Laminated solar cell top cell and preparation method thereof
A stacked solar and top cell technology, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve the problems of low photoelectric conversion efficiency, low band gap, lead-containing perovskite, etc., and achieve rich crust content, high band gap, Effect of low antisite defect density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Cut FTO glass (light transmittance ≥ 90%) into 1.5cm×2.0cm, then use glass cleaning agent to clean FTO glass, soak it in deionized water containing glass cleaning agent, acetone, alcohol, deionized Sonicate in water for 15 minutes, and blow dry with high-purity nitrogen to obtain a clean FTO conductive glass substrate.
[0034] Use ZnSO 4 , ammonia water and thiourea were used to prepare a layer of ZnS electron transport layer on the FTO conductive glass substrate by chemical water bath method at 80°C. The film had a bandgap width of 3.4eV and a thickness of about 60nm.
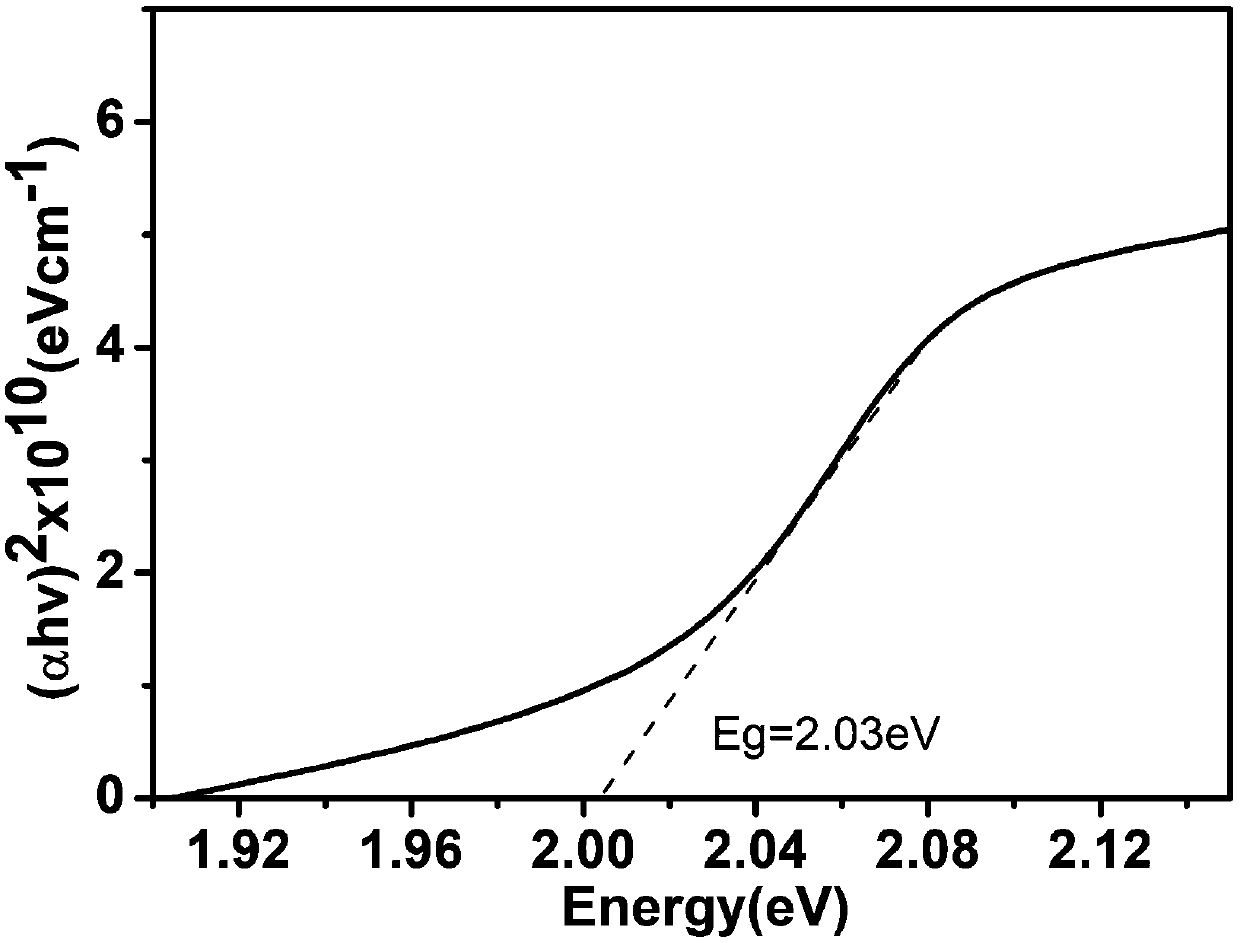
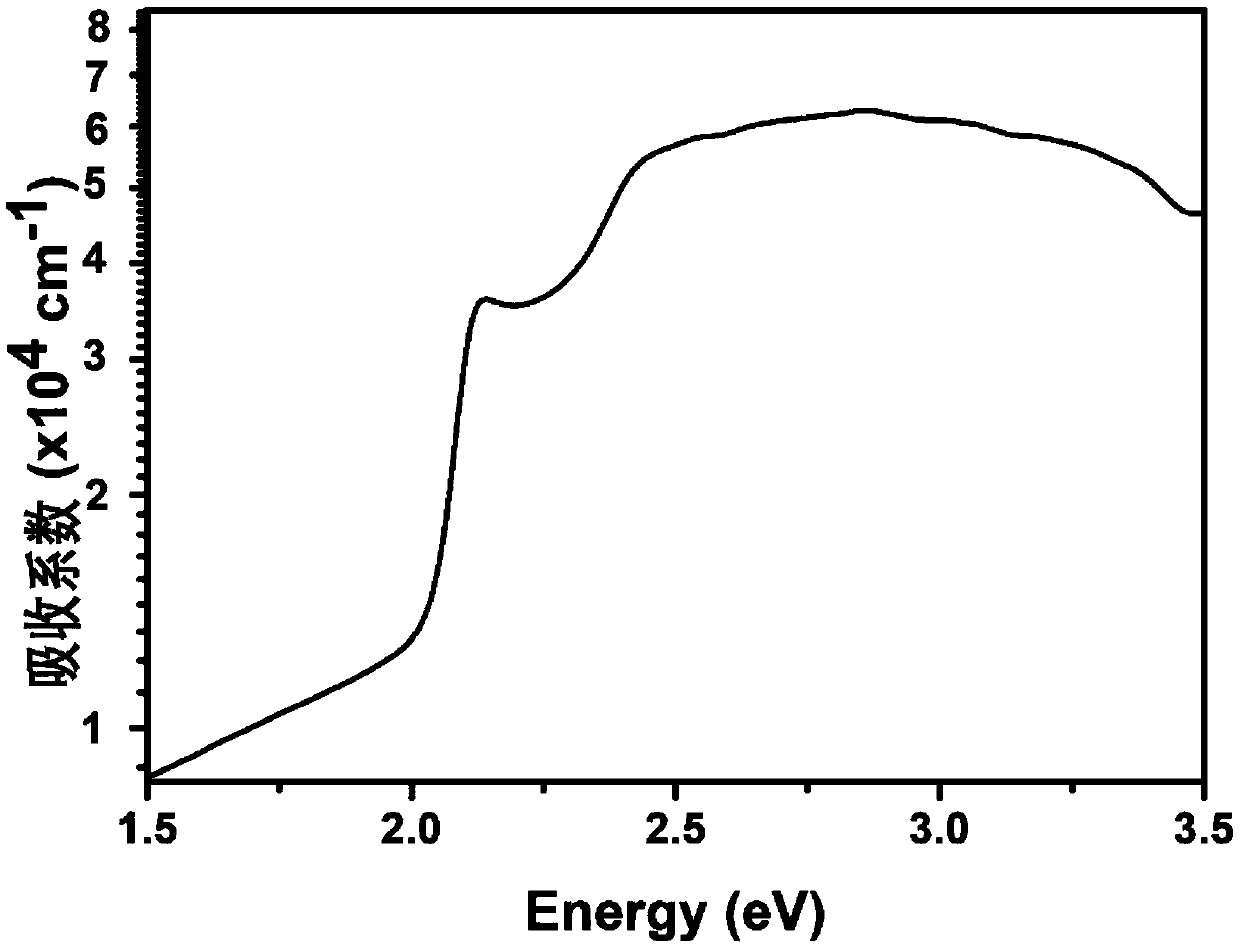
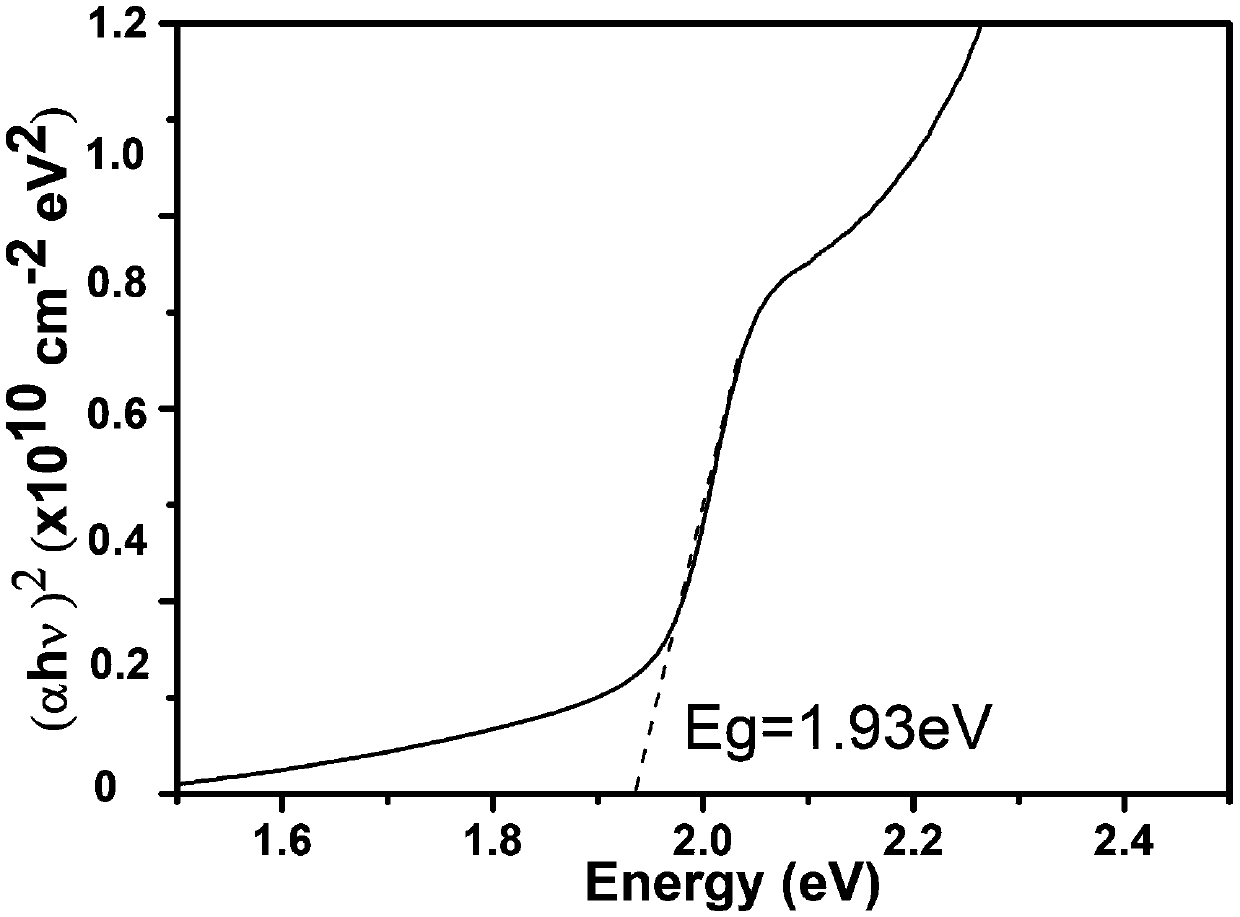
[0035] Prepare a layer of CBTS light absorption layer on the above-mentioned ZnS electron transport layer by sol-gel method; at the same time, in order to measure the forbidden band width and light absorption coefficient of the CBTS, prepare a CBTS film on a piece of white glass with the same size and cleaned according to the above method . The above two pieces of glass were annealed at 500°C for 60 ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] On the cleaned ITO transparent conductive glass substrate (light transmittance ≥ 90%), a layer of Zn(O, S) electron transport layer was prepared by ZnO and ZnS double target co-sputtering method, which can be adjusted by adjusting ZnO and ZnS The sputtering power of the target changes the ratio of O and S in the material to achieve the purpose of controlling the band gap. The final Zn(O, S) band gap is 3.05eV and the thickness is 30nm.
[0040]Then use the sol-gel method to prepare one deck of CSTS light-absorbing layer on the above-mentioned Zn (O, S) electron transport layer; simultaneously in order to measure the forbidden band width and light absorption coefficient of this CBTS thin film, in a piece of the same size, according to embodiment 1 CSTS thin films were prepared on cleaned white glass as in the method. The above two pieces of glass were annealed at 400°C for 40 minutes in a sulfide atmosphere.
[0041] Then a layer of FTO transparent top electrode was fab...
Embodiment 3
[0044] On the cleaned ATO transparent conductive glass substrate, a layer of ZnS electron transport layer was prepared by sputtering method, and then a layer of CBTS light absorption layer was prepared by sputtering method. A layer of ITO transparent top electrode was prepared by magnetron sputtering. The thicknesses of the ZnS electron transport layer, the CBTS light absorption layer, and the ITO transparent top electrode are measured to be about 80nm, 700nm, and 150nm, respectively.
[0045] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the photoelectric conversion performance of the above device was measured, and the open circuit voltage was 0.7V, and the short circuit current density was 5.25mA / cm 2 , The photoelectric conversion efficiency is 1.72%. It can be seen that the open circuit voltage of 0.7V is significantly higher than the open circuit voltage of the current 12.6% world record CZTSSe device (less than 0.6V), indicating that CBTS is a very suitable light absorbing layer materia...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com