Method of recycling zinc from zinc ferrite resource by using calcium roasting-ammonia leaching process
A technology of calcification roasting and zinc ferrite, which is applied in the field of zinc recovery, can solve the problems of not developing a method for the clean and efficient utilization of zinc ferrite resources, the utilization rate of less than 20%, and the inability to effectively recover and utilize the zinc ferrite resource. The effect of easy leaching, filtration and separation, fast reaction rate and low leaching cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
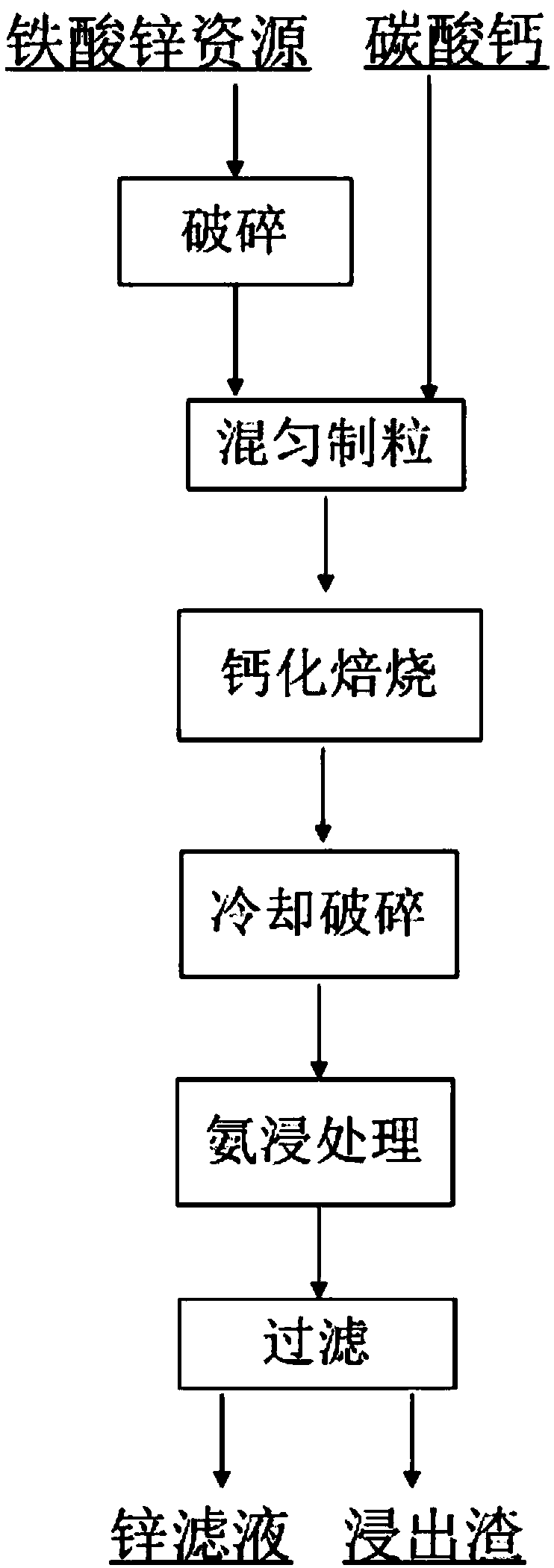
[0030] Zinc-containing dust (TZn 5.67%, ZnFe 2 o 4 55.72%), crush the raw ore to -1mm, add calcium carbonate, control the molar ratio of effective CaO content in calcium carbonate to zinc ferrite to 2.4:1, mix well and granulate into small balls of 3-20mm, mix The material is placed in a rotary kiln for calcification and roasting to complete the reconstruction of mineral phases. The roasting temperature is 1220°C, the roasting time is 120 minutes, cooled naturally, broken to -3mm, and then subjected to ammonia leaching treatment. The ammonia leaching system is: the solid-liquid ratio is 100g / L, the leaching temperature is 40°C, the leaching time is 120min, and the leaching solution is NH 4 Cl-NH 3 ·H 2 O solution (NH 4 Cl and NH 3 ·H 2 The molar concentration ratio of O is 1:1), the total ammonia concentration in the leaching solution is 6mol / L, and the zinc leaching rate is 93.65% after the leaching solution is filtered.
Embodiment 2
[0032] Zinc-containing dust (TZn 5.67%, ZnFe 2 o 4 55.72%), crush the raw ore to -1mm, add calcium carbonate, control the molar ratio of effective CaO content in calcium carbonate to zinc ferrite to 2.4:1, mix well and granulate into small balls of 3-20mm, mix The material is placed in a rotary kiln for calcification and roasting to complete the reconstruction of mineral phases. The roasting temperature is 1240 ° C, the roasting time is 120 minutes, natural cooling, crushed to -3mm, and ammonia leaching treatment. The ammonia leaching system is: the solid-liquid ratio is 120g / L, the leaching temperature is 40°C, the leaching time is 100min, and the leaching solution is NH 4 Cl-NH 3 ·H 2 O solution (NH 4 Cl and NH 3 ·H 2 The molar concentration ratio of O is 1:1), the total ammonia concentration in the leaching solution is 6mol / L, and the zinc leaching rate is 93.31% after the leaching solution is filtered.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Zinc-containing dust (TZn 5.67%, ZnFe 2 o 4 55.72%), crush the raw ore to -1mm, add calcium oxide, control the molar ratio of effective CaO content to zinc ferrite to 2.5:1, mix well and granulate into small balls of 3-20mm, place the mixture in Carry out calcification and roasting in a rotary kiln to complete mineral phase reconstruction. The roasting temperature is 1220°C and the roasting time is 120 minutes. Natural cooling, crushing to -3mm, and ammonia leaching treatment are carried out. The ammonia leaching system is: the solid-to-liquid ratio is 100g / L, The leaching temperature is 60°C, the leaching time is 110min, and the leaching solution is NH 4 Cl-NH 3 ·H 2 O solution (NH 4 Cl and NH 3 ·H 2 The molar concentration ratio of O is 1:1), the total ammonia concentration in the leaching solution is 6mol / L, and the zinc leaching rate is 94.71% after the leaching solution is filtered.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com