A kind of preparation method of zirconium-based amorphous alloy surface nanostructure layer
A zirconium-based amorphous alloy and nanostructure technology, applied in the field of metal surface treatment, can solve the problems of osseointegration and poor corrosion resistance of target tissue, and achieve the effect of avoiding adverse effects and good corrosion resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0024] The preparation method of the nanostructure layer on the surface of the zirconium-based amorphous alloy comprises the following specific steps: putting the three electrodes into the electrolyte solution containing fluorine ions, adjusting the voltage of the working electrode, the rotating speed of the working electrode, the temperature of the electrolyte solution and the voltage output time, applying the voltage , to prepare nanostructured layers.
[0025] Among them, the three electrodes are: working electrode: disc made of zirconium-based amorphous alloy, reference electrode: saturated calomel electrode (potential at room temperature is 0.241V), auxiliary electrode: square graphite or platinum sheet.
[0026] The electrolyte is an aqueous solution of ethylene glycol containing fluorine ions.
[0027] Zirconium-based amorphous alloys are composed of five elements: Zr, Cu, Ni, Ti, and Al. The mass percentages of each element are Zr 50-65%, Cu 15-25%, Ni 10-15%, Ti 5-10%...
Embodiment 1
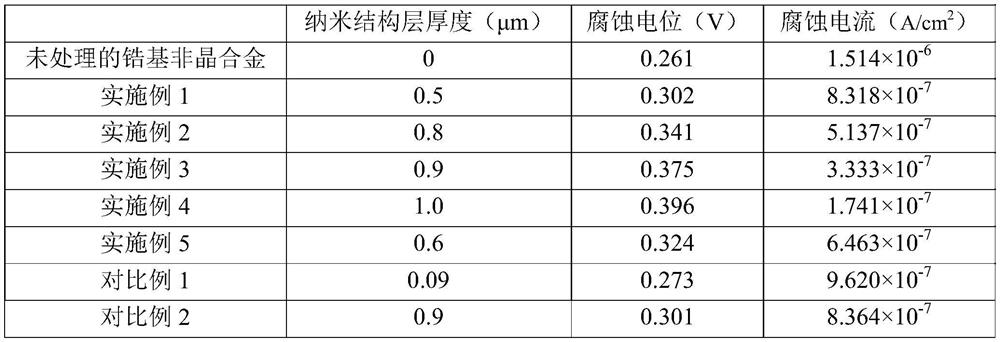
[0030] Put the working electrode, saturated calomel electrode and auxiliary electrode (square platinum sheet) into the electrolyte, adjust the working electrode voltage to 8V (vs SCE), the working electrode speed to 800rpm, the electrolyte temperature to 25°C, and the voltage output time to After 40 minutes, voltage was applied, and the disc was taken out after power off, cleaned and dried to obtain a zirconium-based amorphous alloy with a nanostructure layer on the surface.
[0031] Wherein, the electrolytic solution is obtained by dissolving sodium fluoride in water, and then mixing the aqueous solution of sodium fluoride and ethylene glycol, the fluoride ion concentration is 0.4mol / L, and the volume percentage of water is 5%.
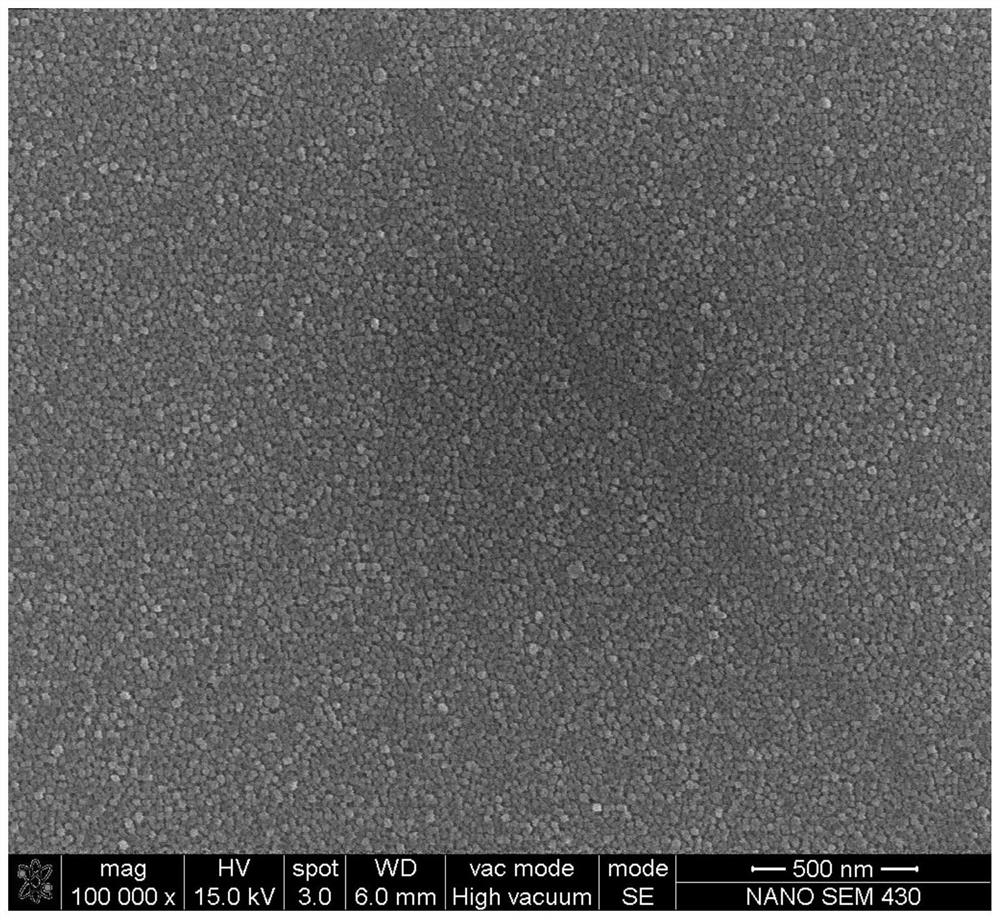
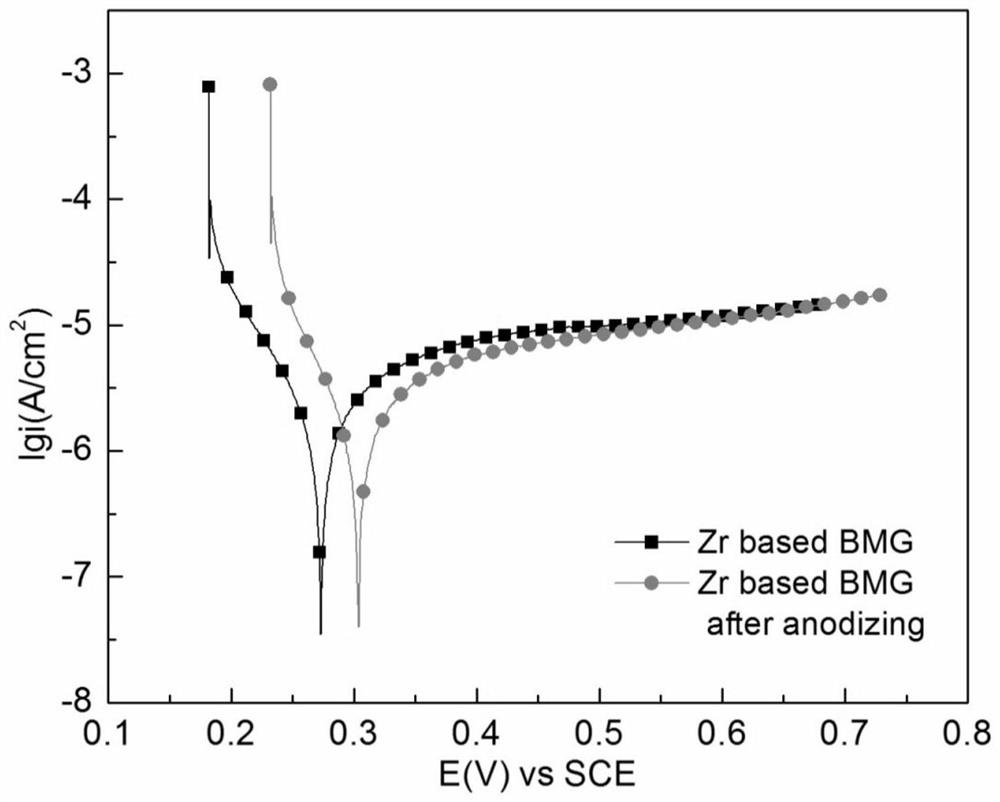
[0032] figure 1 It is the scanning electron micrograph of the nanostructure layer prepared in embodiment 1, from figure 1 It can be seen that a uniform and dense nanostructure layer is formed on the surface of the treated zirconium-based amorphous a...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Put the working electrode, saturated calomel electrode and auxiliary electrode (square platinum sheet) into the electrolyte, adjust the working electrode voltage to 10V (vs SCE), the working electrode speed to 1000rpm, the electrolyte temperature to 25°C, and the voltage output time to After 40 minutes, voltage was applied, and the disc was taken out after power off, cleaned and dried to obtain a zirconium-based amorphous alloy with a nanostructure layer on the surface.
[0036] Wherein, the electrolytic solution is obtained by dissolving sodium fluoride in water, and then mixing the sodium fluoride aqueous solution with ethylene glycol, the fluoride ion concentration is 0.4mol / L, and the volume percentage of water is 10%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com