Amphoteric-polymer-based marine antifouling surface and preparation method thereof
An amphoteric polymer, marine antifouling technology, used in antifouling/underwater coatings, coatings, biocide-containing paints, etc., to achieve the effect of easy operation, prevention of marine biofouling, and good marine antifouling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
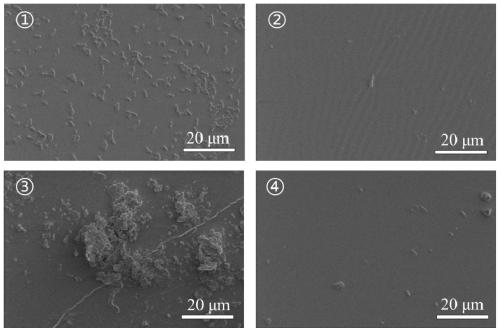
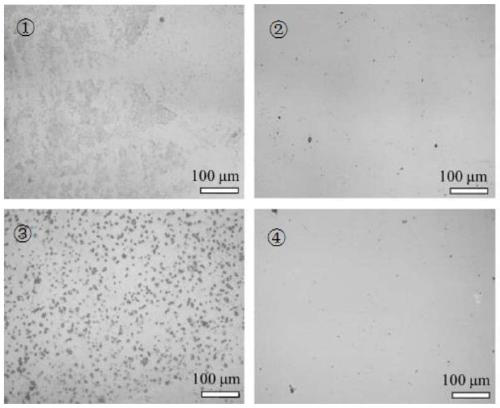
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] This embodiment provides a method for preparing an amphoteric polymer-based marine antifouling surface, comprising the following steps:
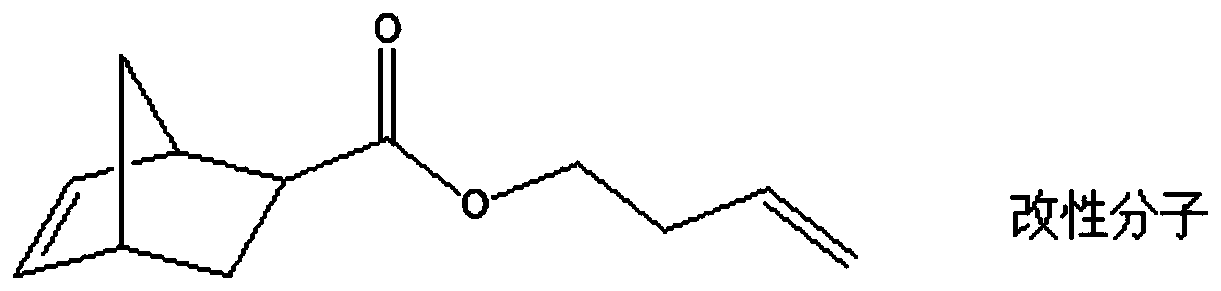
[0033] S1. Preparation of zwitterionic monomers:
[0034] Take 1.38g of norbornene acid and 1.34g of hydroxyethylimidazole into a 100ml round bottom flask, add 50ml of dichloromethane and stir to dissolve, then add 1.86g of N,N-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and 0.06g of 4 - Dimethylaminopyridine. The temperature of the reaction was controlled at 0° C., and the reaction was completed after 24 hours. The precipitate was removed by filtration, and the obtained solution was washed with water, sodium bicarbonate and a saturated solution of sodium chloride in sequence, and after drying, the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. Then, 1.46 g of 1,3-propane sultone and 4 ml of acetonitrile were added to the product of the first step. After 48 hours of reaction at room temperature, ether was added to precipitate a white solid, which wa...
Embodiment 2
[0040] S1. Preparation of zwitterionic monomers:
[0041] Take 1.38g of norbornene acid and 1.23g of hydroxyethylimidazole into a 100ml round bottom flask, add 50ml of dichloromethane and stir to dissolve, then add 1.86g of N,N-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and 0.06g of 4 - Dimethylaminopyridine. The temperature of the reaction was controlled at 20°C. After 18 hours, the reaction was completed, and the precipitate was removed by filtration. The resulting solution was washed with water, sodium bicarbonate and a saturated solution of sodium chloride in sequence, and after drying, the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. Then, 1.22 g of 1,3-propane sultone and 3 ml of acetonitrile were added to the product of the first step. After reacting at room temperature for 24 hours, ether was added to precipitate a white solid, which was dried at room temperature to obtain a zwitterionic monomer.
[0042] S2, preparation of modified polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS):
[0043] Take 10g ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] S1. Preparation of zwitterionic monomers:
[0048] Take 1.38g of norbornene acid and 1.34g of hydroxyethylimidazole into a 100ml round bottom flask, add 50ml of dichloromethane and stir to dissolve, then add 1.86g of N,N-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and 0.06g of 4 - Dimethylaminopyridine. The temperature of the reaction was controlled at 10°C. After 36 hours, the reaction was completed, and the precipitate was removed by filtration. The resulting solution was washed with water, sodium bicarbonate and a saturated solution of sodium chloride in sequence, and after drying, the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. Then, 1.34 g of 1,3-propane sultone and 6 ml of acetonitrile were added to the product of the first step. After reacting at room temperature for 48 hours, diethyl ether was added to precipitate a white solid, which was dried at room temperature to obtain a zwitterionic monomer.
[0049] S2, preparation of modified polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS):
[0050] T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com