Method of preparing TiO2-modified P/C composite anode material
A technology of titanium dioxide and negative electrode materials, applied in battery electrodes, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of low electrode utilization, poor cycle stability, and low practical ability, and achieve low price, good cycle performance, and simple preparation process Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: Titanium dioxide modified phosphorus / carbon composite negative electrode material I
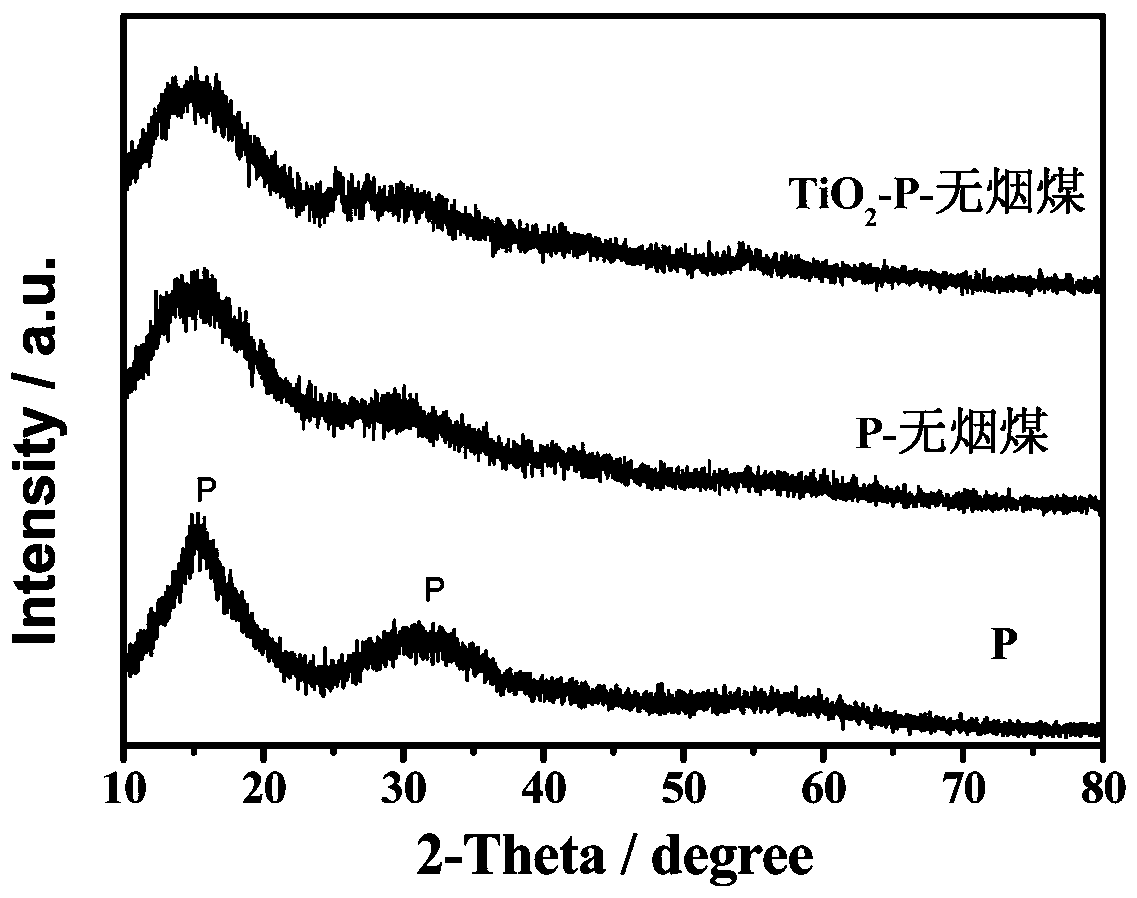
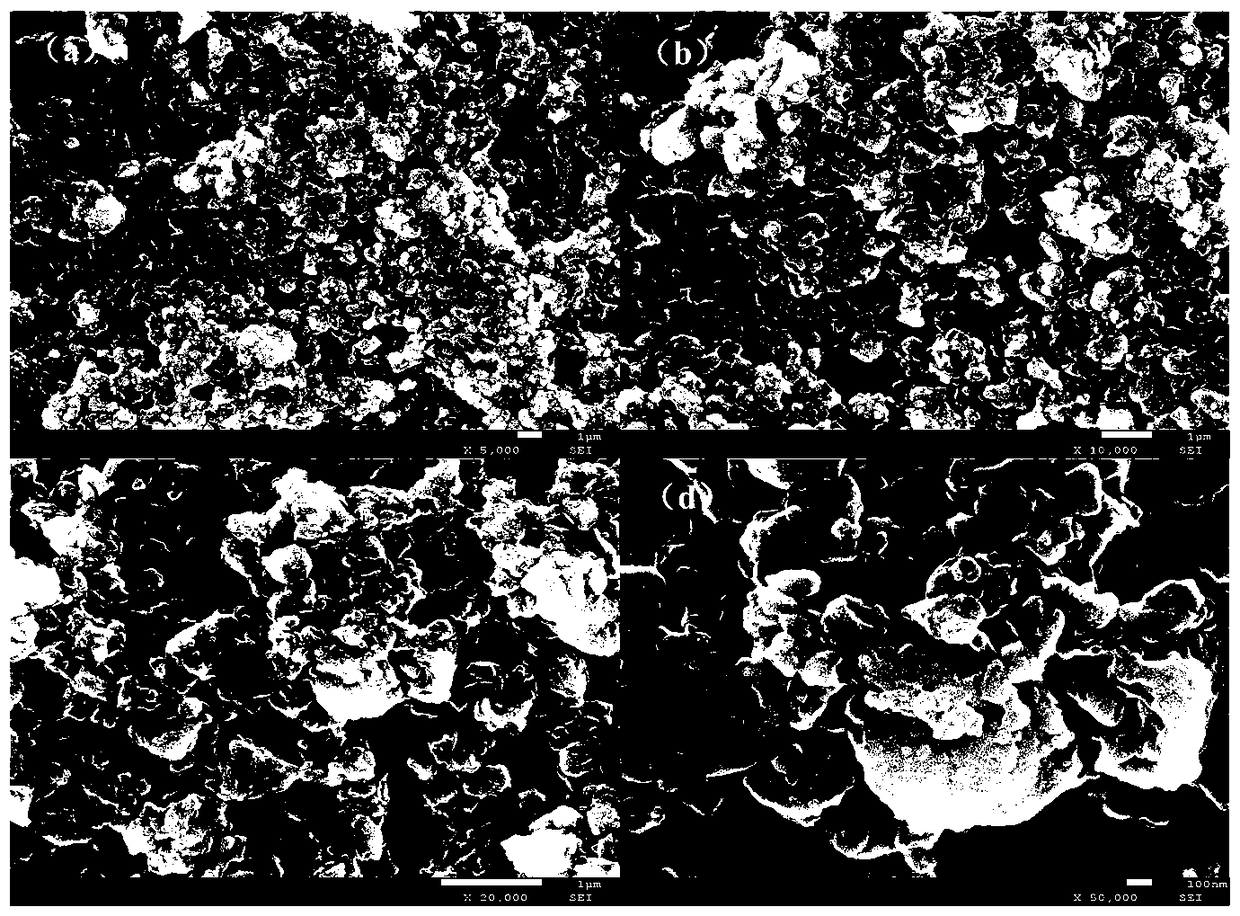
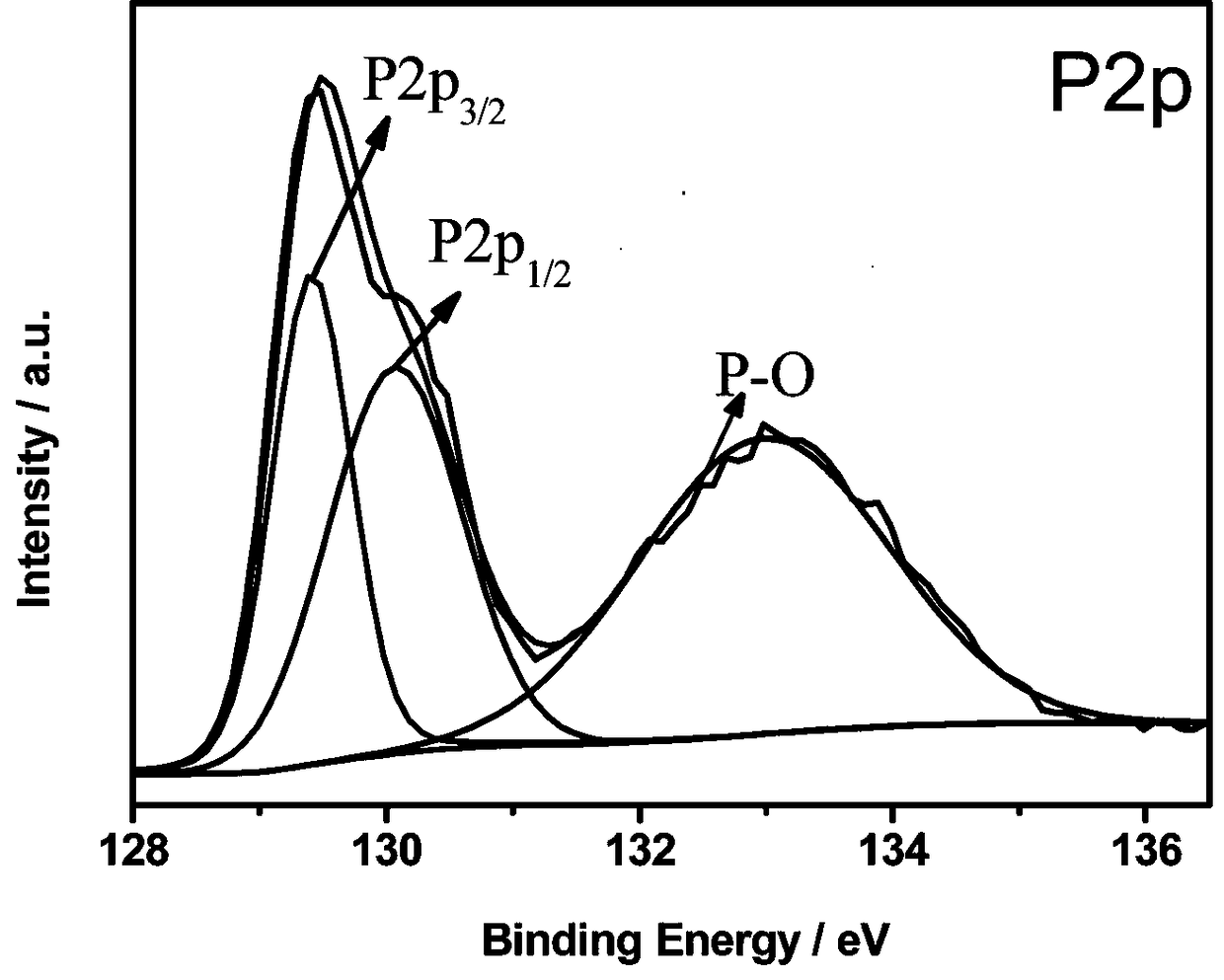
[0023] Anthracite tailings (0.4 g) were ball milled with red phosphorus (0.6 g) and titanium dioxide (0.1 g) for 20 hours at a speed of 1200 rpm. After the materials were cooled and sieved, the negative electrode material for titanium dioxide modified phosphorus / carbon sodium ion batteries was obtained. figure 1 XRD pattern of the prepared titanium dioxide modified phosphorus / carbon composite anode material. It can be seen from the spectrum that the prepared titanium dioxide modified phosphorus / carbon negative electrode material is an amorphous material, and the main peak is still the diffraction peak of P. figure 2 The SEM photo of the prepared titanium dioxide modified phosphorus / carbon composite negative electrode material shows that the material has a granular structure with a diameter of about 0.1-1 micron. image 3 The high-resolution XPS P2p spectrum of the prepared...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Example 2: Titanium dioxide modified phosphorus / carbon composite negative electrode material II
[0026] Anthracite (0.4 g), red phosphorus (0.6 g), and titanium dioxide (0.1 g) were ball milled for 12 hours at a speed of 800 rpm. After the materials were cooled and sieved, the negative electrode material for titanium dioxide modified phosphorus / carbon sodium ion batteries was obtained. The electrode material test conditions are as described in Example 1, and titanium dioxide modified phosphorus / carbon is used as the negative electrode material of sodium ion battery, with 100 mA g -1 The current density is charged and discharged, and the first reversible capacity is 810 mAh g under the test voltage of 0-2.5 V -1 , with an initial Coulombic efficiency of 78.5%, and a reversible capacity of 620 mAh g after 80 cycles -1 .
Embodiment 3
[0027] Example 3: Titanium dioxide modified phosphorus / carbon composite negative electrode material III
[0028]Anthracite tailings (0.4 g), red phosphorus (0.6 g), and titanium dioxide (0.1 g) were ball milled for 8 hours at a speed of 600 rpm. After the materials were cooled and sieved, the negative electrode material for titanium dioxide modified phosphorus / carbon sodium ion batteries was obtained. The electrode material test conditions are as described in Example 1, and titanium dioxide modified phosphorus / carbon is used as the negative electrode material of sodium ion battery, with 100 mA g -1 The current density is charged and discharged, and the first reversible capacity is 786 mAh g under the test voltage of 0-2.5 V -1 , with an initial Coulombic efficiency of 75.6%, and a reversible capacity of 574 mAh g after 80 cycles -1 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com