Preparation method of vanadium tetrasulfide/carbon nanotube as negative electrode material for sodium ion battery
A sodium-ion battery and negative electrode material technology, which is applied in the direction of battery electrodes, negative electrodes, secondary batteries, etc., can solve the problems of easy deposition of compounds on the surface of particles, reduce the electrochemical performance of materials, and reduce the conductivity of materials, so as to shorten the ion Diffusion distance, stable Coulombic efficiency, and low cost effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] (1) Add 0.5mmol (58.5mg) ammonium metavanadate to 10mL ultrapure water, heat to 65°C, and keep stirring at 450 rpm until dissolved, then add 2.5mmol (187.5mg) thioethyl Amide, heated to 55°C, and kept stirring at 550 rpm until dissolved to obtain solution A;
[0040] (2) Add 2 mmol (24 mg) of multi-walled carbon nanotubes into 15 mL of ultrapure water, and ultrasonicate for 5 h at 450 W until the CNTs are uniformly dispersed to obtain suspension B;
[0041] (3) Add solution A obtained in step (1) into suspension B, and continue stirring at 500 rpm for 2.5 hours to obtain suspension C;
[0042] (4) Heat the suspension C obtained in step (3), conduct a hydrothermal reaction at 160°C for 24 hours, then cross-wash with deionized water and ethanol for 5 times, centrifuge at 7000 rpm, and then place at 60°C , and dried for 16 hours to obtain vanadium tetrasulfide / carbon nanotubes, a negative electrode material for sodium ion batteries.
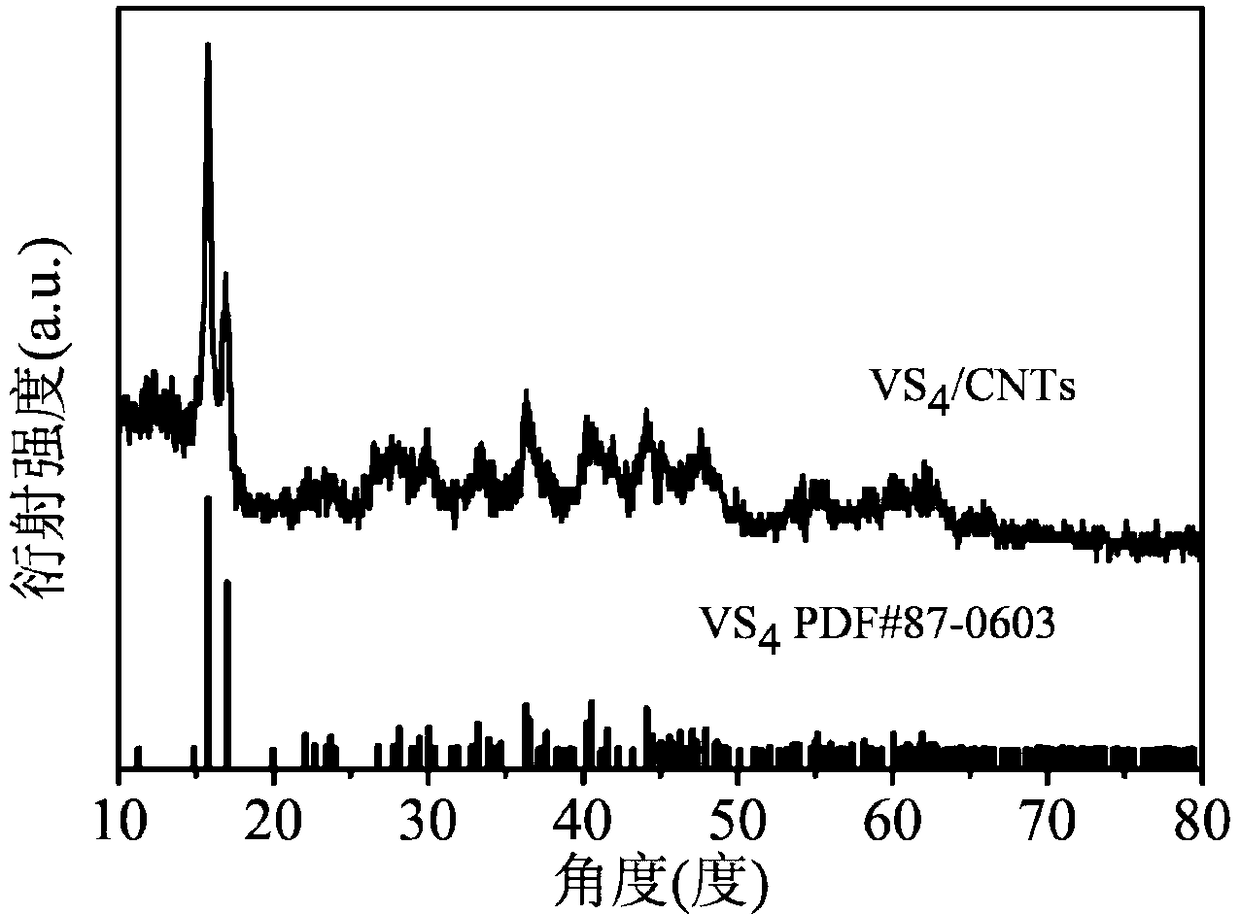
[0043] Such as figure 1 As shown, the...
Embodiment 2
[0050] (1) Add 0.1mmol (13.8mg) potassium metavanadate to 10mL ultrapure water, heat to 70°C, and keep stirring at 550 rpm until dissolved, then add 0.55mmol (41.25mg) thioethyl Amide, heated to 50°C, and kept stirring at 600 rpm until dissolved to obtain solution A;
[0051] (2) Add 3 mmol (36 mg) of multi-walled carbon nanotubes into 20 mL of ultrapure water, and ultrasonicate for 6 h at 350 W until the CNTs are uniformly dispersed to obtain suspension B;
[0052] (3) Add solution A obtained in step (1) into suspension B, and continue stirring at 400 rpm for 4 hours to obtain suspension C;
[0053] (4) Heat the suspension C obtained in step (3), conduct a hydrothermal reaction at 230°C for 36 hours, then cross-wash with deionized water and ethanol for 5 times, centrifuge at 8500 rpm, and then place at 80°C , and dried for 12 hours to obtain vanadium tetrasulfide / carbon nanotubes, a negative electrode material for sodium ion batteries.
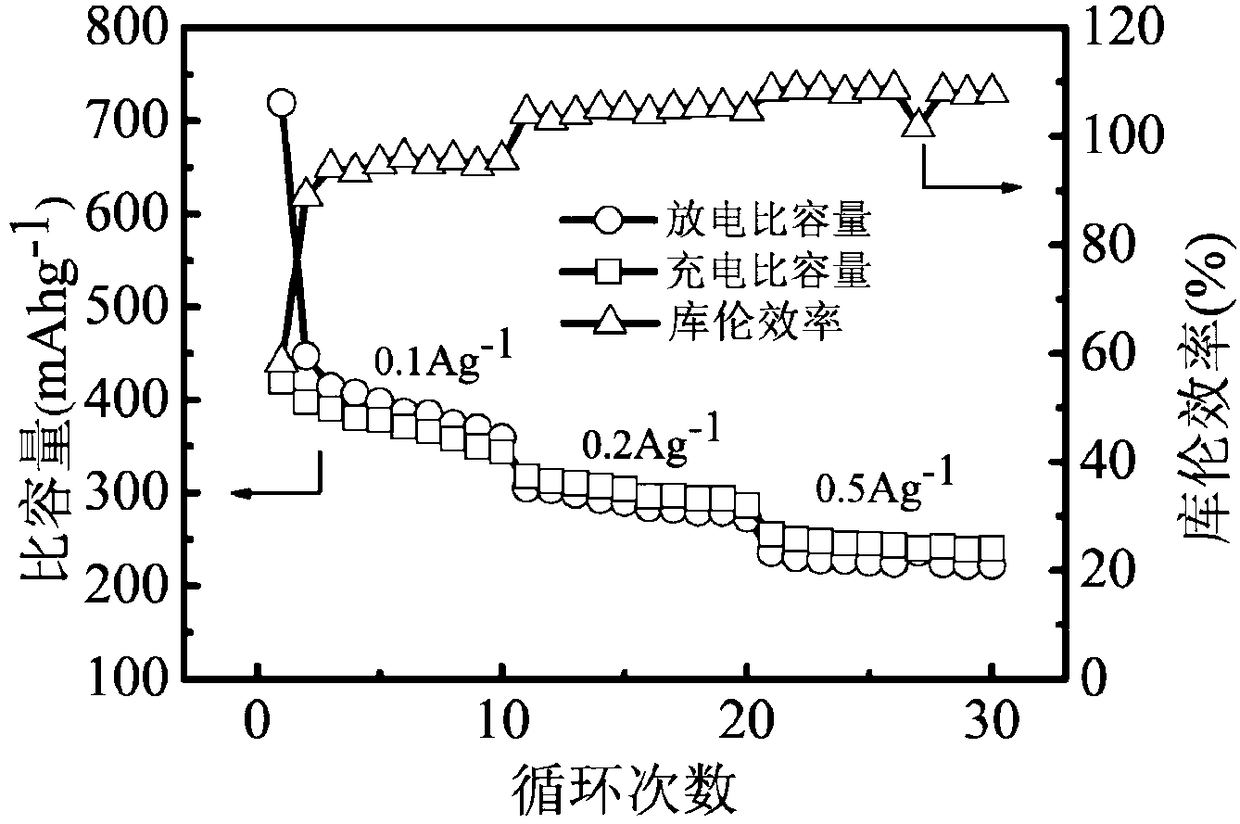
[0054] The peak value of the vanadiu...
Embodiment 3
[0061] (1) Add 1mmol (121.9mg) sodium metavanadate to 15mL ultrapure water, heat to 50°C, and keep stirring at 250 rpm until dissolved, then add 5.7mmol (427.5mg) thioacetamide , heated to 90°C, and kept stirring at 600 rpm until dissolved to obtain solution A;
[0062] (2) Add 20mmol (240mg) of multi-walled carbon nanotubes into 15mL of ultrapure water, and ultrasonicate for 5h at 500W until the CNTs are uniformly dispersed to obtain suspension B;
[0063] (3) Add the solution A obtained in step (1) into the suspension B, and continue stirring at 300 rpm for 3.5 hours to obtain the suspension C;
[0064] (4) Heat the suspension C obtained in step (3), conduct a hydrothermal reaction at 210°C for 20 hours, then cross-wash with deionized water and ethanol for 5 times, centrifuge at 6500 rpm, and then place at 55°C , and dried for 17 hours to obtain vanadium tetrasulfide / carbon nanotubes, a negative electrode material for sodium ion batteries.
[0065] The peak value of the va...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com