Fabrication process of samarium-cobalt magnet
A preparation process, the technology of samarium cobalt magnets, applied in the direction of magnetic objects, inductors/transformers/magnets manufacturing, magnetic materials, etc., can solve the problems of large difference in magnetic properties, over-burning or insufficient sintering, poor product consistency, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
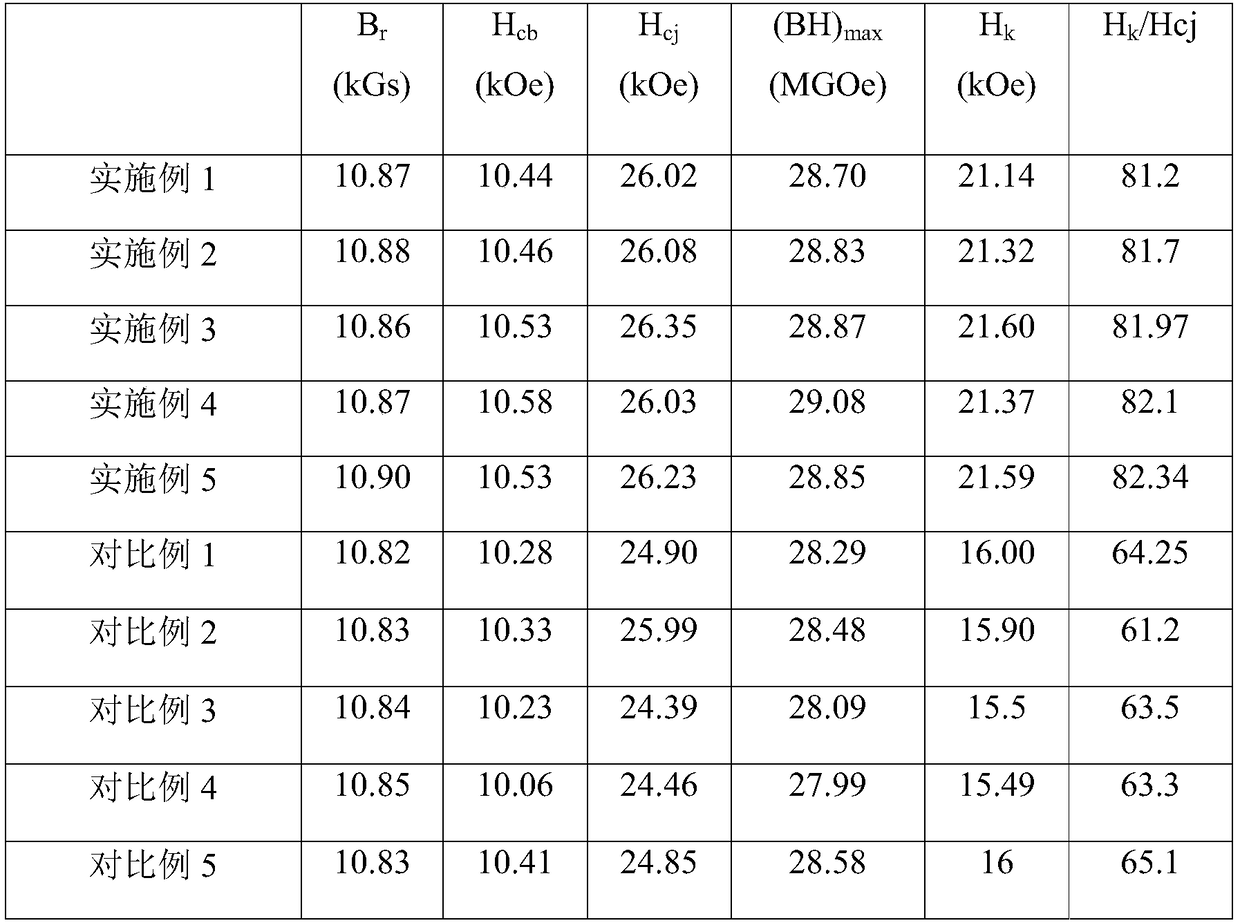
Embodiment 1
[0031] In this embodiment, the raw materials are in parts by weight: Sm 25.5g; Co 51g; Cu 5.8g; Zr 2.7g; Nb 0.05g;
[0032] Concrete preparation process is as follows:
[0033] Melting: The raw materials are added to the vacuum melting furnace in the order of Fe-Cu-Co-Zr-Nb-Sm, vacuumed to 0.08Pa or below, filled with inert gas to make the vacuum degree -0.06MPa, and the melting power is increased to melt the raw materials. When all the raw materials are melted and the color of the molten liquid surface changes from orange red to green, continue refining for 2 to 5 minutes to obtain the alloy molten liquid.
[0034] Ingot casting: The melt is poured into a 25mm wide red copper plate condensation mold with 8°C circulating water or chilled water for cooling.
[0035] Powder making: After primary and secondary crushing, the cast ingot enters the jet mill for powder making. The oxygen content in the jet mill is <200ppm, the grinding pressure is 0.4MPa, and the particle size of th...
Embodiment 2
[0039] In this embodiment, the raw materials are in parts by weight: Sm 26g; Co 50.9g; Cu 5.8g; Zr 2.8g; Nb 0.15g;
[0040] Concrete preparation process is as follows:
[0041] Melting: The raw materials are added to the vacuum melting furnace in the order of Fe-Cu-Co-Zr-Nb-Sm, vacuumed to 0.08Pa or below, filled with inert gas to make the vacuum degree -0.06MPa, and the melting power is increased to melt the raw materials. When all the raw materials are melted and the color of the molten liquid surface changes from orange red to green, continue refining for 2 to 5 minutes to obtain the alloy molten liquid.
[0042] Ingot casting: pour the melt into a 25mm wide red copper plate condensation mold with 15°C circulating water or chilled water for cooling.
[0043] Powder making: After primary and secondary crushing, the cast ingot enters the jet mill for powder making. The oxygen content in the jet mill is <200ppm, the grinding pressure is 0.5MPa, and the particle size of the ob...
Embodiment 3
[0047] In this embodiment, the raw materials are in parts by weight: Sm 26g; Co 50.8g; Cu 5.8g; Zr 3.0g; Nb 0.25g; Fe 15g.
[0048] Concrete preparation process is as follows:
[0049] Melting: The raw materials are added to the vacuum melting furnace in the order of Fe-Cu-Co-Zr-Nb-Sm, vacuumed to 0.08Pa or below, filled with inert gas to make the vacuum degree -0.06MPa, and the melting power is increased to melt the raw materials. When all the raw materials are melted and the color of the molten liquid surface changes from orange red to green, continue refining for 2 to 5 minutes to obtain the alloy molten liquid.
[0050] Ingot casting: pour the melt into a 25mm wide red copper plate condensation mold with 15°C circulating water or chilled water for cooling.
[0051] Powder making: after primary and secondary crushing, the cast ingot enters the jet mill for powder making. The oxygen content in the jet mill is <200ppm, the grinding pressure is 0.55MPa, and the particle size ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com