A kind of flexible synaptic bionic device and its preparation method
A technology of devices and synapses, which is applied in the field of flexible synaptic bionic devices and its preparation, can solve the problems of destroying the performance of flexible electronic devices, achieve good time retention and fatigue resistance, improve quality, and achieve the effects of high-efficiency electrical contact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
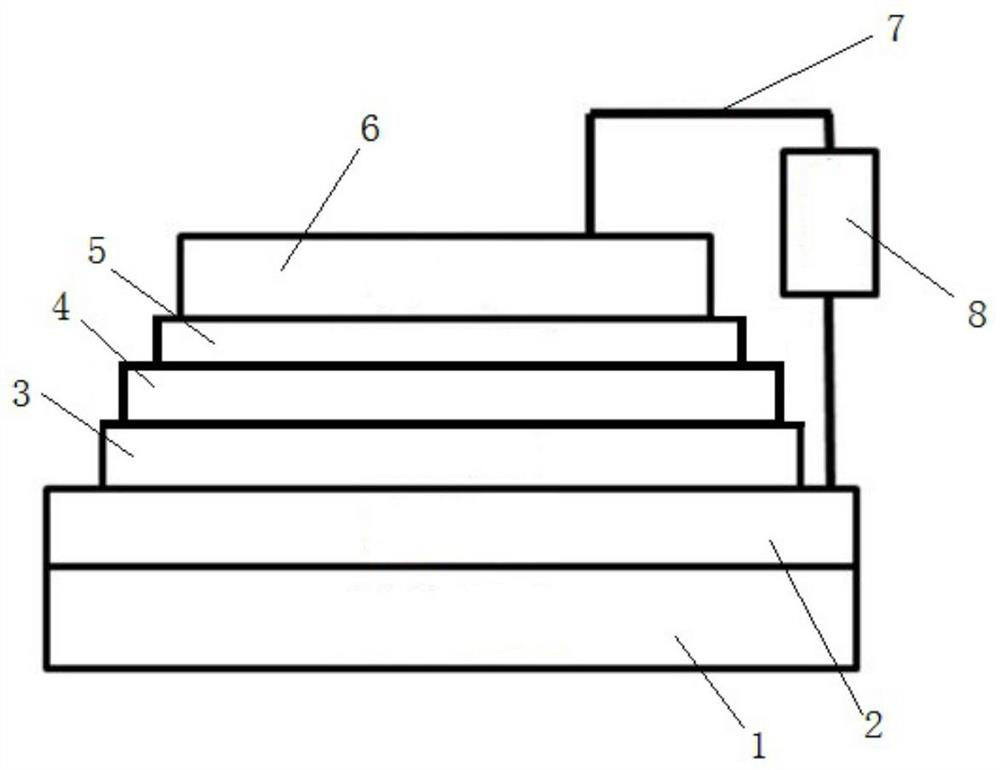
[0018] The flexible synapse bionic device of the present invention comprises a flexible polyimide substrate 1, a bottom electrode tin-doped indium oxide film 2, an oxygen-deficient titanium dioxide film layer 3, a titanium dioxide film layer 4, and a zinc oxide film layer 5 from bottom to top. and top electrode copper thin film 6, such as figure 1 shown. Wherein, the thickness of flexible substrate 1 is 1mm, the thickness of bottom electrode film 2 is 500nm, the thickness of anoxic titanium dioxide film 3 is 25nm, the thickness of titanium dioxide film layer 4 is 500nm, the thickness of zinc oxide film layer 5 is 1000nm, the top electrode Thin film 6 has a thickness of 70 nm.
[0019] The method for preparing the flexible synaptic bionic device of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0020] (1) The bottom electrode film was prepared on a flexible substrate by magnetron sputtering: tin-doped indium oxide was used as the sputtering target, argon was used as t...
Embodiment 2
[0027] The flexible synapse bionic device of the present invention comprises, from bottom to top, a flexible polyethylene terephthalate substrate 1, a bottom electrode aluminum-doped zinc oxide film 2, an oxygen-deficient titanium dioxide film layer 3, a titanium dioxide film layer 4, Zinc oxide thin film layer 5 and top electrode platinum thin film 6. Among them, the thickness of the flexible substrate 1 is 1.5mm, the thickness of the bottom electrode film 2 is 800nm, the thickness of the oxygen-deficient titanium dioxide film 3 is 40nm, the thickness of the titanium dioxide film layer 4 is 300nm, and the thickness of the zinc oxide film layer 5 is 500nm. The electrode thin film 6 has a thickness of 80 nm.
[0028] The method for preparing the flexible synaptic bionic device of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0029] (1) The bottom electrode film was prepared on a flexible substrate by magnetron sputtering: aluminum-doped zinc oxide was used as the sput...
Embodiment 3
[0036] The flexible synaptic bionic device of the present invention comprises a flexible polyethylene naphthalate substrate 1, a bottom electrode fluorine-doped tin oxide film 2, an oxygen-deficient titanium dioxide film layer 3, a titanium dioxide film layer 4, and zinc oxide from bottom to top. Thin film layer 5 and top electrode gold thin film 6. Among them, the thickness of the flexible substrate 1 is 0.5mm, the thickness of the bottom electrode film 2 is 50nm, the thickness of the oxygen-deficient titanium dioxide film 3 is 10nm, the thickness of the titanium dioxide film layer 4 is 100nm, and the thickness of the zinc oxide film layer 5 is 200nm. The electrode thin film 6 has a thickness of 20 nm.
[0037] The method for preparing the flexible synapse bionic device of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0038] (1) The bottom electrode film was prepared on a flexible substrate by magnetron sputtering: fluorine-doped tin oxide was used as the sputtering...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com