A kind of positive electrode material of sodium ion battery and its preparation method and sodium ion battery comprising it
A technology for sodium ion batteries and positive electrode materials, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of capacity fading, cycle performance difficult to meet the requirements of practical applications, etc., and achieve less preparation process steps, suitable for The effects of large-scale promotion of production and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0033] Further, the present invention also provides the above chemical composition (NA 0.6 Mn 0.8 CO 0.2 O 2 The preparation method of sodium ion battery positive material, including:
[0034] (a) The soluble carbonate, manganese salt, and cobalt salt are added to the water to stir, and the resulting precipitate is collected;
[0035] Among them, raw material soluble carbonate includes: at least one of sodium carbonate, or potassium carbonate;
[0036] Soluble manganese salts include at least one of manganese sulfate, manganese nitrate, or manganese chloride;
[0037] The soluble cobalt salt includes at least one of cobalt sulfate, cobalt chloride, or cobalt nitrate.
[0038] Raw soluble carbonate, soluble manganese salts, and molar ratio of carbonate, manganese ions, and cobalt ions in soluble cobalt salts are: 1: a: b;
[0039] Among them, 0.5 <1 (for example, A can be 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, or 0.9, etc.), and A + b = 1;
[0040] Preferred, raw material soluble carbonate, manganese salt...
Embodiment 1
[0055] The sodium carbonate and manganese sulfate and cobalt sulfate were added in water according to the ratio of molar ratio 1: 0.9: 0.1, and stirred at normal temperature for 6 hours, and the precipitate was collected, dried, pulverized, and then the dried precipitate and NaOH were mixed according to mass ratio 2 : 1 of the proportion of ball milling, then sintered in the air for 500 ° C for 5 hours, sintering 6 hours, i.e., a layer-tunnel structure, a sodium ion battery positive material Na 0.6 Mn 0.8 CO 0.2 O 2 .
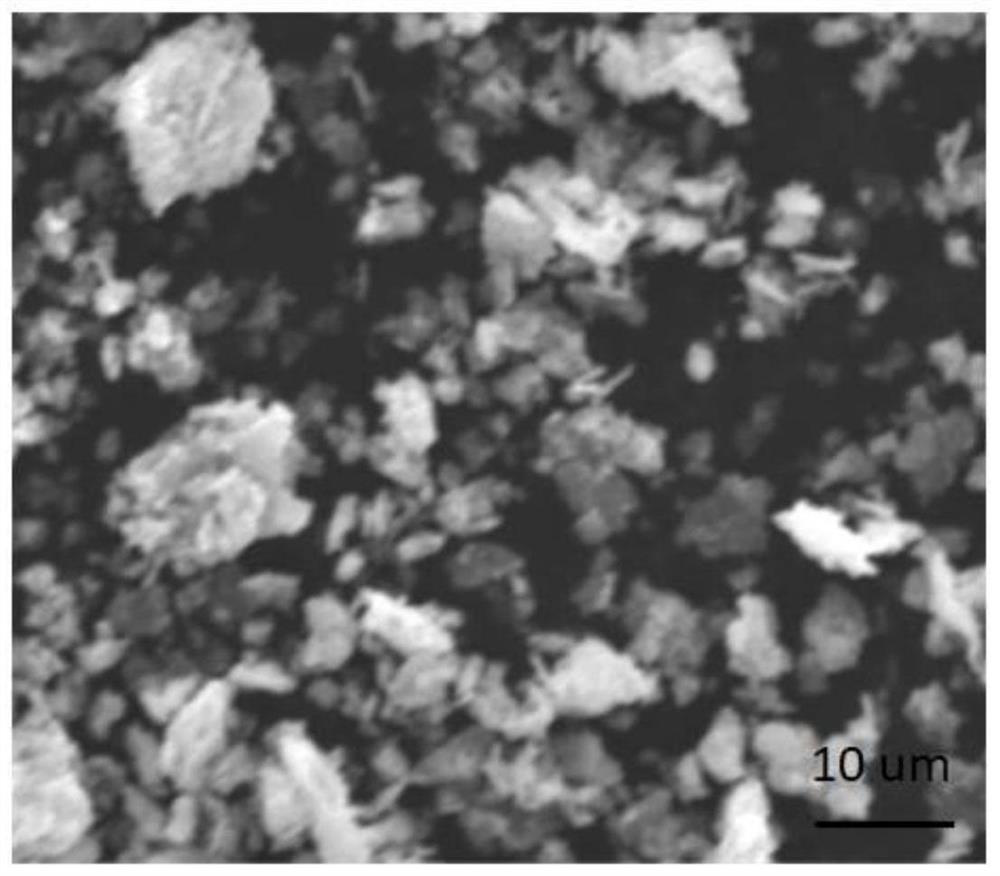
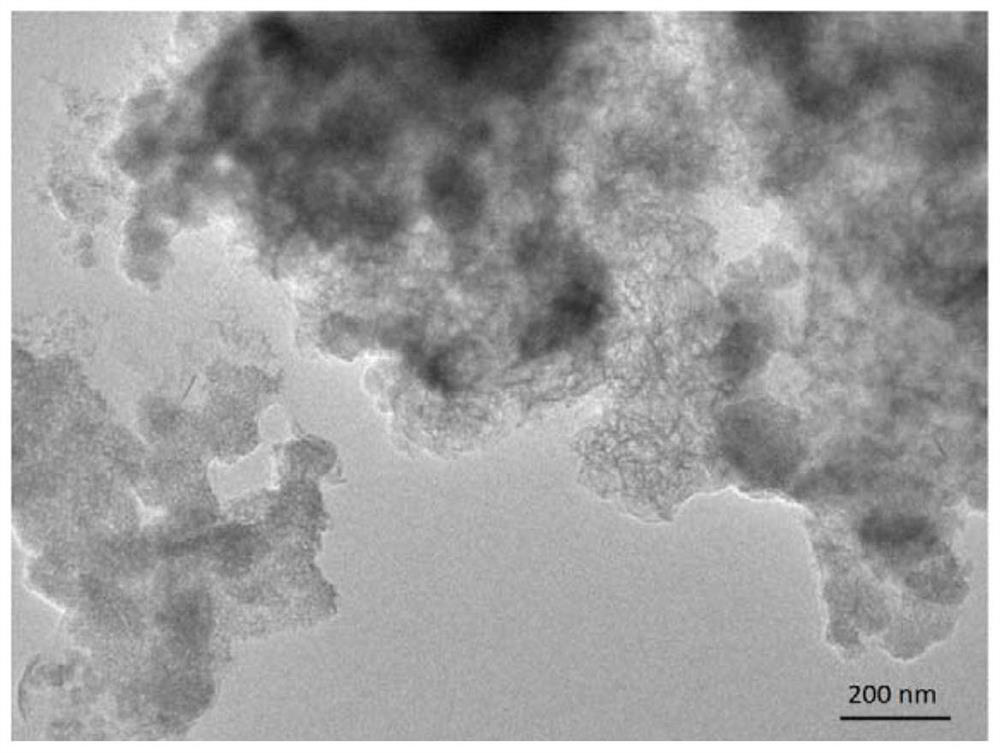
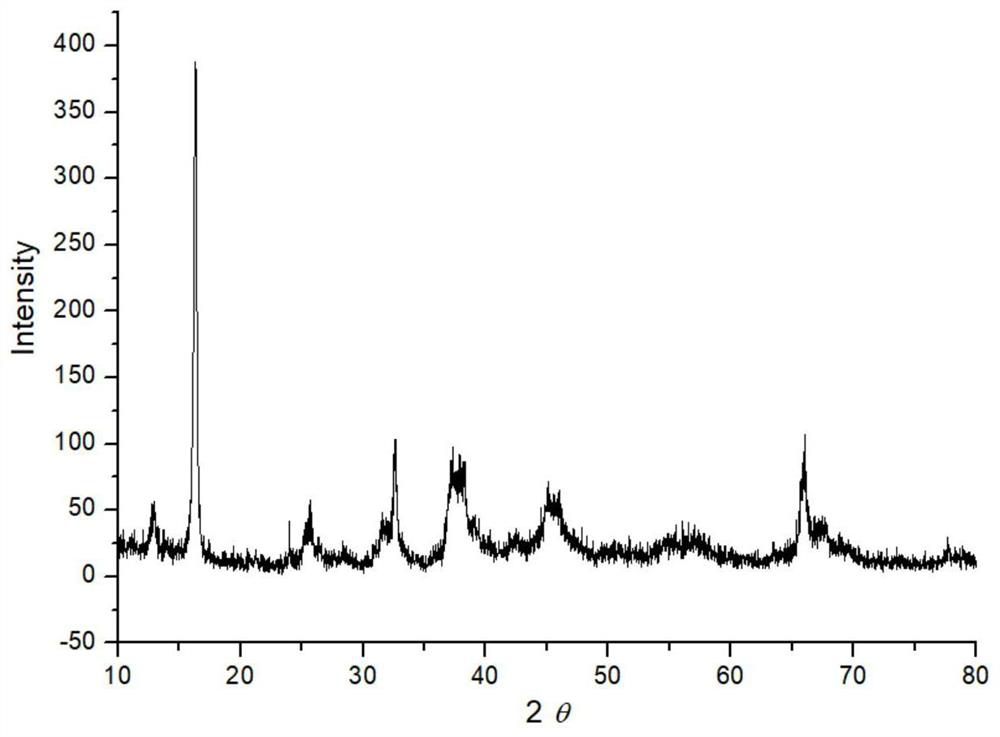
[0056] Example 1 Scanning electron microscope detection diagram and transmission electron microscope of a structure sodium-tunneling structure prepared figure 1 with 2 As shown, it is a nano-chip structure. Crystal powder diffraction diagram image 3 As shown, a comparison diffraction standard card tunnel structure manganese oxide (JCPDS No. 27-0750), a layered manganese oxide (JCPDSNO. 27-0752), the synthesized substance is a layered-tunnel symbiosis structure.
Embodiment 2
[0058] The sodium carbonate, manganese chloride and cobalt sulfate were added in water according to the ratio of molar ratio 1: 0.9: 0.1, and stirred at normal temperature for 6 hours, and the precipitate was collected, dried, pulverized, and then the dried precipitate and NaOH were taken according to quality ratio. The proportion of ball mills were uniform, followed by sintering 550 ° C in the air for 5 hours, 900 ° C for 5 hours, i.e., a layer-tunnel structure symbiotic sodium ion battery positive material NA 0.6 Mn 0.8 CO 0.2 O 2 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com