treatment of embodiment 1 utilizes the method for extracting chitin from shrimp and crab shells, and its flow chart is shown in figure 1 , including the following steps:
[0025] Step 1, raw material pretreatment: take 500g of discarded crab shells, wash and break;
[0026] Step 2, decalcification: Put the crushed crab shells into 5000mL glutamic acid solution with a concentration of 5%, stir and react at a temperature of 75°C for 4-10 hours, and replace once with a new 5000mL solution with a concentration of 5% glutamic acid solution, continue to stir and react at a temperature of 75° C. for 2 to 6 hours, decalcify the crab shells, and filter while hot to obtain filtrate A containing calcium glutamate and decalcified crab shells;
[0027] Step 3, deproteinization: mix decalcified crab shells with 5% potassium hydroxide solution at a solid-liquid ratio of 1:8, react at a temperature of 90°C for 6 hours, and hydrolyze and deproteinize crab shells. Fil...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The comprehensive treatment of embodiment 2 utilizes the method for extracting chitin from shrimp and crab shells, and its flow chart is shown in figure 1 , including the following steps:
[0034] Step 1, raw material pretreatment: take 500g of discarded crab shells, wash and break;
[0035] Step 2, decalcification: Put the broken crab shells into 4000mL of glutamic acid solution with a concentration of 6.5%, soak and react for 4-8 hours at a temperature of 80°C, and replace once with a new 4000mL solution with a concentration of 6.5% glutamic acid solution, continue to soak and react at a temperature of 80°C for 2 to 6 hours, decalcify the crab shells, and filter while hot to obtain filtrate A containing calcium glutamate and decalcified crab shells;
[0036] Step 3, deproteinization: mix decalcified crab shells with potassium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 7.5% at a ratio of 1:6, and react at a temperature of 85°C for 4 hours to hydrolyze and deproteinize...
Embodiment 3
[0042] The comprehensive treatment of embodiment 3 utilizes the method for extracting chitin from shrimp and crab shells, and its flow chart is shown in figure 1 , including the following steps:
[0043] Step 1, raw material pretreatment: Weigh 500g of discarded shrimp and crab shells, wash and break;
[0044] Step 2. Decalcification: Put the broken shrimp and crab shells into 3000mL glutamic acid solution with a concentration of 7.5%, and react with gas blowing at 85°C for 4-12 hours, then replace with a new 3000mL glutamic acid solution once. The glutamic acid solution with a concentration of 7.5% is continuously aerated at a temperature of 85°C for 4 to 8 hours, and the shrimp and crab shells are decalcified, filtered while hot, and the filtrate A containing calcium glutamate and the decalcified filtrate are obtained. Shrimp and crab shells;
[0045] Step 3, deproteinization: mix the decalcified shrimp and crab shells with 6% potassium hydroxide solution at a ratio of 1:7...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com