New ratio-type label-free fluorescence sensor and application thereof
A ratio-based, label-free technology, applied in the field of detection and chemical analysis, can solve the problems of false positives and false negatives, and achieve the effect of strong specificity, simple operation and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
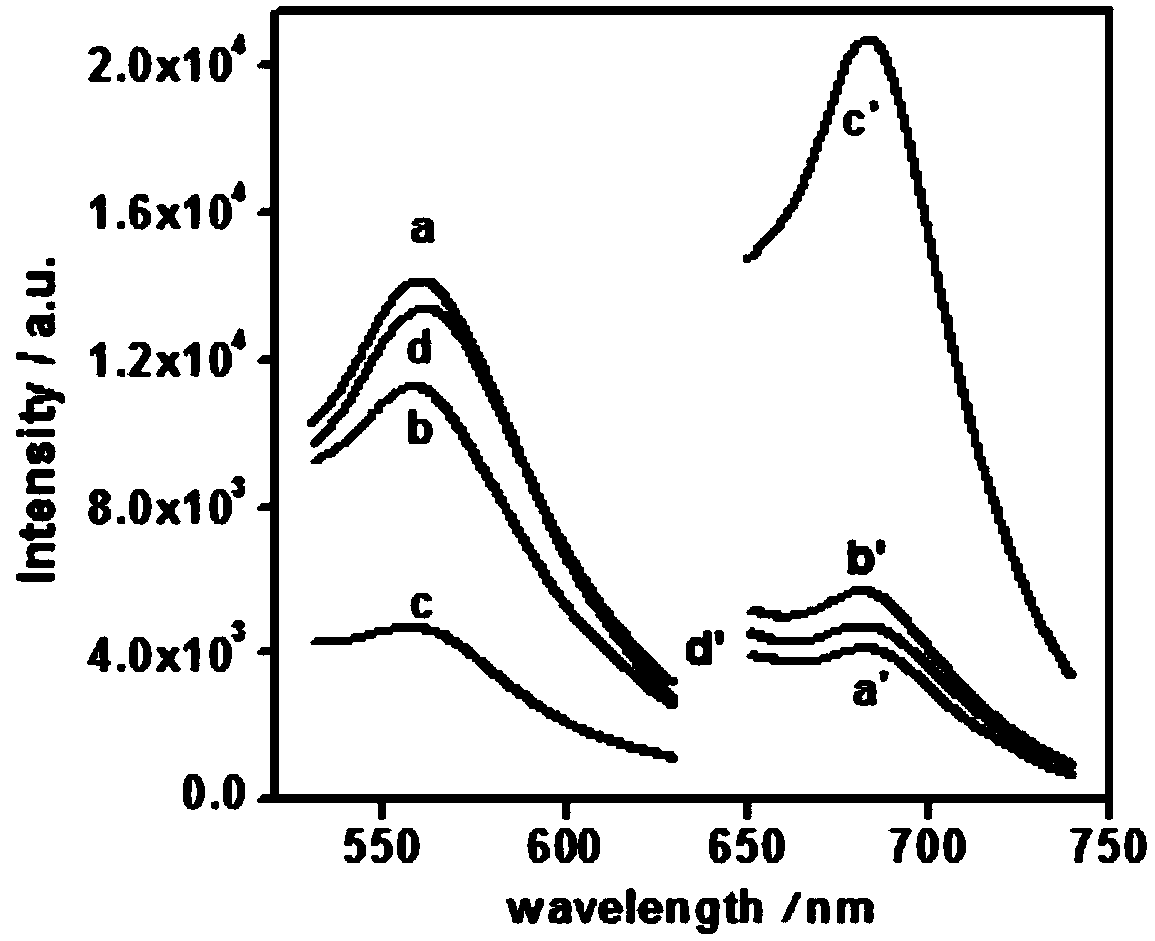
[0023] (1) Synthesis of G-DNA-AgNCs nanoclusters: First, 0.5 μM G-DNA template was annealed (90°C, 8 min), and then 3.0 μM AgNO was added after cooling down to room temperature 3 solution and 3.0 μM NaBH 4 Solution, after overnight reaction at 4°C, the fluorescence intensity of the system was detected with a fluorescence spectrophotometer. The generated G-DNA-AgNCs nanoclusters emit green fluorescence when excited at a wavelength of 470nm, and reach the maximum fluorescence intensity F at 560nm 560 , emits weak red fluorescence under excitation at 610nm wavelength, and reaches the maximum fluorescence intensity F at 685nm 685 ;
[0024] (2)Pb 2+ Construction of sensing system: R-DNA was added to the G-DNA-AgNCs system for hybridization reaction to form silver nanoclusters ( Named ds-DNA-AgNCs), the fluorescence of silver nanoclusters decreased at 560 nm and was greatly enhanced at 685 nm due to the formation of double strands. The novel ratiometric label-free fluorescent ...
Embodiment 2
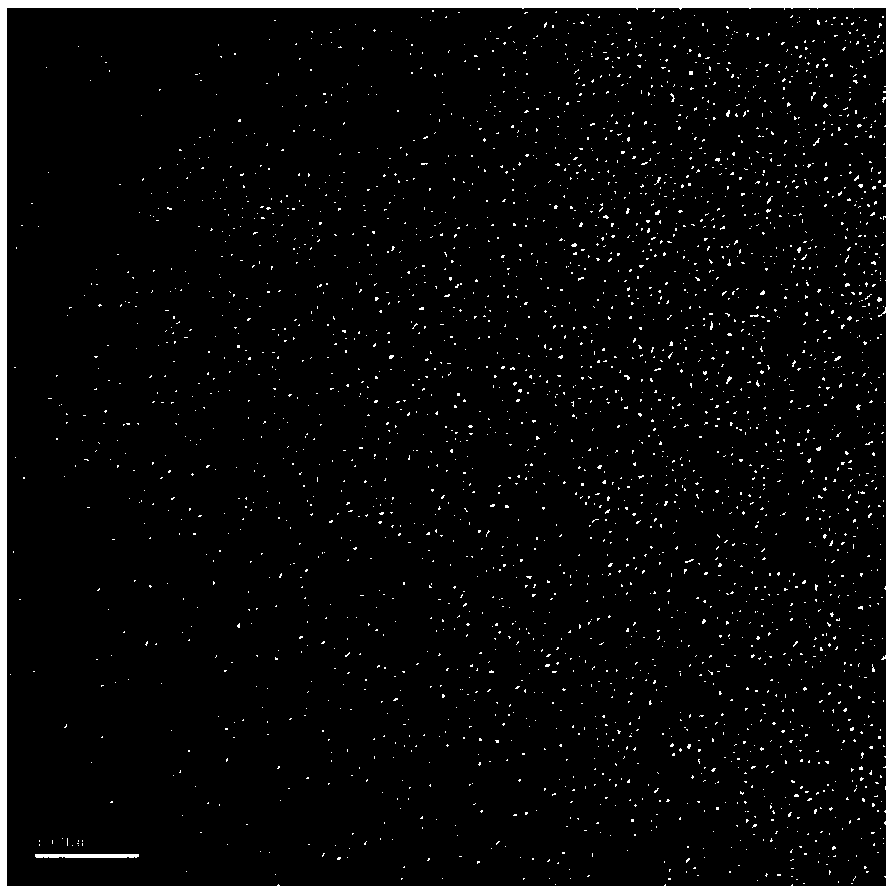
[0027] figure 2 It is a transmission electron microscope of DNA-AgNCs, which shows that the particle size of ds-DNA-AgNCs is about 3nm.
Embodiment 3
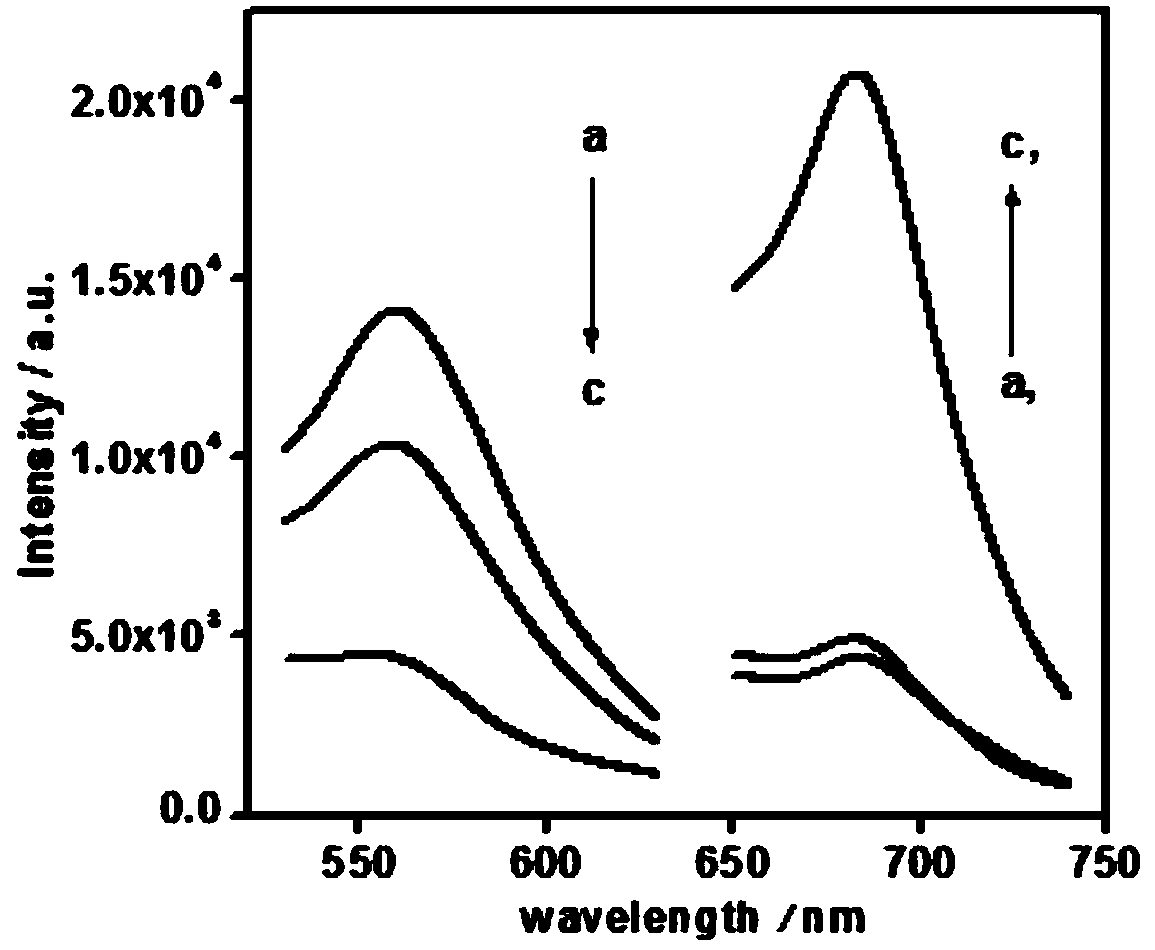
[0029] Optimizing the fluorescence response of the base pair sensing system contained in the duplex formed by R2-1 and G2-1 (F 560 / F 685 ) impact: explore the impact of Pb 2+ In the experiment of fluorescent sensing system factors, Pb 2+ The ratio detection is based on the signal change caused by the release of R2 in G-DNA / R-DNA, and the number of base pairs is an important factor affecting the hybridization process of G-DNA / R-DNA. If the number of complementary base pairs is too small, the Pb-dependent 2+ cleavage site, then Pb 2+ The resulting signal change is not obvious. When the number of complementary base pairs is more, the double-strand is more stable, and it is more difficult to release R2, thereby reducing the detection sensitivity. from image 3 It is known that when the number of complementary base pairs is 9, the presence of R-DNA can effectively convert the green-emitting G-DNA-AgNCs to the red-emitting ds-DNA-AgNCs. Join Pb 2+ Afterwards, green fluoresc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com