Preparation method of superplastic zinc alloy stent material
A zinc alloy and superplastic technology, applied in the fields of medical devices and biomedical materials, to achieve the effects of easy processing and molding, promoting the recovery and maintenance of normal function of vascular endothelium, and improving mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1: Zinc-iron-copper alloy
[0037] The zinc-based alloy material of this embodiment is a zinc-iron-copper alloy, and the preparation process specifically includes the following steps:
[0038] 1) According to the mass percentage, 12wt% Fe, 1.8wt% Cu and the rest Zn (total impurity content 6 (1 vol.%) and CO 2 In the atmosphere, add high-purity graphite crucible to mix and smelt to obtain zinc-based alloy.
[0039] 2) After smelting, extrude the obtained zinc-based alloy into rods with a diameter of 100 mm and a length of 50 cm.
[0040] 3) After multiple annealing (temperature 200°C-500°C, 30min), the obtained rod is drilled and finally drawn to form a capillary with a diameter of 1.58mm and a wall thickness of 0.127mm, which is engraved by a femtosecond laser (engraving see flower type figure 1 ), intended for coronary stents.
[0041] Effect verification:
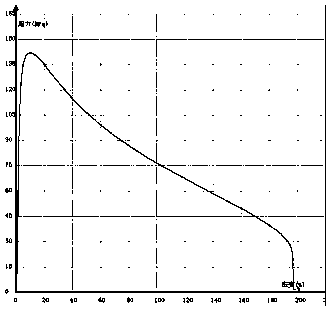
[0042] The zinc-based alloy material prepared by the above method has a yield strength of about...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Embodiment 2: zinc-iron-copper alloy
[0046] The zinc-based alloy material in this embodiment is a zinc-iron-copper alloy, which contains 0.2wt% iron, 0.5wt% copper, the balance is zinc, and the total impurity content is <0.001wt%. The preparation process is as follows:
[0047] 1) Put the raw materials into the smelting furnace according to the mass percentage and smelt them under the protection of inert gas to obtain a rod with a diameter of 100mm and a length of 500mm;
[0048] 2) Cut the rods into zinc alloy rods with a diameter of 8~10mm;
[0049] 3) Draw the medium bar in 2) to a thin cylindrical bar with a diameter of 3mm
Embodiment 3
[0050] Embodiment 3: zinc-copper alloy
[0051] The zinc-based alloy material in this embodiment is a zinc-copper alloy, which contains 0.80wt% copper, the balance is zinc, and the total impurity content is <0.001%. The preparation process is as follows (method 1):
[0052] 1) Copper and zinc are mixed and smelted in a high-purity graphite crucible according to the mass percentage, and the SF 6 and CO 2 Protected under the mixed gas atmosphere;
[0053] 2) Transfer the alloy melt to the mold, place a high-energy ultrasonic probe, and cool down step by step to form a rod with a diameter of 100mm and a length of 500mm;
[0054] 3) Heated and extruded into zinc alloy rods with a diameter of 8~10mm;
[0055] 4) 50 wires are drawn in each pass, and the thin alloy rod in 2) is drawn to a thin wire with a diameter of 3mm;
[0056] 5) Anneal the filament at 250°C for 10min.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com