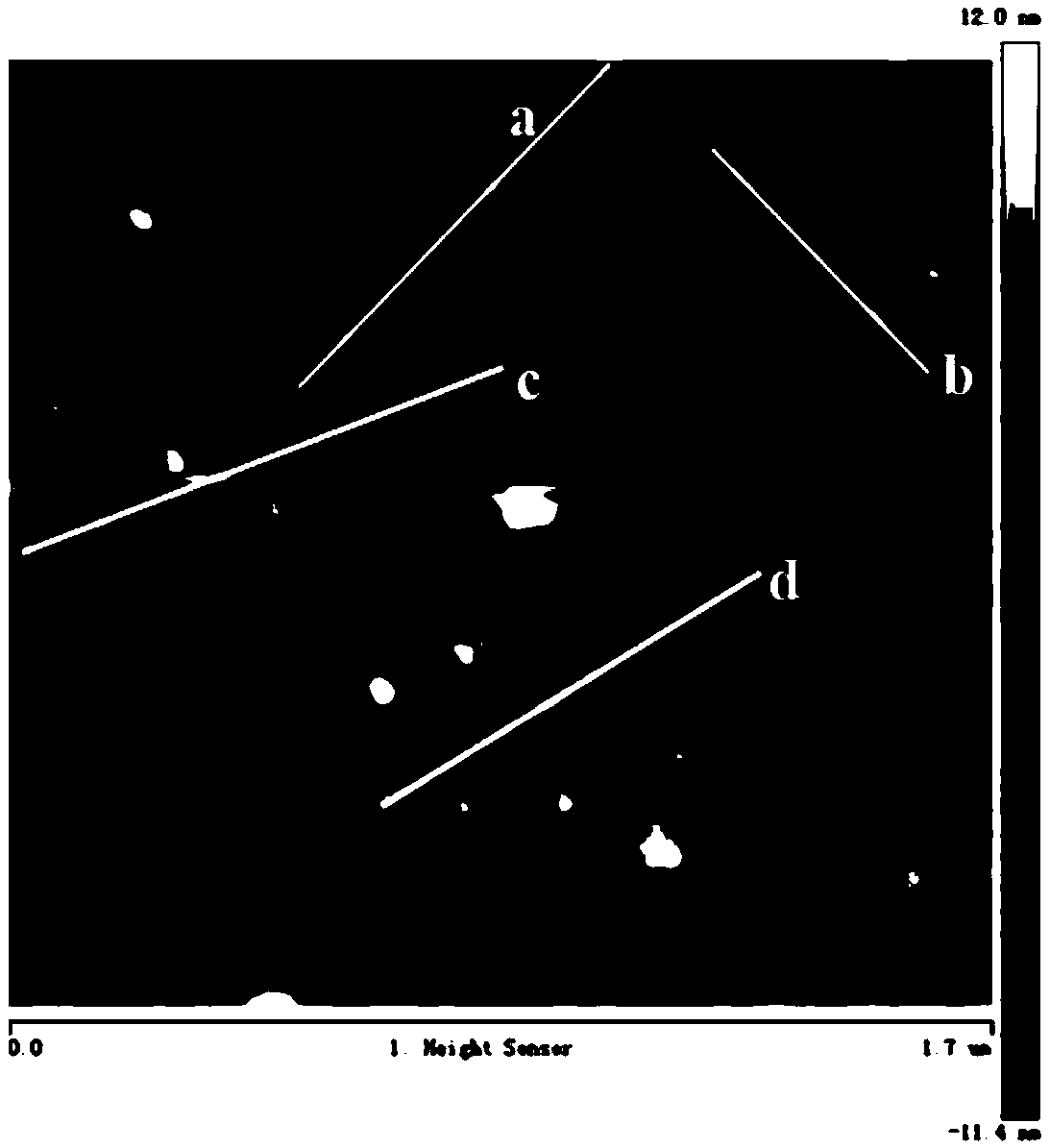
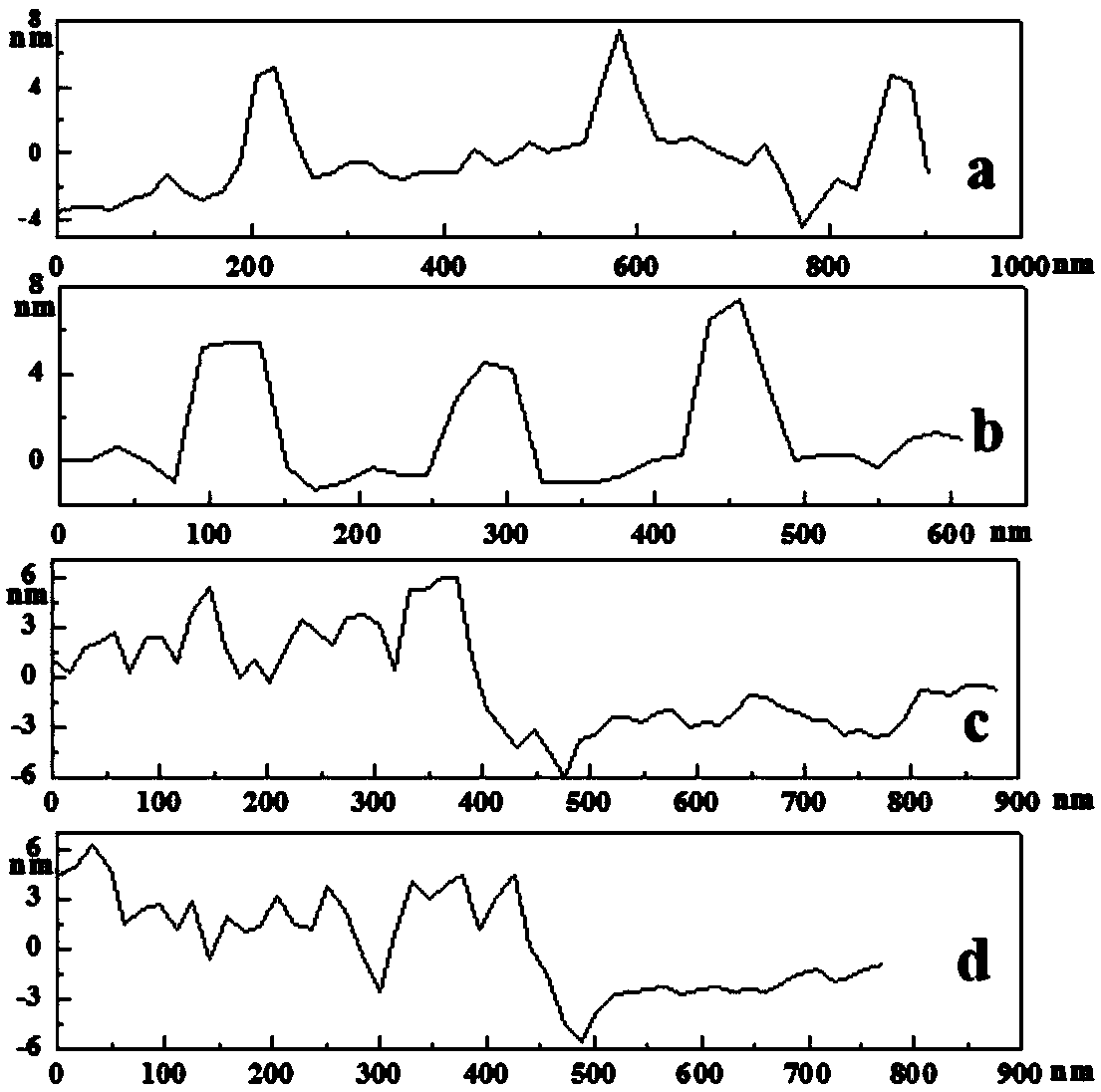
Copper ion electrochemical sensor and preparation method and application thereof
A copper ion, sensor technology, applied in analytical chemistry, life science and medical fields, can solve the problem of no regeneration, and it is difficult to obtain information on the continuous change of Cu2+ level.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
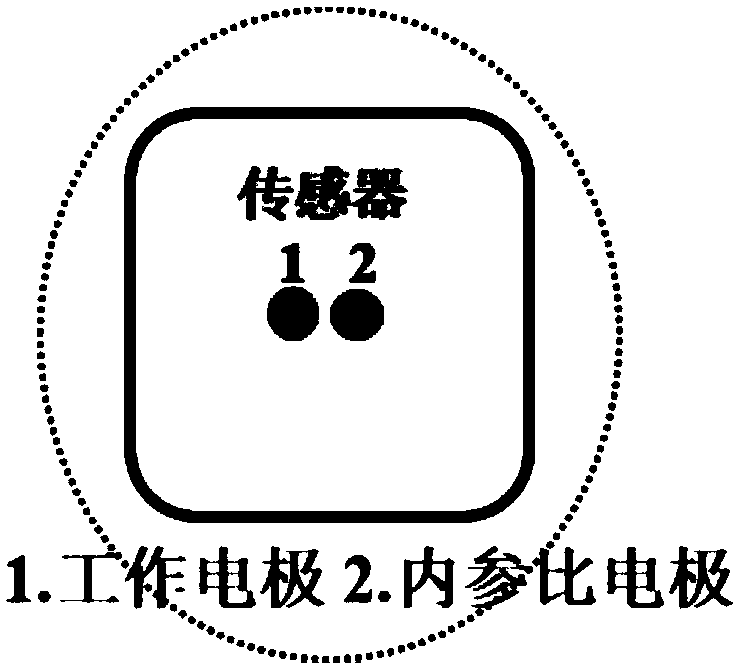
[0054] figure 2 For the preparation process of copper ion electrochemical sensor of the present invention, comprise the following steps:
[0055] Step 1. Using dendritic polyethyleneimine as a renewable recognition unit, it is covalently modified onto GC electrode 1 by stepwise chemical reaction, and labeled as GC / Cys / Au / MPA / hPEI electrode;
[0056] Step 2, using 6-(ferrocene)hexathiol (FcHT) as a built-in reference unit, adopting a stepwise chemical reaction to covalently modify it onto the GC electrode 2, labeled as GC / Cys / Au / FcHT electrode;
[0057] Step 3: The electrodes prepared in Step 1 and Step 2 are used together to form a reproducible ratiometric copper ion electrochemical sensor.
[0058] image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the equipment connection of the online microdialysis living body sampling-electrochemical sensor system of the present invention. The peristaltic pump is loaded with an airtight syringe to transmit the artificial cerebrospinal solution, and ...
Embodiment 1
[0065] The preparation of GC / Cys / Au electrodes using glassy carbon sheets includes the following steps:
[0066] 1) The bare double glassy carbon block electrode (including GC electrode 1 and GC electrode 2) was polished with 0.05 μm alumina on a polishing cloth, and placed in acetone, nitric acid (1:1, v / v), hydrogen Sodium oxide (50%, w / w) and distilled water were sonicated for 5 minutes in sequence;
[0067] 2) Put the electrode prepared in step 1) in 0.5M H 2 SO 4 Use cyclic voltammetry to scan until the current is stable, the scanning voltage ranges from -1V to +1V, the scanning speed is 0.1V / s, and rinse with distilled water;
[0068] 3) Soak the electrode prepared in step 2) in 10mM cysteine, 10mM EDC, and 10mM NHS solution for 2 hours in sequence, and wash with distilled water;
[0069] 4) Soak the electrode prepared in step 3) in the gold nanoparticle solution synthesized with trisodium citrate for 2 hours, and wash with distilled water to obtain GC1 / Cys / Au electro...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Using the GC1 / Cys / Au electrode obtained in Example 1 to prepare a GC1 / Cys / Au / MPA / hPEI electrode comprises the following steps:
[0073] 5) Soak the GC1 / Cys / Au electrode in 10mM mercaptopropionic acid solution for 2h, and wash it with distilled water;
[0074]6) Soak the prepared electrode in 1 mM dendrimer polyethyleneimine, 10 mM EDC, and 10 mM NHS solution for 2 hours, and wash it with distilled water.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com