Pediococcus acidilactici strain high in stress resistance and capable of utilizing various carbon sources, and method for producing lactic acid through strain
A technology of Pediococcus lactis and lactic acid, applied in the field of microbial fermentation, to achieve the effects of increased acid production speed, good adaptability, and low fermentation cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1: Strain isolation, high temperature resistant strain screening and strain identification
[0046] Strain isolation: mash 1g Daqu sample and dissolve it with 10mL sterile saline, mix well for 30min; take the above dilution 10-fold and apply it to 1% (w / v) CaCO 3 (Neutralizer) MRS solid medium, culture at 37°C for 24 hours, pick a single colony with a larger transparent circle to inoculate the screening medium, incubate at 37°C for 24 hours, measure the total lactic acid content with high performance liquid chromatography, select lactic acid High-yield strains are lactic acid bacteria with high lactic acid content in the fermentation product.
[0047] Screening of high-temperature resistant strains: Select a batch of lactic acid-producing strains from the above-isolated lactic acid bacteria, inoculate MRS medium, culture at 37°C at 150 rpm for 1 hour, take 5μl of culture medium and spot it on MRS+CaCO 3 On a solid plate, place the plate in an incubator at 45°C for 40 ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2: Strain fermentation to produce lactic acid
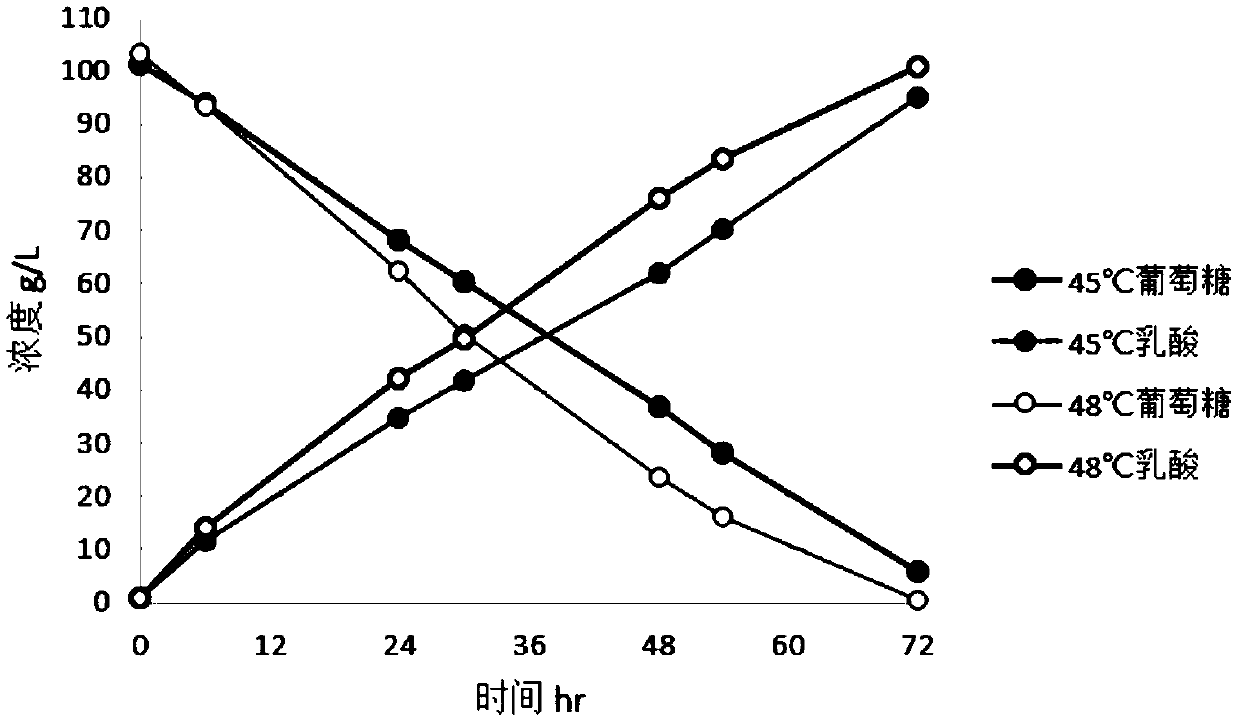
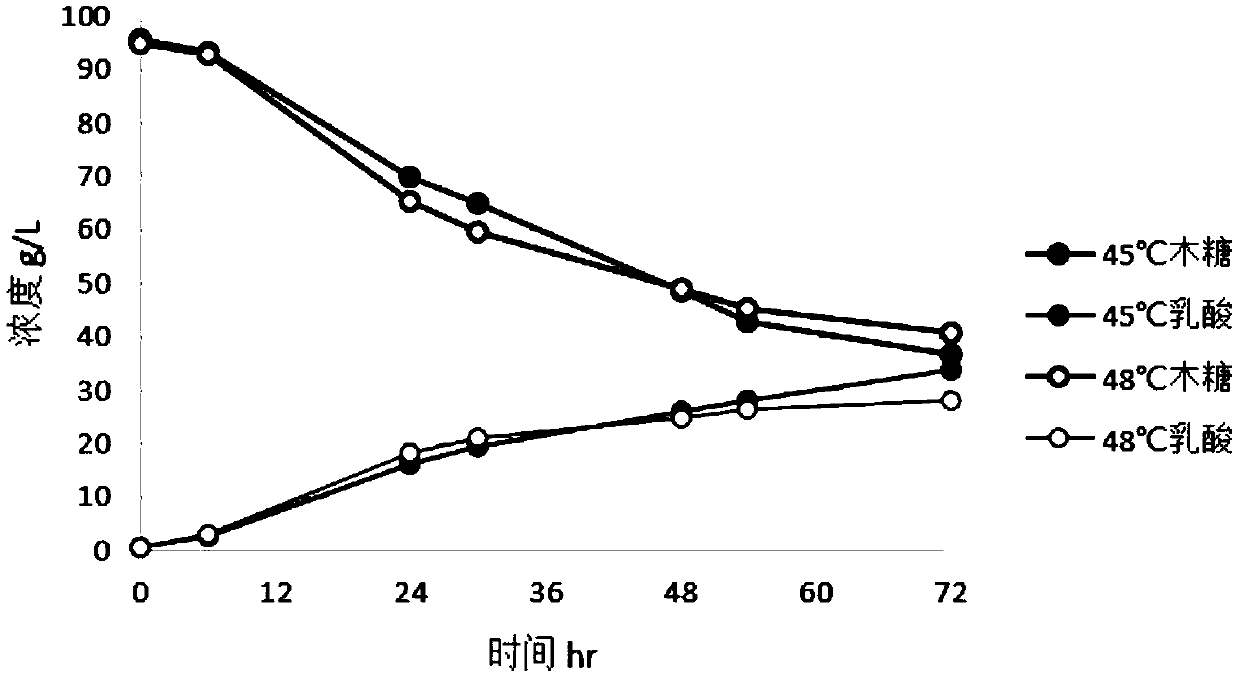
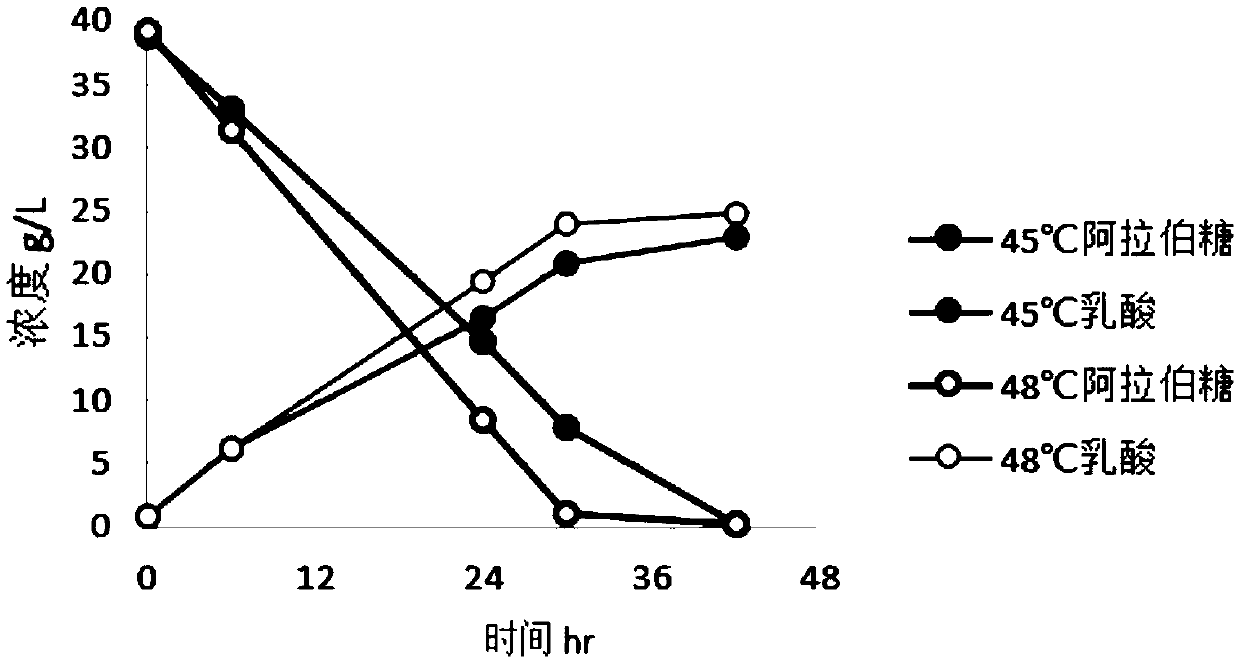
[0053] The lactic acid producing strain Pa-COT obtained in Example 1 was inoculated with MRS medium and cultured overnight at 37°C at 150 rpm to obtain seed liquid. Then, inoculate the above-mentioned seed liquid at a ratio of 10% (v / v) in 200 mL of acid-producing fermentation medium containing different carbon sources (100 g / L glucose, 100 g / L xylose or 40 g / L arabinose, respectively), Cultivate the strain on a shaker at 37°C and 150rpm for 3-5 hours to allow the strain to grow, and then increase the temperature to 45°C or 48°C, and continue to cultivate on a shaker at 150rpm for 72 hours to obtain a fermentation broth. After the fermentation, the lactic acid production was measured by high performance liquid chromatography.
[0054] As a result, when different monosaccharides are used as carbon sources, the Pediococcus lactis strain Pa-COT can ferment to produce 100.9g / L of lactic acid in 72 hours when using glucose ...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Example 3: Strains use cellulose hydrolysate to produce lactic acid
[0056] In this example 3, a straw enzymatic hydrolysate medium was used as an acid-producing fermentation medium, which contained the following components: straw enzymatic hydrolysate (the main components are glucose, xylose and arabinose, used as a carbon source), 5% (v / v) Concentrated corn steep liquor (about 60% water content), KH 2 PO 4 1g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.5g / L, MnSO 4 ·H 2 O 0.25g / L, CaCO 3 50g / L, pH is about 6.
[0057] The lactic acid producing strain Pa-COT was inoculated with MRS medium and cultured overnight at 37°C at 150 rpm to obtain seed liquid. Take 20ml of the seed solution and centrifuge for 5min at 6000rpm, discard the supernatant, and inoculate 200ml of straw enzymatic hydrolysis medium with 1ml of saline suspension. Cultivate for 4 hours on a shaker at 37°C and 180rpm to allow the strain to grow rapidly, and then warm to 45°C, continue Incubate for 92 hours on a shaker at 180 rpm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com