Lignin/microcrystalline cellulose complex, reinforced polylactic acid 3D printing material and preparation method thereof
A microcrystalline cellulose and 3D printing technology, applied in the direction of additive processing, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to use lignin and poor compatibility of cellulose, and achieve the goal of improving poor compatibility, good compatibility and wide application range Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] A preparation method of reinforced polylactic acid 3D printing material, comprising the following steps:
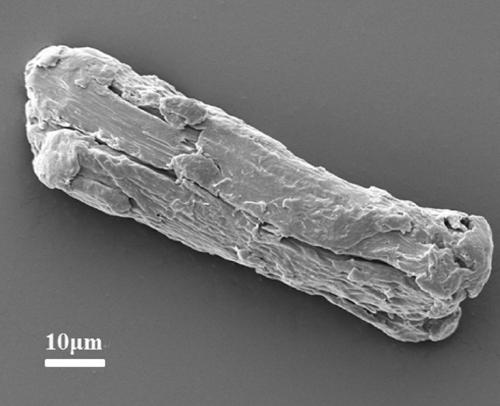
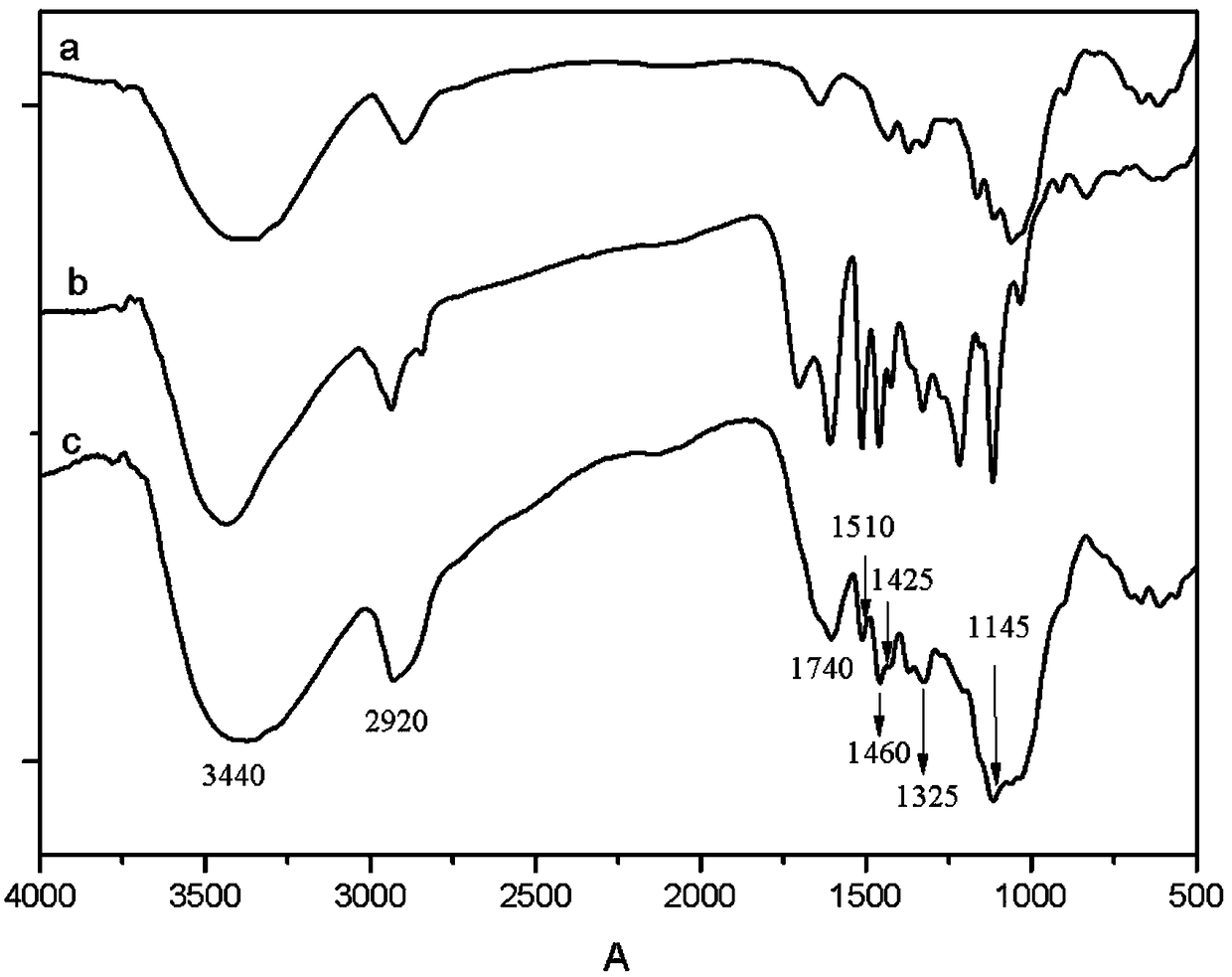
[0041] (1) Pulverize the ordinary cellulose made from cotton fiber and pass it through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain cellulose powder with uniform particle size; then use 30% sulfuric acid solution to acidify the cellulose for 8 h, filter to remove the amorphous cellulose, Dry in an oven at 80°C for 12 h to obtain microcrystalline cellulose, whose infrared spectrum and scanning electron microscope photos are shown in figure 1 a and figure 2 ;
[0042] (2) Mix the microcrystalline cellulose obtained in step (1) with ethanol at a mass ratio of 1:2. The mixture was placed in a water bath at 80°C for 0.5 h to a constant temperature, and then silane coupling agent KH550 and organic solvent lignin (infrared The spectra and scanning electron microscope pictures are shown in figure 1 b and image 3 ), stirred and reacted for 4 h at a constant temperature of 80 °C under ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] A preparation method of reinforced polylactic acid 3D printing material, comprising the following steps:
[0051] (1) Pulverize the ordinary cellulose made from flax fiber and pass through a 150-mesh sieve to obtain cellulose powder with uniform particle size; then acidify the cellulose with 30% hydrochloric acid solution for 8 h, and filter to remove the amorphous cellulose, drying in an oven at 80°C for 12 h to obtain microcrystalline cellulose;
[0052] (2) Mix the microcrystalline cellulose obtained in step (1) with ethanol at a mass ratio of 1:3. Place this mixture in a water bath at 80°C for 0.5 h to a constant temperature, then add silane coupling agent KH560 and sulfuric acid lignin at a ratio of 1:5 and 1:5 to microcrystalline cellulose, respectively, at 80°C Stir the reaction at a constant temperature of ℃ and under sealed conditions for 5 h;
[0053] (3) Filter the viscous mixture obtained in step (2), wash it with ethanol until the washing liquid is transp...
Embodiment 3
[0057] A preparation method of reinforced polylactic acid 3D printing material, comprising the following steps:
[0058] (1) Pulverize the ordinary cellulose made from jute fiber and pass it through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain cellulose powder with uniform particle size; then use 30% phosphoric acid solution to acidify the cellulose for 10 h, filter to remove the amorphous cellulose, drying in an oven at 80°C for 12 h to obtain microcrystalline cellulose;
[0059] (2) Mix the microcrystalline cellulose obtained in step (1) with ethanol at a mass ratio of 1:2. Place this mixture in a water bath at 80°C for 0.5 h to a constant temperature, then add silane coupling agent KH570 and alkali lignin at a ratio of 1:5 and 1:3 to microcrystalline cellulose, respectively, at 80°C The reaction was stirred at a constant temperature of ℃ and sealed for 6 h.
[0060] (3) Filter the viscous mixture obtained in step (2), wash it with ethanol until the washing liquid is transparent and colorle...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com