Preparation method for extracting phycoerythrobilin, polysaccharides and dietary fibers from low valued lavers and application of preparation method
A technology of seaweed polysaccharides and dietary fiber, applied to bacteria used in food preparation, polysaccharide/gum-containing food ingredients, applications, etc., can solve the problems of high industrial production costs, complex and cumbersome processes, etc., achieve obvious health effects and enhance curative effect , The preparation process is simple, stable and efficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Example 1: Ultra-clinical extraction process of phycoerythrin and laver polysaccharide
[0025] (1) Supercritical extraction process screening
[0026] Put the fresh laver at the end of water into a centrifugal dehydrator to remove water, chop it up, add entrainer and soak it overnight. Divided into two methods of extraction:
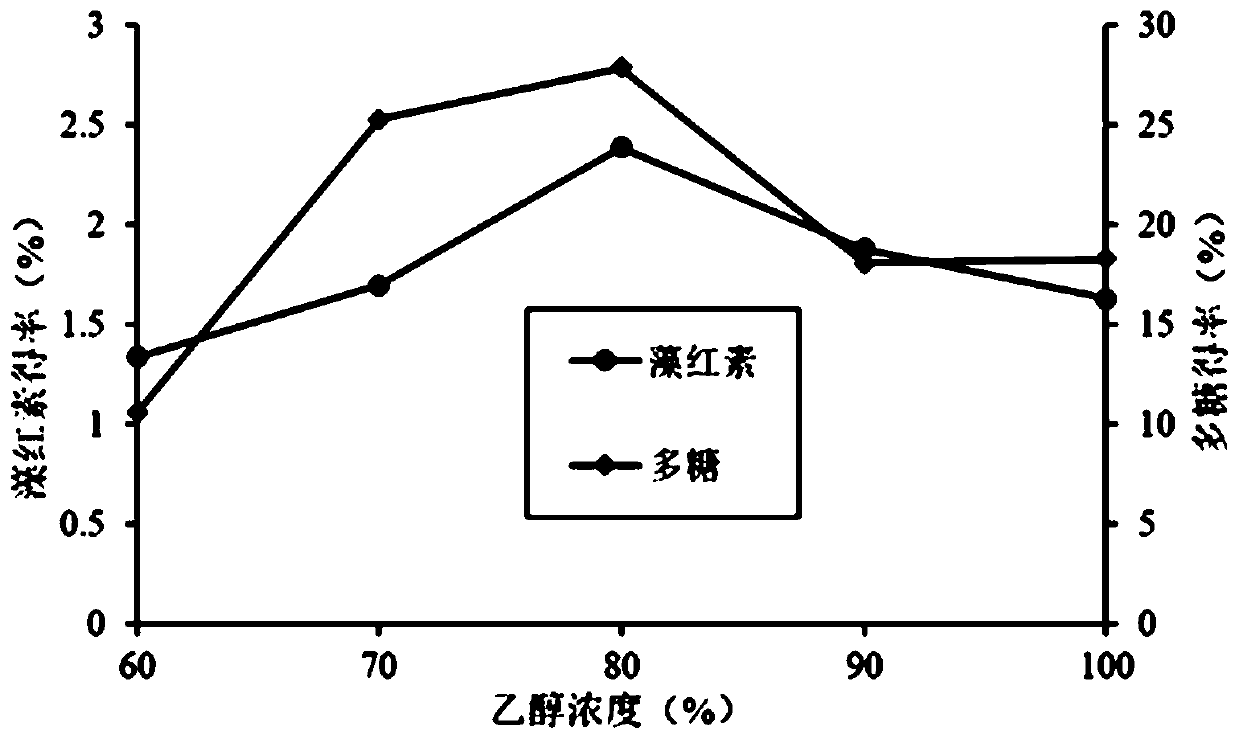
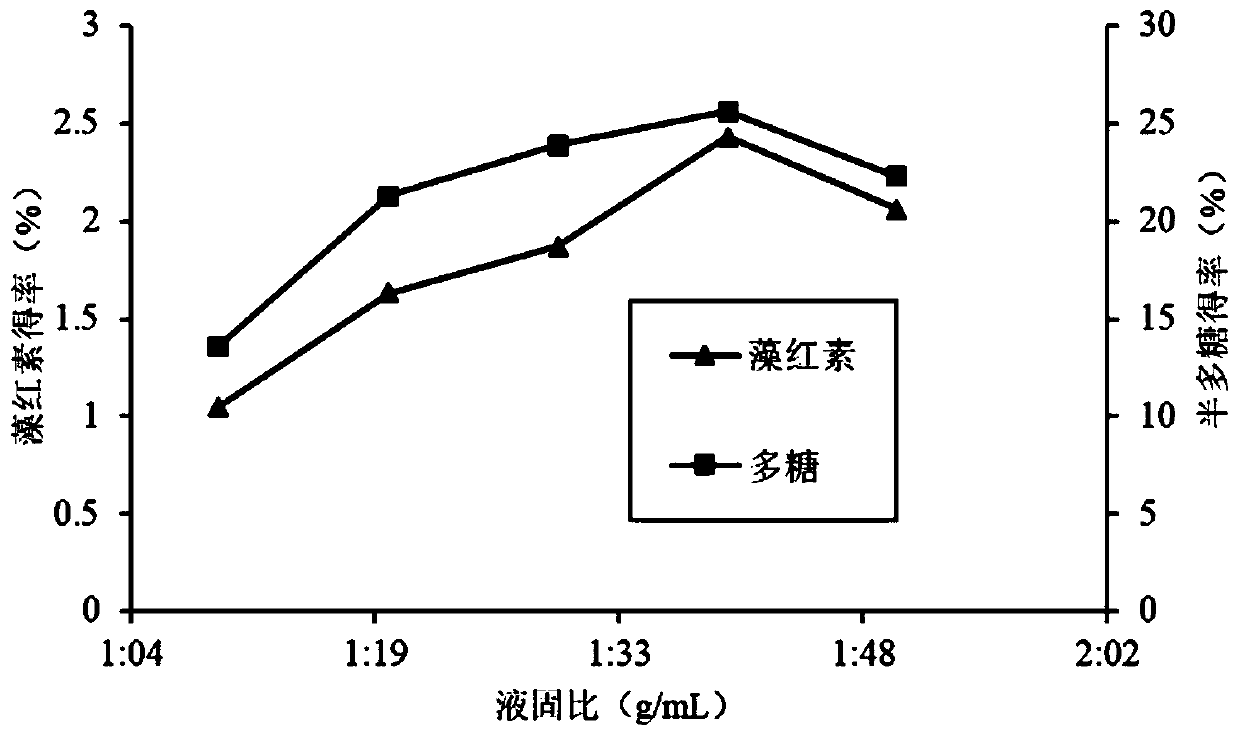
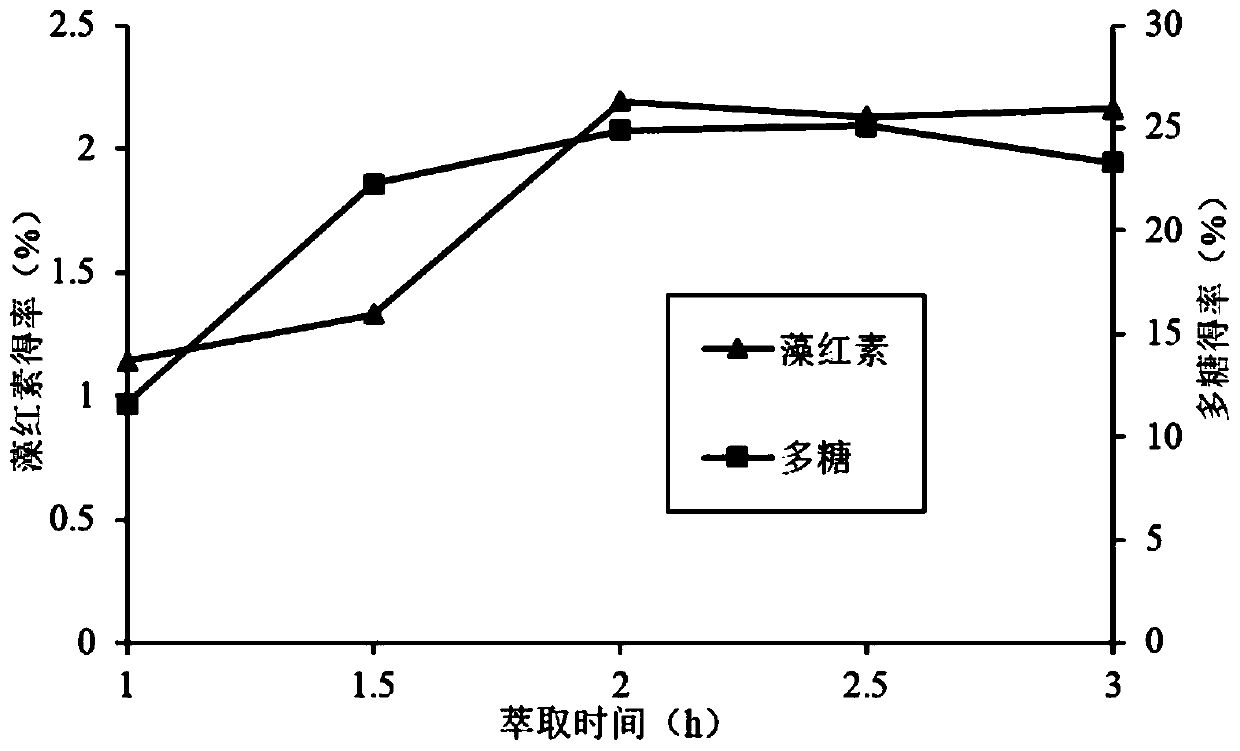
[0027] Method I: Put the dried seaweed soaked overnight and entrainer into supercritical CO 2 In the fluid extraction tank, the liquid-solid ratio of the filler is 1:40, the extraction temperature is 32°C, the extraction pressure is 60MPa, and the dynamic extraction is carried out for 2h at the flow rate of the entrainer at 10mL / min.
[0028] Method II: Put the dried seaweed soaked overnight and the entrainer into supercritical CO 2 In the fluid extraction tank, the liquid-solid ratio of the filler is 1:40, the extraction temperature is 32°C, and the extraction pressure is 60 MPa. Static extraction is performed for 1 hour, and then entrainer i...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Embodiment 2: Preparation and purification process of phycoerythrin
[0046] After the extract was concentrated under reduced pressure, 20% ammonium sulfate solution was added, centrifuged at 10000r / min for 20min, and the supernatant was taken to continue to add ammonium sulfate solution to 60%, after standing for 12h, centrifuged at 10000r / min for 20min, the supernatant was used for later use. After the precipitate was reconstituted, it was dialyzed with a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 1000 Da until no salt ions existed, and then freeze-dried to obtain purified phycoerythrin with a calculated yield of 2.4%. Measure the absorbance at 280nm and 562nm, and calculate the purity of phycoerythrin to reach 2.1. Figure 5 Shown is the ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum of phycoerythrin at 400nm-700nm. It can be seen from the figure that phycoerythrin has two complete absorption peaks and one absorption shoulder peak, the absorption peaks are located at ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3: Hygroscopic and moisturizing activity of phycoerythrin
[0048] Clean and dry the desiccator and weighing bottle, and put the color-changing silica gel in the desiccator. Accurately weigh 0.25g of dried phycoerythrin into a dry weighing bottle, add 1mL of distilled water each, and accurately weigh the total weight. Open the cap of the weighing bottle and place it in a desiccator, seal the desiccator, and put it into a 25°C incubator. Accurately weigh after 2h, 4h, 6h, 12h, 24h, 48h, and 72h, respectively weigh the water content Hn and the added water content H after the sample is placed 0 . Calculate the moisture retention rate according to the following formula: moisture retention rate / %=100Hn / H 0 . . Take 2 desiccators and 10 weighing bottles, clean and dry them, and divide them into two groups, one group is potassium acetate saturated solution group, and the other group is ammonium sulfate saturated solution group. Take an appropriate amount of sa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com