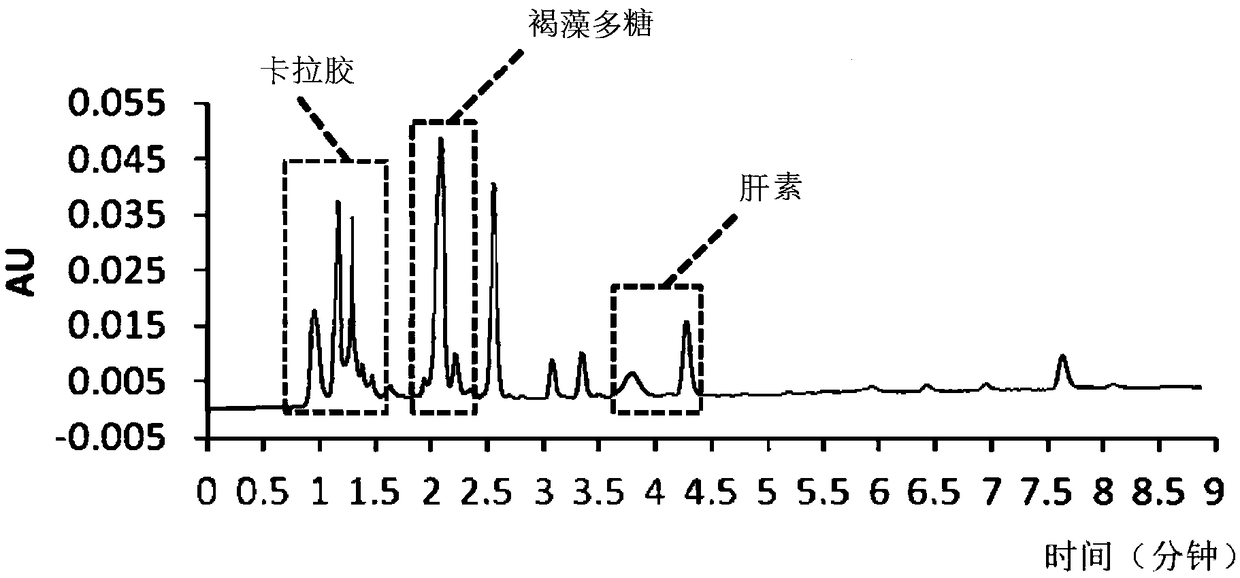
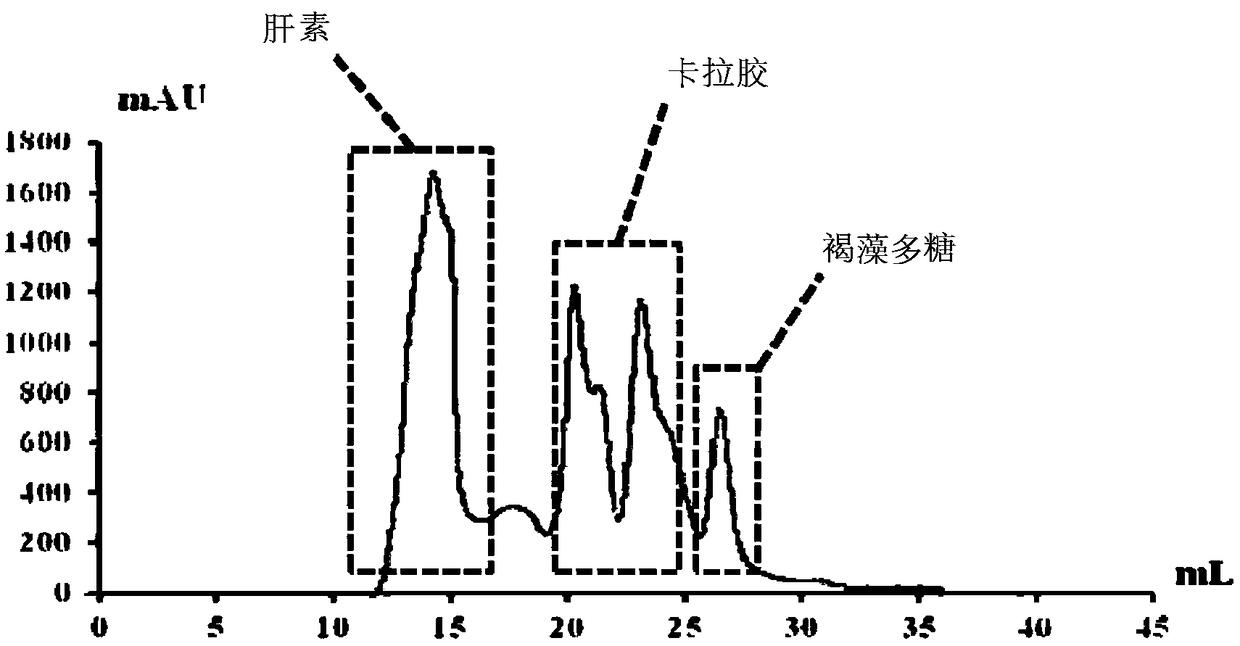
Method for extracting and purifying sulfated polysaccharides by using activated sludge from municipal sewage treatment plant as raw material
A technology of activated sludge and sulfated polysaccharides, which is applied in the fields of environmental engineering and chemical engineering, can solve the problems of limited extraction rate, limited suitable breeding area, and high dependence on weather and seawater conditions, and achieves simple extraction methods, good application prospects, and resource utilization. effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] The present embodiment provides a method for extracting and purifying sulfated polysaccharides from activated sludge, comprising steps:
[0032] S1: Take 500g of concentrated sludge (water content about 98%) from the secondary sedimentation tank of a municipal sewage treatment plant, then add the same volume of distilled water, shake well and centrifuge, discard the upper liquid phase, repeat the mud washing step 4 times, 4500rpm Retain solid phase mud cake after centrifugation;
[0033] S2: Mix and shake the solid phase mud cake and distilled water, so that the suspended solids concentration (MLSS) of the obtained mixed solution is 5000 mg / L, and the water content is not less than 90%; the mixed solution is heated to 50 ° C, and simultaneously A 10V direct current is passed through the mixture for 15 minutes;
[0034] S3: Centrifuge the product obtained by S2 at 4500 rpm, discard the solid phase mud cake, and collect the upper liquid phase;
[0035] S4: Ultrafiltrati...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The present embodiment provides a method for extracting and purifying sulfated polysaccharides from activated sludge, comprising steps:
[0040]S1: Take 1L of mud-water mixture (activated sludge) in the biological aeration tank of a municipal sewage treatment plant, add the same volume of distilled water, shake well and centrifuge, discard the upper liquid phase, repeat the mud washing step twice, centrifuge at 4500rpm and keep solid phase mud cake;
[0041] S2: Mix and shake the solid phase mud cake and distilled water, so that the suspended solids concentration (MLSS) of the obtained mixed solution is 8000 mg / L, and the water content is not less than 90%; the mixed solution is heated to 30 ° C, and simultaneously A 20V direct current is passed through the mixture for 30 minutes;
[0042] S3: Centrifuge the product obtained by S2 at 4500 rpm, discard the solid phase mud cake, and collect the upper liquid phase;
[0043] S4: Ultrafiltration is performed on the upper l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com