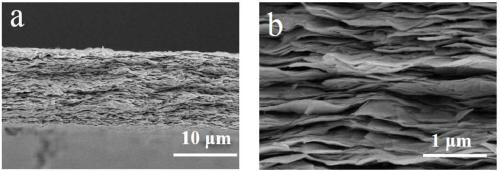
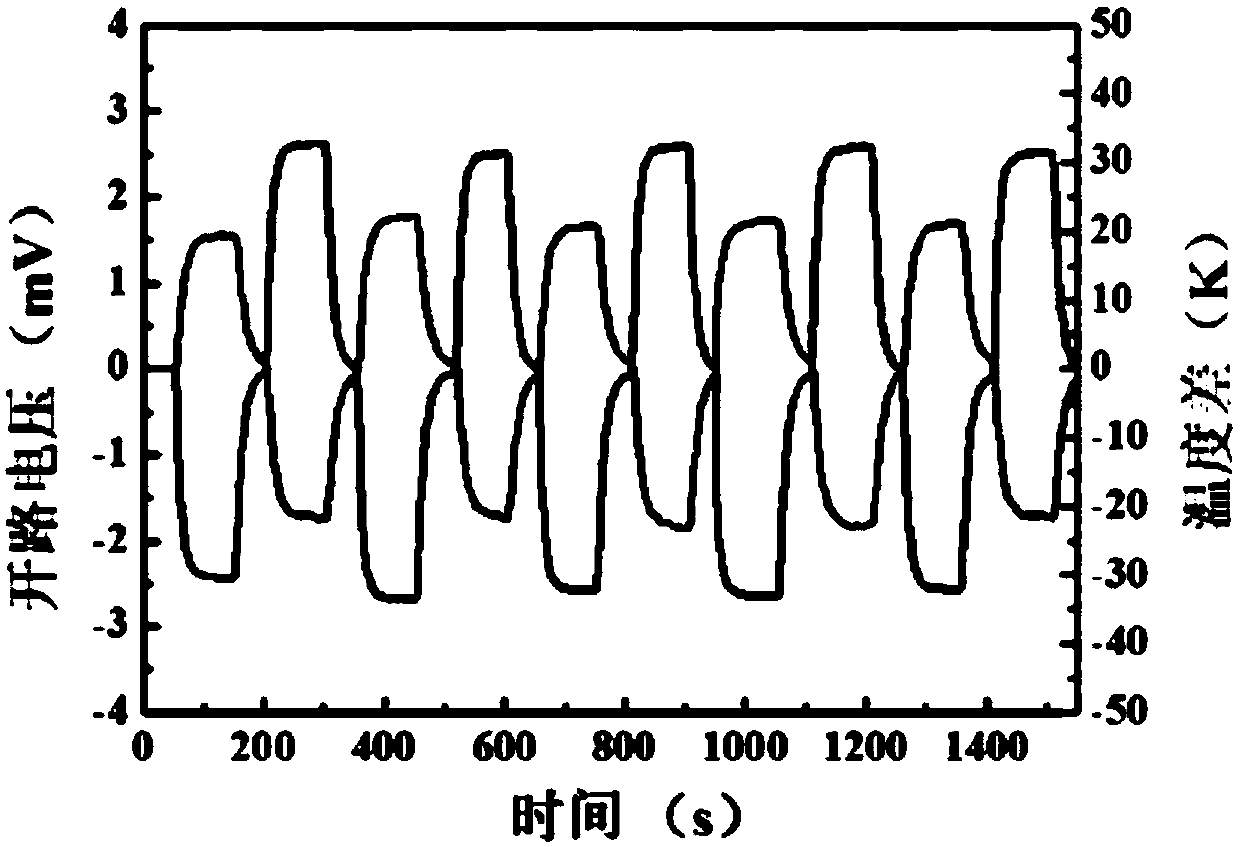
N-type thermoelectric thin film and preparation method and application thereof
A thermoelectric thin film, N-type technology, applied in the manufacture/processing of thermoelectric devices, thermoelectric device junction lead materials, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problem of low Seebeck coefficient of composite thermoelectric thin films, and achieve excellent electrical and mechanical properties Performance, improvement of thermoelectric conversion efficiency, effect of improving thermoelectric conversion efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] (1) Weigh 50 mg of bismuth telluride powder in a crucible, place it in a tube furnace and continuously feed in N at a rate of 100 mL / min. 2 Air, and raised to 150°C at a heating rate of 3°C / min, kept for 1 hour, cooled to room temperature naturally, and taken out for later use.
[0031] (2) Weigh 0.5 mg of graphite oxide, and simultaneously disperse the heat-treated bismuth telluride powder in 50 mL of deionized water to obtain a graphene oxide-bismuth telluride mixed dispersion; filter the mixed dispersion to form a film , and then dried in a vacuum oven at 60°C for 6 hours; the dried film was placed in a crucible, placed in a tube furnace and continuously fed with NH at a rate of 100mL / min 3 Gas, and the temperature was raised to 400 °C at a rate of 3 °C / min, and then naturally cooled to room temperature after holding for 1 h to obtain a graphene-bismuth telluride composite N-type thermoelectric thin film. The conductivity of the thermoelectric thin film is 14.6S cm ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] (1) Weigh 250mg of bismuth telluride powder in a crucible, place it in a tube furnace and continuously feed N at a rate of 200mL / min 2 The temperature was raised to 200°C at a rate of 4°C / min, kept for 2 hours, then cooled to room temperature naturally, and taken out for later use.
[0035] (2) Weigh 50 mg of graphite oxide, and simultaneously disperse the heat-treated bismuth telluride powder in 50 mL of deionized water to obtain a graphene oxide-bismuth telluride mixed dispersion; the mixed dispersion is suction-filtered to form a film, Then place it in a vacuum oven at 70°C to dry for 12 hours; put the dried film in a crucible, and place it in a tube furnace to continuously feed NH at a rate of 200mL / min. 3 Gas, and the temperature was raised to 500 °C at a rate of 4 °C / min, and then naturally cooled to room temperature after holding for 2 hours to obtain a graphene-bismuth telluride composite N-type thermoelectric thin film. The conductivity of the thermoelectric t...
Embodiment 3
[0038] (1) Weigh 500mg of bismuth telluride powder in a crucible, place it in a tube furnace and continuously feed in N at a rate of 300mL / min 2 Gas, and raised to 250°C at a rate of 5°C / min, kept for 3 hours, then cooled to room temperature naturally, and taken out for later use.
[0039] (2) Weigh 100 mg of graphite oxide, and simultaneously disperse the heat-treated bismuth telluride powder in 50 mL of deionized water to obtain a graphene oxide-bismuth telluride mixed dispersion; the mixed dispersion is suction-filtered to form a film, Then place it in a vacuum oven at 80°C for 24 hours; put the dried film in a crucible, and place it in a tube furnace to continuously feed NH at a rate of 300mL / min. 3 Gas, and the temperature was raised to 600°C at a rate of 5°C / min, and then naturally cooled to room temperature after holding for 3 hours to obtain a graphene-bismuth telluride composite N-type thermoelectric thin film. The conductivity of the thermoelectric thin film is 44.4...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com