A kind of enzyme treatment method of wool fabric and the method for inkjet printing of wool fabric
An inkjet printing and fabric technology, applied in the field of wool printing, can solve problems such as unfavorable large-scale production, strong fabric damage, long process flow, etc., and achieve the effects of excellent color fastness index, small fiber damage, and short process flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
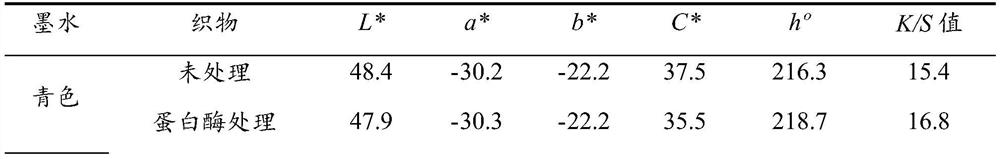
[0052] First soak the wool fabric in the 50°C treatment solution (JFC penetrant 1g / L) for 30s, and pass through the padding machine once; / L, Savinase 16L 1.3g / L, 50°C, bath ratio 1:100) soaked for 30s, passed through a rolling mill once (time 10s, liquid carrying rate 85%). Continuous immersion and liquid squeezing for 5 times, the error range of the control liquid carrying rate is within 1%. Immediately after continuous padding, soak the fabric in hot water at 80°C for 10 minutes to inactivate protease, then wash it in cold water for 10 minutes, and then dry it in an oven at 100°C to obtain enzyme-treated woolen fabric for later use.
[0053] The breaking strength of the fabric after enzyme treatment is tested; the breaking strength of the fabric is operated according to the method described in GB / T3923.1-2003 "Tensile Properties of Textile Fabrics Part One Determination of Breaking Strength and Elongation at Break" . The test fabric is a cloth strip with a length of 30 cm...
Embodiment 2
[0059] First soak the wool fabric in the 50°C pretreatment solution (JFC penetrant 1g / L) for 30s, and pass through the padding machine once; / L, Savinase 16L 1.3g / L, 50°C, bath ratio 1:100) for 200s; soak the soaked fabric in 80°C hot water for 10 minutes to inactivate protease, then wash in cold water for 10 minutes, and wash thoroughly Put it into an oven for drying at 100° C. to obtain the wool fabric after enzyme treatment.
[0060] This enzyme treatment method can also improve the inkjet printing effect of wool fabrics, but the final effect is not as good as that of continuous padding.
Embodiment 3
[0066] Prepare 2wt% sodium alginate printing paste: First, dissolve 10g of urea and 2g of ammonium sulfate in 86g of distilled water under the action of mechanical stirring, stir with a stirrer RW20 at a speed of 1000r / min, and then slowly mix 2g of sodium alginate Pour into the dissolved solution to obtain the sodium alginate printing paste with a pH value of 5.6-6.6 and a viscosity of 1000-2000mPa·s.
[0067] Use the P-B0 horizontal padding machine to pad the prepared printing paste onto the wool fabrics obtained in Example 1 and Comparative Examples 1-2 respectively, and the pressure on both sides of the roll is 0.1kg / cm 2 , The roll speed is 12r / min, and the liquid carrying rate of the fabric is (80±1)%. The padded fabrics were dried in an oven at 80° C. to obtain modified wool fabrics respectively.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com