Preparation method of cellulose conducting hydrogel for 3D printing
A conductive hydrogel, 3D printing technology, applied in the direction of additive processing, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the practical application of hydrogels, unable to manufacture complex structures, etc., achieving good thermal reversible mechanical properties, good freeze resistance, gelatin fast effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
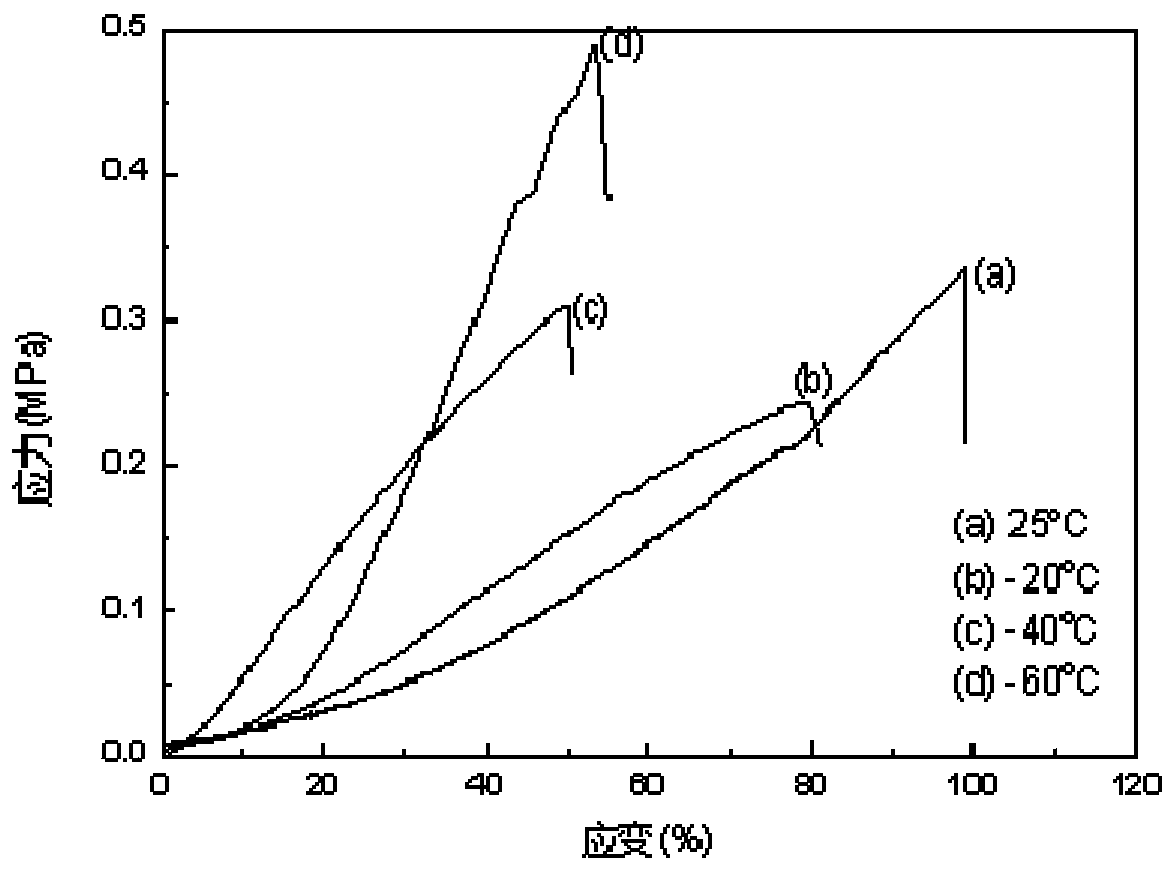
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] (1) Accurately weigh 10.21g of ZnCl 2 and 0.35gCaCl 2 Dissolve in 4g of deionized water, add 0.2g of cotton linters after centrifugation, and dissolve with magnetic stirring at 75°C for 30 minutes until completely dissolved to obtain a cellulose solution;
[0030] (2) Add 2.5 g of water to the cellulose solution obtained in step (1), and stir evenly at 75°C through magnetic force;
[0031] (3) The cellulose solution obtained in step (2) is ultrasonically debubbled at 90° C., and then the cellulose solution is cooled and gelled at room temperature to obtain a cellulose hydrogel that can be used for 3D printing;
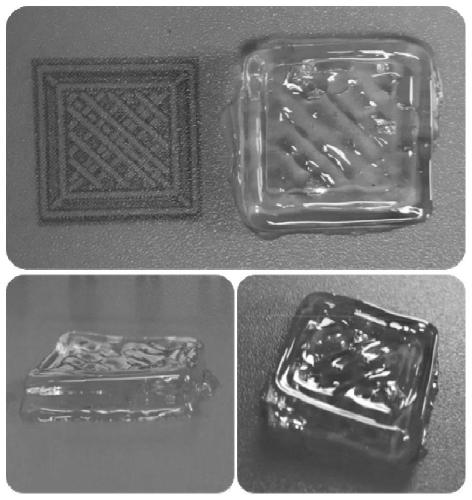
[0032] (4) The slicing software of the 3D printing system uses the UltimakerCura3.4.1 instruction software to divide the graphics, set the printing parameters, and export the printing model. The 3D X-Y-Z movable 304 stainless steel control nozzle is installed in the printing equipment, the temperature of the barrel is adjusted to 69°C, the diameter of the nozz...
Embodiment 2
[0035] (1) Accurately weigh 9.5g of ZnCl 2 and 0.25gCaCl 2 Dissolve in 3.5g of deionized water, add 0.18g of cotton linters after centrifugation, and dissolve with magnetic stirring at 75°C for 30 minutes until completely dissolved to obtain a cellulose solution;
[0036] (2) Add 0.8 g of glycerol to the cellulose solution obtained in step (1), and stir evenly at 75° C. by magnetic force;
[0037] (3) The cellulose solution obtained in step (2) is ultrasonically debubbled at 80° C., and then the cellulose solution is cooled and gelled at room temperature to obtain a cellulose hydrogel that can be used for 3D printing;
[0038] (4) With embodiment 1 step (4).
[0039] Using the method of this embodiment, the gel time is 25-30s. Put the cellulose hydrogel in a water bath at 75°C and heat it at a constant temperature for 5 minutes to 10 minutes to return to the state of the sol.
Embodiment 3
[0041] (1) Accurately weigh 10.21g of ZnCl 2 and 0.33gCaCl 2 Dissolve in 3.63g of deionized water, add 0.3g of cotton linters after centrifugation, and dissolve with magnetic stirring at 75°C for 40 minutes until completely dissolved to obtain a cellulose solution;
[0042] (2) Add 3 g of water to the cellulose solution obtained in step (1), and stir evenly at 75° C. by magnetic force;
[0043] (3) Put the cellulose solution obtained in step (2) at a constant temperature of 90° C. for defoaming, and then cool the cellulose solution to gel at room temperature to obtain a cellulose hydrogel that can be used for 3D printing;
[0044] (4) With embodiment 1 step (4).
[0045] Using the method of this embodiment, the gel time is 8s. Put the cellulose hydrogel in a water bath at 85°C and heat it at a constant temperature for 5 minutes to 10 minutes to return to the state of the sol. ,
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| transmittivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com