Method for preparing plate from construction waste
A construction waste and plate technology, applied in the field of building materials, can solve the problems of low added value, high water absorption rate of unburned bricks, and large property differences, achieving less organic impurities, good properties such as impermeability, and less impurity content Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
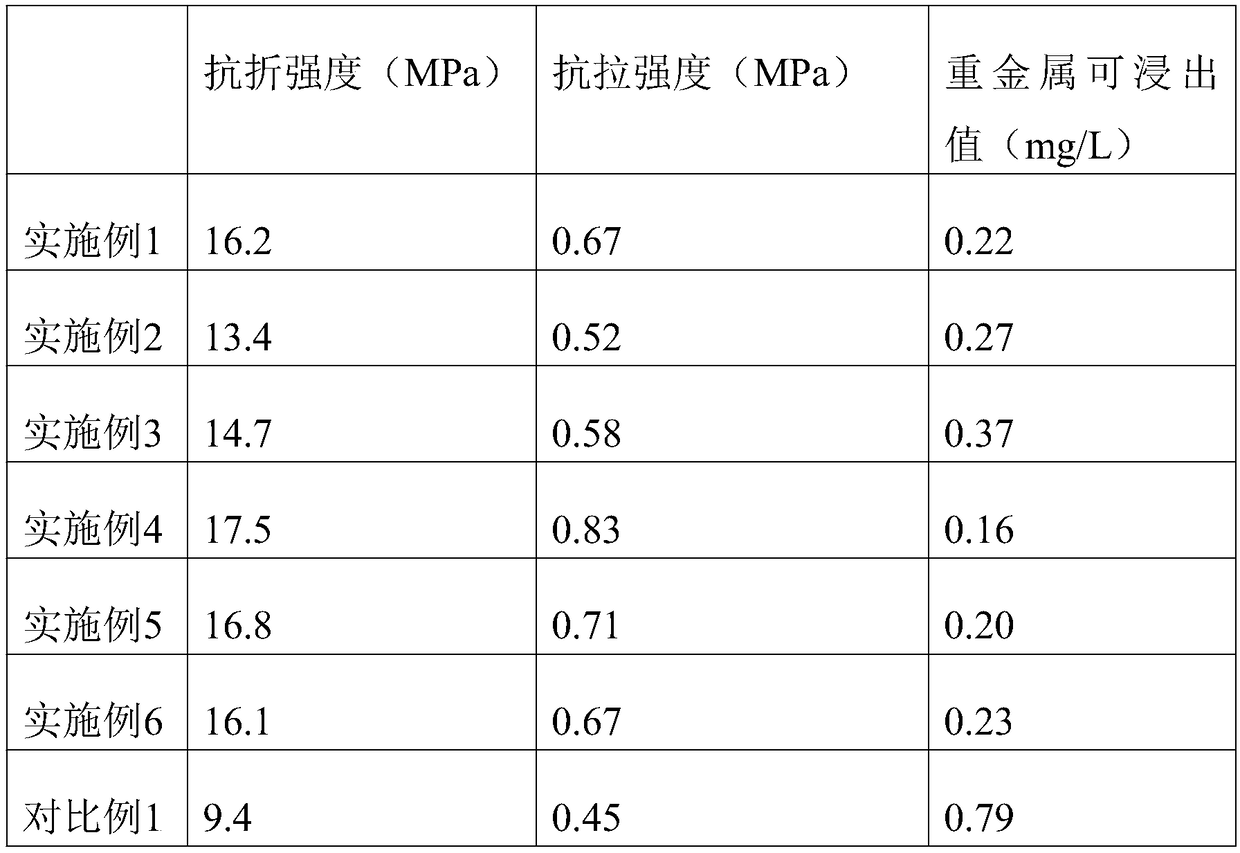
Embodiment 1
[0031] (1) 100kg of construction waste is crushed by a crusher until the particle size is below 5cm, and treated at 300°C for 2.5 hours;
[0032] (2) Moisten the broken mixture with water, evenly sprinkle 0.3% microbial inoculum, treat for 3 days, keep the mixture moist during the treatment process, and the microbial inoculum is obtained by mixing the following microorganisms: Thiobacillus ferrooxidans 18kg , Microspirillum ferrooxidans 9kg, Lactobacillus 8kg, Acinetobacter johnsonii 5kg, Pseudomonas putida 7kg, metal-resistant copper greedy bacteria 13kg;
[0033] (3) Drain the liquid in the microbially treated mixture, and rinse the solid with water 4 times;
[0034] (4) Grinding the washed solid to a particle size below 0.5 mm, and calcining at high temperature;
[0035] (5) add 21.5% lignocellulosic pulp, 20% calcium hydroxide, 10.5% calcium silicate, 9% peach gum, 60% cement, 40% water to calcined, mix uniformly, then Fully react at 180℃ for 10h;
[0036] (6) After ful...
Embodiment 2
[0039] (1) 100kg of construction waste is crushed by a crusher until the particle size is below 5cm, and treated at 280°C for 4 hours;
[0040] (2) Moisten the broken mixture with water, evenly sprinkle 0.1% microbial inoculum, treat for 5 days, keep the mixture moist during the treatment process, and the microbial inoculum is obtained by mixing the following microorganisms: Thiobacillus ferrooxidans 16kg , 7kg of Microspirillum ferrooxidans, 10kg of Lactobacillus, 7kg of Acinetobacter johnsonii, 9kg of Pseudomonas putida, and 10kg of metal-resistant Copper greedy bacteria;
[0041] (3) Drain the liquid in the microbially treated mixture, and rinse the solid with water for 3 times;
[0042] (4) Grinding the washed solid to a particle size below 0.5 mm, and calcining at high temperature;
[0043] (5) Add 15% lignocellulosic pulp, 15% calcium hydroxide, 8% calcium silicate, 7% peach gum, 50% cement, 30% water to calcined, mix uniformly, then Fully react at 160°C for 15 hours; ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] (1) 100kg of construction waste is crushed by a crusher until the particle size is below 5cm, and treated at 320°C for 1 hour;
[0048] (2) Moisten the broken mixture with water, evenly sprinkle 0.5% microbial inoculant, treat for 1d, keep the mixture moist during the treatment process, and the microbial inoculum is obtained by mixing the following microorganisms: Thiobacillus ferrooxidans 20kg , Microspiral ferrooxidans 11kg, Lactobacillus 6kg, Acinetobacter johnsonii 3kg, Pseudomonas putida 5kg, metal-resistant copper greedy bacteria 16kg;
[0049] (3) Drain the liquid in the microbially treated mixture, and rinse the solid with water 5 times;
[0050] (4) Grinding the washed solid to a particle size below 0.5 mm, and calcining at high temperature;
[0051] (5) add 28% lignocellulosic pulp, 25% calcium hydroxide, 8-13% calcium silicate, 11% peach gum, 70% cement, 50% water to calcined, mix uniformly, Then fully react at 200°C for 5h;
[0052] (6) After fully reacti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com