Preparation method for sulfur-containing 3-methylene isoindoline-1-one derivative
A methylene isoindoline and derivative technology, applied in the direction of organic chemistry, can solve the problem of thiol catalyst poisoning, etc., and achieve the effects of simple operation, easy product availability, and emission reduction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
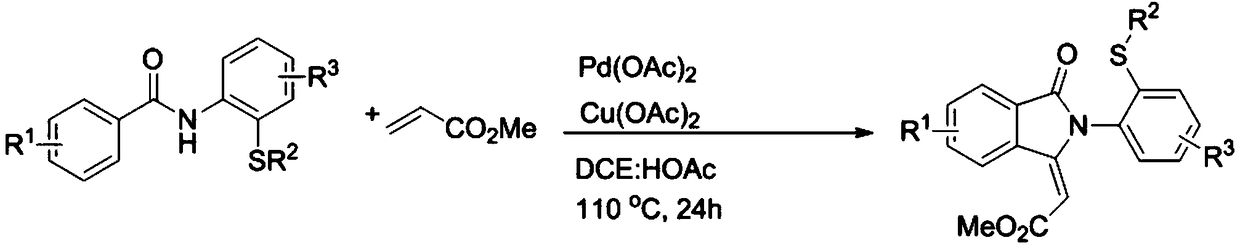
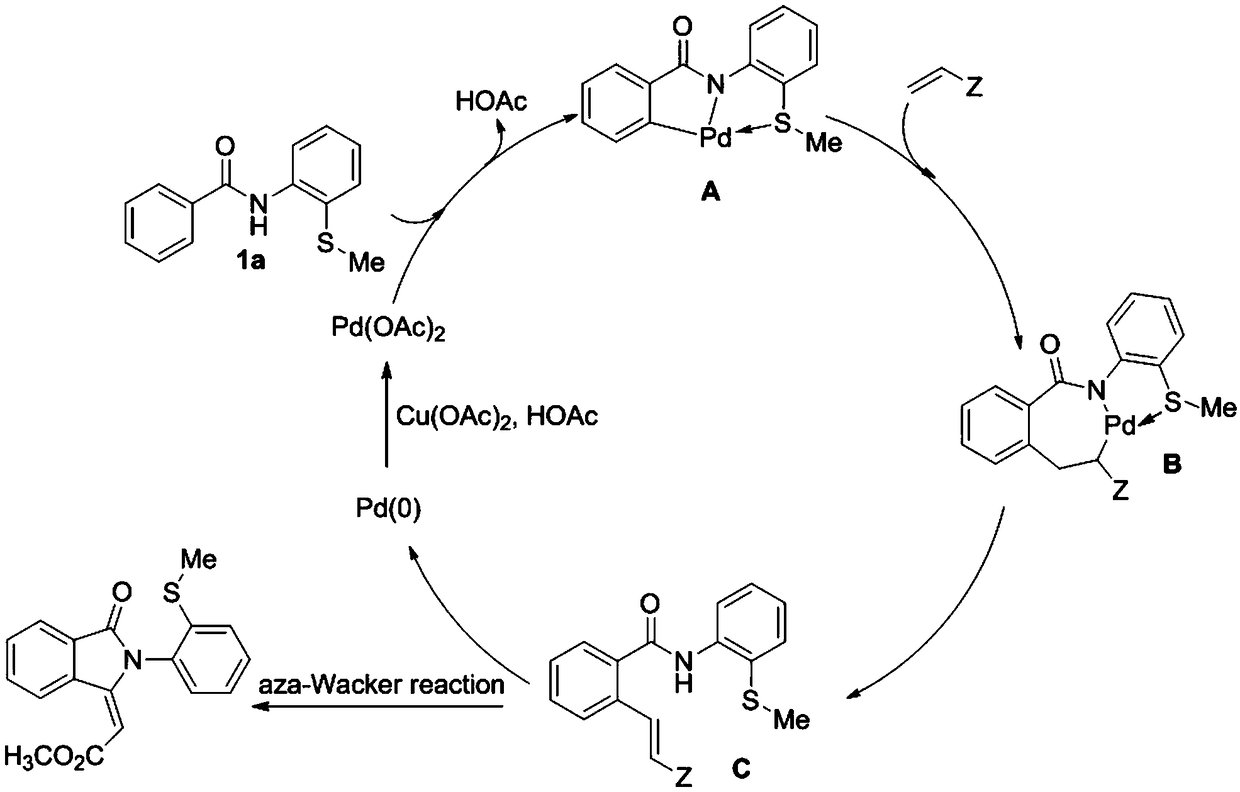
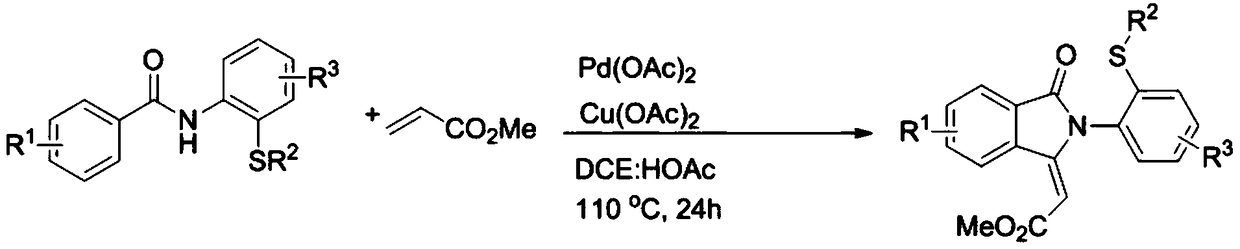
[0026] Specific example one: with 0.2mmol N-(2-(methylthio)phenyl)benzamide and 13.5mmol methyl acrylate as substrate, 0.02mmol Pd(OAc) 2 As a catalyst, 0.24 mmol of anhydrous copper acetate was used as an oxidant, and the mixture was placed in a mixture of 1,2-dichloroethane and glacial acetic acid for 24 hours in an oil bath at 110°C. After the reaction was completed, the mixture was neutralized with glacial acetic acid as a solvent with a saturated sodium bicarbonate solution, and the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by flash column chromatography to give 42.3 mg of (E)-2-(2-(2-(methylthio)phenyl)-3-oxoisoindol-1-ylidene)acetate as a white solid Esters, yield 65%. m.p.180-182℃. 1 H NMR (500MHz, CDCl 3 )δ9.15(d, J=8.0Hz, 1H), 7.97(d, J=7.5Hz, 1H), 7.76–7.73(m, 1H), 7.67–7.64(m, 1H), 7.50–7.47(m ,1H),7.39(d,J=...
specific Embodiment 2
[0027] Specific Example Two: With 0.2mmol 4-methyl-N-(2-(methylthio)phenyl)benzamide and 13.5mmol methyl acrylate as substrate, 0.02mmol Pd(OAc) 2 As a catalyst, 0.24 mmol of anhydrous copper acetate was used as an oxidant, and the mixture was placed in a mixture of 1,2-dichloroethane and glacial acetic acid for 24 hours in an oil bath at 110°C. After the reaction was completed, the mixture was neutralized with glacial acetic acid as a solvent with a saturated sodium bicarbonate solution, and the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. Purification of the residue by flash column chromatography afforded 45.4 mg of (E)-2-(6-methyl-2-(2-(methylthio)phenyl)-3-oxoisoindole-1- as a white solid Subunit) methyl acetate, yield 67%. m.p.175-177℃. 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ8.98(s,1H),7.84(d,J=7.6Hz,1H),7.49–7.45(m,2H),7.36(d,J=7.6Hz,1H),7.31–7.27(m,1H )...
specific Embodiment 3
[0028] Specific Example Three: With 0.2mmol 2-methyl-N-(2-(methylthio)phenyl)benzamide and 13.5mmol methyl acrylate as substrate, 0.02mmol Pd(OAc) 2 As a catalyst, 0.24 mmol of anhydrous copper acetate was used as an oxidant, and the mixture was placed in a mixture of 1,2-dichloroethane and glacial acetic acid for 24 hours in an oil bath at 110°C. After the reaction was completed, the mixture was neutralized with glacial acetic acid as a solvent with a saturated sodium bicarbonate solution, and the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. Purification of the residue by flash column chromatography afforded 35.9 mg of (E)-2-(4-methyl-2-(2-(methylthio)phenyl)-3-oxoisoindole-1- as a white solid Subunit) methyl acetate, yield 53%. m.p.123-125℃. 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ9.03(d,J=8.0Hz,1H),7.61–7.58(m,1H),7.49–7.45(m,1H),7.41–7.35(m,2H),7.31–7.27(m,1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com