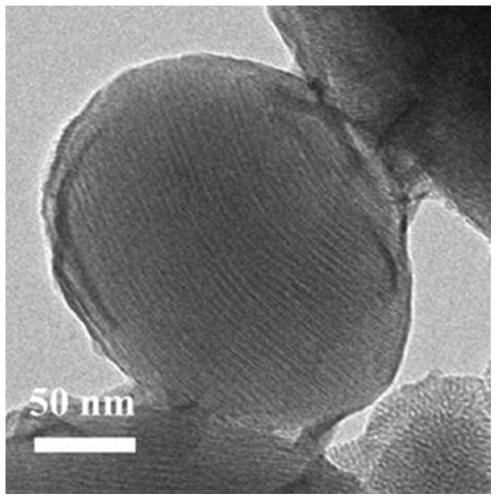
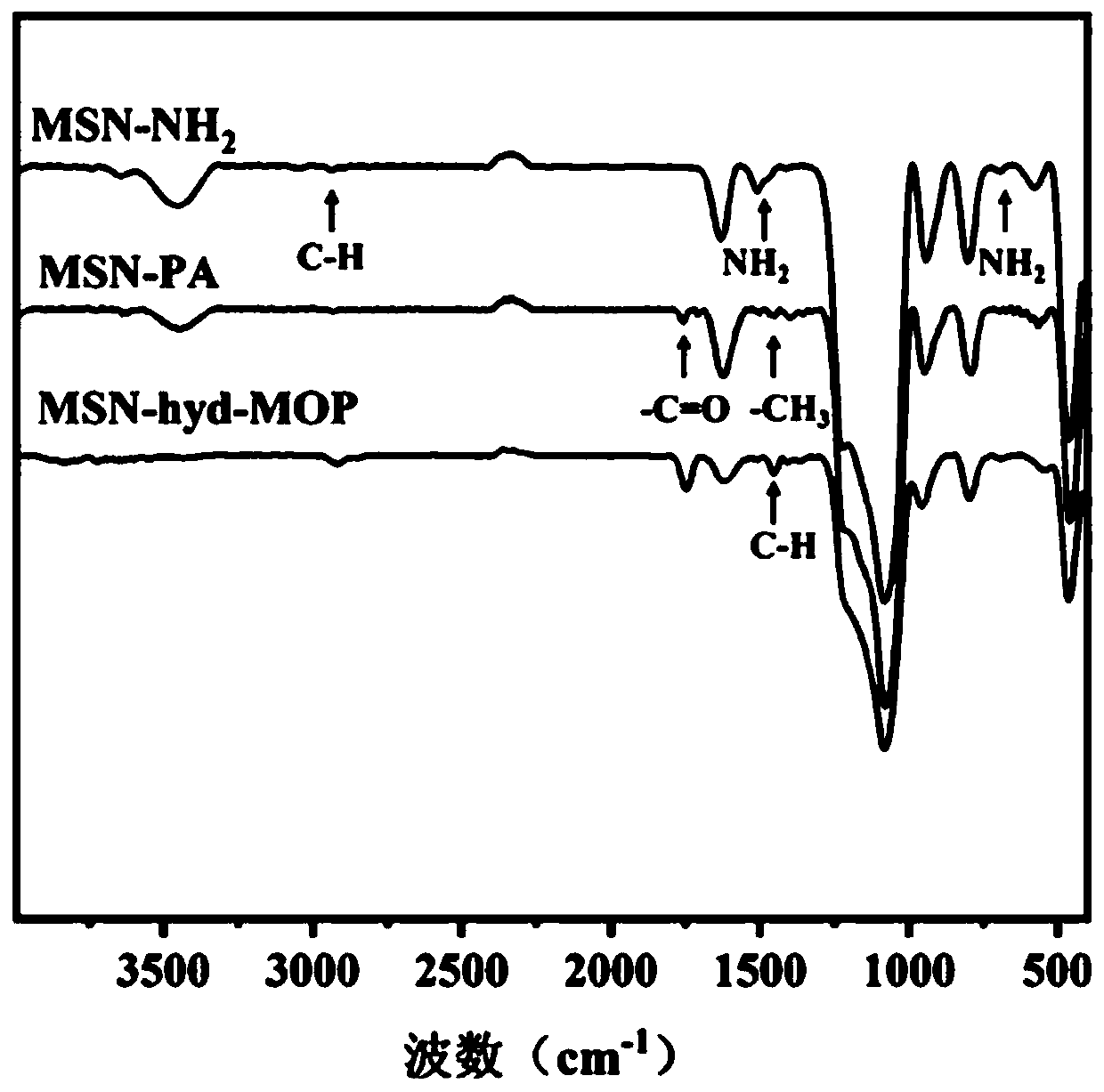
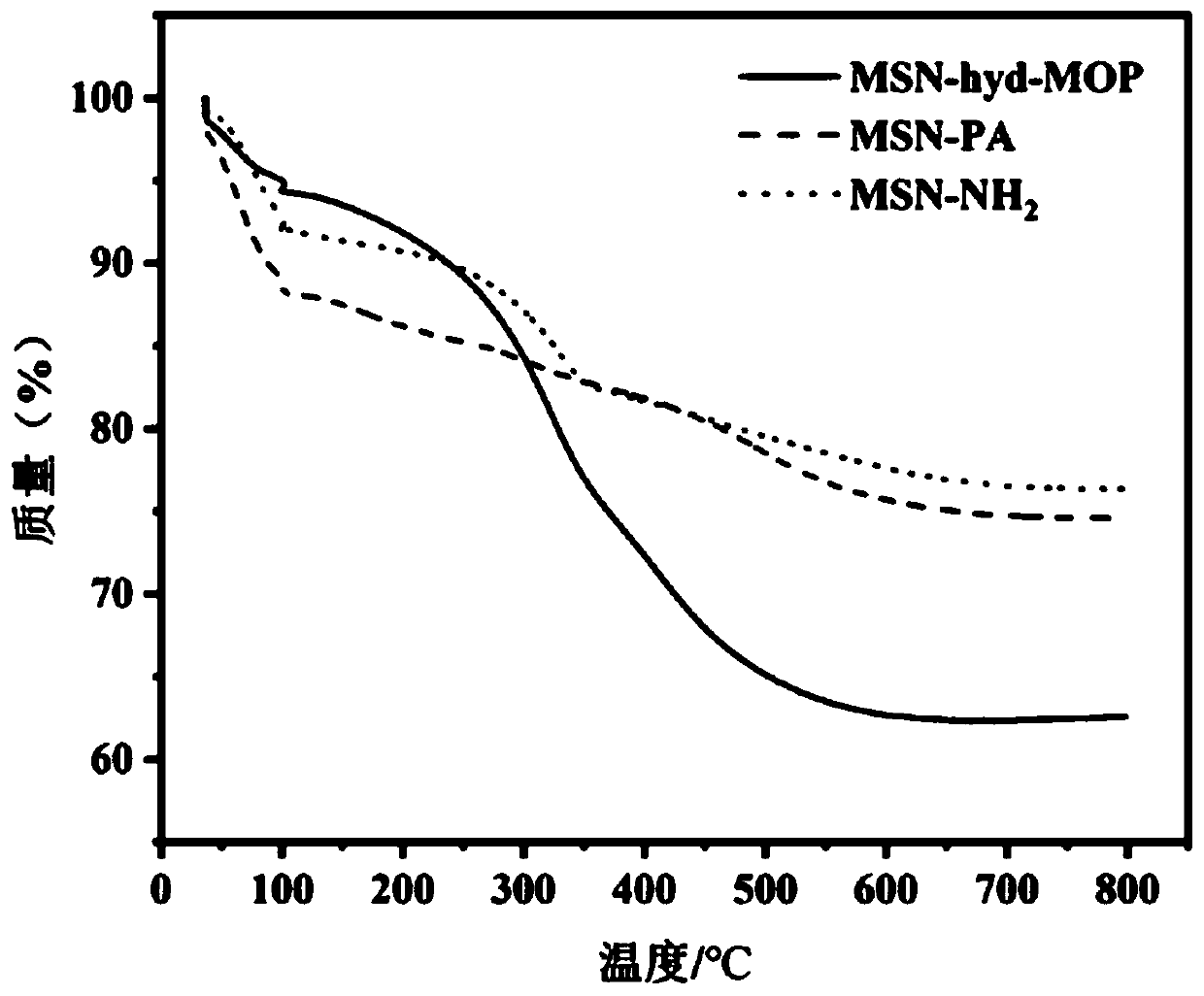
A kind of multilevel pH response mesoporous silica composite nanoparticle and its application
A technology of mesoporous silica and composite nanoparticles, applied in the field of nanomaterials, can solve the problems of inability to achieve therapeutic effect, low cell uptake rate, low therapeutic level of drug concentration, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] Example 1: Preparation of multi-stage pH-responsive mesoporous silica composite nanoparticles, the dosage ratio of each component is calculated according to the mass volume mole fraction, g / mL / mmol:
[0079] (1) Preparation of mesoporous silica containing surfactant: Weigh CTAB (0.2 parts by mass) and add 96 parts by volume of water, heat to 80°C, add sodium hydroxide solution (2M, 0.7 parts by volume), and stir for 30min , so that the templating agent forms micelles. Then TEOS (1.0 parts by volume) was added dropwise, and reacted at 80° C. for 2 h. After the reaction was completed, it was cooled to room temperature, centrifuged at 10,000 rpm, washed with water several times, and vacuum-dried at 30°C for 24 hours to obtain a white powder (MSN@CTAB).
[0080] The parts by weight of the reactants in the step (1) are as follows: 0.20 parts of CTAB; 0.06 parts of sodium hydroxide; 0.96 parts of TEOS; 98.78 parts of water;
[0081] (2) Preparation of surface aminated mesop...
Embodiment 2
[0122] Example 2: Preparation of loaded doxorubicin nanoparticles
[0123] MSN-PA (0.1 parts by mass) and doxorubicin hydrochloride (Dox) (0.02 parts by mass) were dispersed in 10 parts by volume of PBS (pH7.4) buffer solution, and stirred at room temperature for 24 hours in the dark. Add 2 drops of acetic acid dropwise, add catalyst system EDC (0.02 parts by mass) and NHS (0.01 parts by mass) and stir for 2 h. Polymer MOP-NHNH 2 (0.18 parts by mass, 0.03 parts by mole) were dissolved in 1 part by volume of THF solution. The polymer solution was slowly added dropwise into the mixed solution using a syringe, and stirred at room temperature for 24 h. After the reaction was completed, it was centrifuged at 5600 rpm, washed with PBS buffer solution (pH 7.4) until the supernatant was almost colorless, and freeze-dried to obtain drug-loaded particles (MSN-hyd-MOP@Dox). The drug loading is 12wt%, and the encapsulation efficiency is 87%.
Embodiment 3
[0124] Embodiment 3: release experiment
[0125] Determination of release performance: Accurately weigh 25 mg of doxorubicin nanoparticles and disperse them in 40 mL of pH 7.4 phosphate buffer solution, pH 6.5 phosphate buffer solution and pH 5.0 acetate buffer solution, and then place them in air at a temperature of 37.2 °C and a rotation speed of 150 rpm. in the shaker. Take a sample at a certain time interval, take out 4 parts by volume of the suspension each time, centrifuge, pour out the supernatant, transfer the precipitate to the original suspension, and add 4 parts by volume of fresh buffer. Measure the absorbance of the supernatant taken out at 480nm with an ultraviolet spectrophotometer, calculate the concentration of doxorubicin in the release liquid at different times, repeat each experiment three times, get the average value and draw the release curve, the results are shown in Figure 8 .
[0126] Depend on Figure 8 It can be seen that the drug-loaded particle...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com