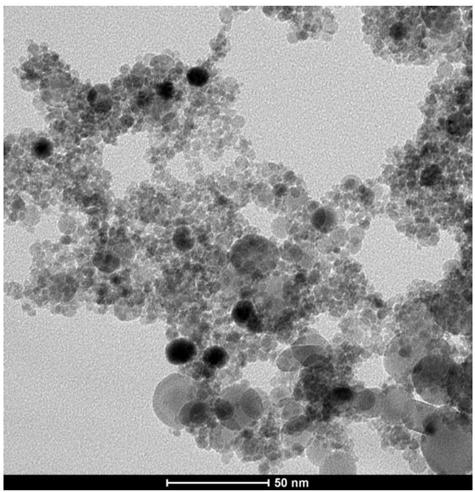
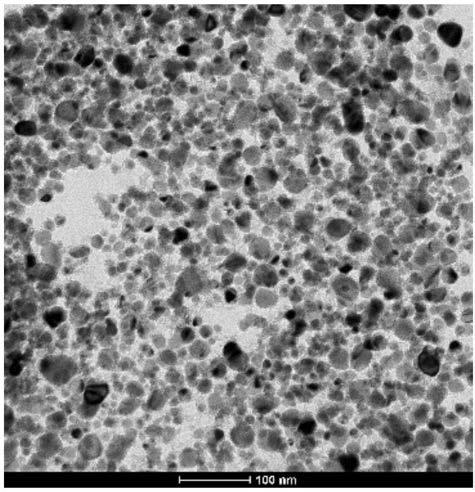
Preparation method of metal oxide nanoparticles and metal nanoparticles
A metal nanoparticle, nanoparticle technology, applied in the preparation of oxide/hydroxide, ferrous oxide, nanotechnology and other directions, to achieve the effects of good crystallinity, simple preparation method and easy large-scale production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1: Prepare a solution with a concentration of 0.1 mol / L with iron acetylacetonate and ethanol, impregnate potassium sulfate powder, remove excess impregnating liquid, and dry the powder. The dried powder is calcined at 200°C to below 500°C, washed with water and dried to obtain γ ferric oxide nanoparticles; if calcined at 500°C to 1000°C for 2 hours, washed with water and dried to obtain α ferric oxide nanoparticles Particles; if reduced between 400°C and 500°C, ferric oxide nanoparticles can be obtained after washing and drying.
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: Prepare a solution with a concentration of 0.1 mol / L with iron acetylacetonate and chloroform, impregnate potassium sulfate powder, remove excess impregnating liquid, and dry the powder. The dried powder is calcined at 200°C to below 500°C, washed with water and dried to obtain γ ferric oxide nanoparticles; if calcined at 500°C to 1000°C for 2 hours, washed with water and dried to obtain α ferric oxide nanoparticles Particles; if reduced between 400°C and 500°C, ferric oxide nanoparticles can be obtained after washing and drying.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3: A solution with a concentration of 0.1 mol / L was prepared with iron acetylacetonate and acetone, impregnated with potassium sulfate powder, and after removing excess impregnating liquid, the powder was dried. The dried powder is calcined at 200°C to below 500°C, washed with water and dried to obtain γ ferric oxide nanoparticles; if calcined at 500°C to 1000°C for 2 hours, washed with water and dried to obtain α ferric oxide nanoparticles Particles; if reduced between 400°C and 500°C, ferric oxide nanoparticles can be obtained after washing and drying.
[0039]Example 3: Prepare a solution with a concentration of 0.01 mol / L with iron acetylacetonate and chloroform, impregnate potassium sulfate powder, remove excess impregnating liquid, and dry the powder. The dried powder is calcined at 200°C to below 500°C, washed with water and dried to obtain γ ferric oxide nanoparticles; if calcined at 500°C to 1000°C for 2 hours, washed with water and dried to obtain α fe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com