Processing method for improving intergranular corrosion resistance of alloy with fcc crystal structure
A technology of intergranular corrosion and processing methods, applied in the field of steel alloy materials, can solve the problems of grain falling off, austenitic stainless steel damage, and weakening of bonding force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] It is smelted according to the set composition to make molten steel. The process is carried out in a vacuum smelting furnace. First, electrolytic chromium, molybdenum, nickel, T10 carbon steel and pure iron are added, heated until all the materials are melted, and then silicon and electrolytic manganese are added to become silicon. and electrolytic manganese are all melted to make molten steel;
[0036] Under the action of electromagnetic stirring, the molten steel is poured into the continuous casting machine for continuous casting. After the continuous casting is completed, the water is cooled to 150°C to obtain the continuous casting billet. The composition contains C 0.058%, Cr 17.8%, Ni 12%, Mo 3%, Si 0.65%, Mn 2%, P 0.015%, S 0.006%, the balance is Fe and unavoidable impurities; slab thickness 200mm;
[0037] Rough rolling, the rolling temperature is 1150°C, the rough rolling deformation is 5% → 6% → 7% → 8% → 9%, a total of 5 passes, the total deformation is 30.5...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Method is with embodiment 1, and difference is:
[0042] (1) The composition of the continuous casting slab contains C 0.022%, Cr 16%, Ni 10.5%, Mo 2.1%, Si0.2%, Mn 1.2%, P 0.02%, S 0.004%, thickness 150mm by mass percentage;
[0043] (2) The starting temperature of rough rolling is 1100°C, the deformation of the rough rolling passes is 6% → 6% → 8% → 10%, a total of 4 passes, the total deformation is 26.7%, and the thickness of the rough rolling plate is 110mm;
[0044] (3) The starting temperature of finish rolling is 950°C, the finish rolling temperature is 760°C, the pass deformation of finish rolling is 5-8%, the total deformation is 90.9%, and the thickness of hot rolled plate is 10mm;
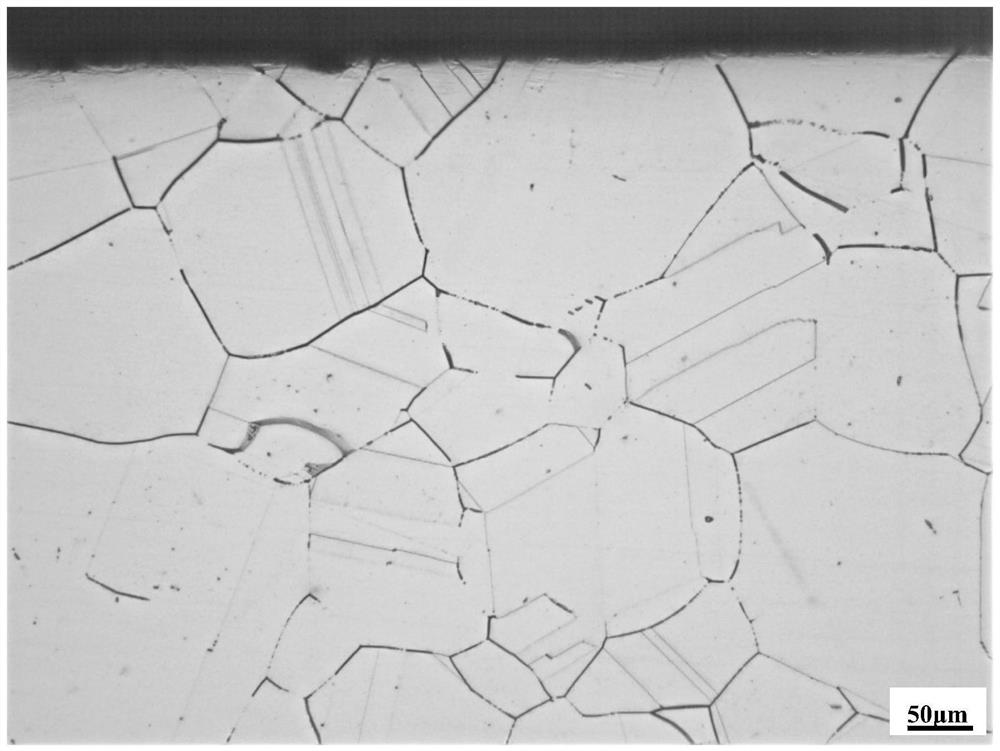
[0045] (4) The hot-rolled sheet is subjected to solution treatment at 1050°C, time t=2h=20min; after intergranular corrosion detection, observe the metallographic structure, such as Figure 4As shown, there is no obvious grain shedding and corrosion tendency; the proportion of CS...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Method is with embodiment 1, and difference is:
[0048] (1) The composition of the continuous casting slab contains C 0.069%, Cr 17.1%, Ni 13%, Mo 1.4%, Si 0.58%, Mn 0.5%, P 0.019%, S 0.002%, thickness 300mm;
[0049] (2) The starting temperature of rough rolling is 1120°C, the rough rolling pass deformation is 4% → 5% → 6% → 7% → 8% → 8%, a total of 6 passes, and the total deformation is 32.7%. Rough rolling plate thickness 202mm;
[0050] (3) The starting temperature of finish rolling is 1020°C, the finish rolling temperature is 800°C, the pass deformation of finish rolling is 5-8%, the total deformation is 75.2%, and the thickness of hot rolled plate is 50mm;
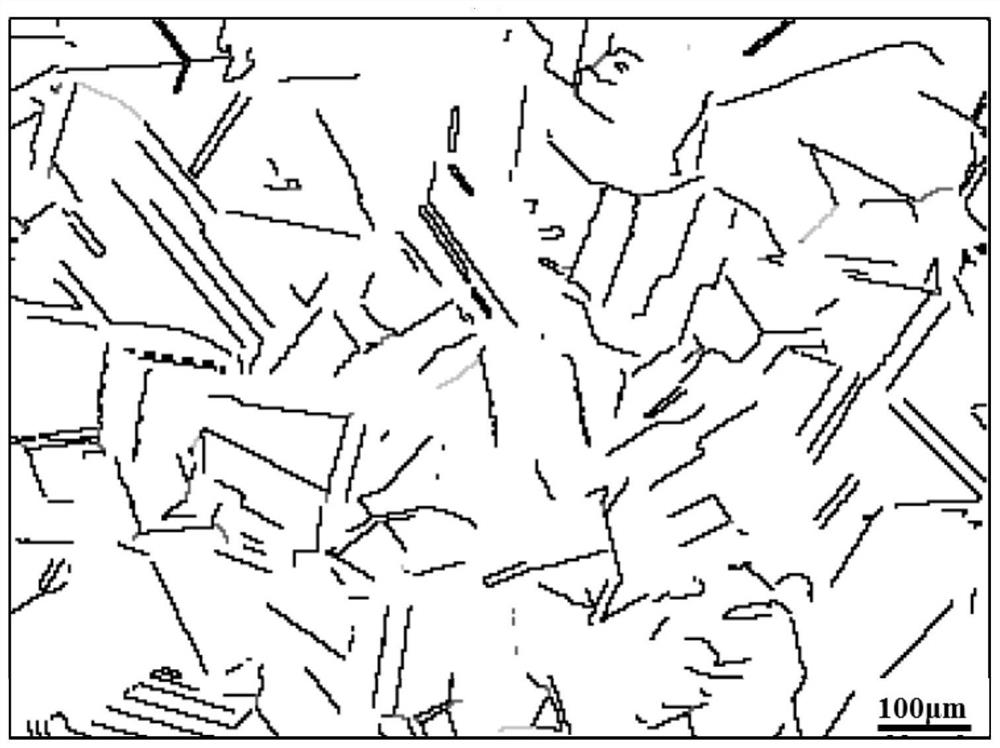
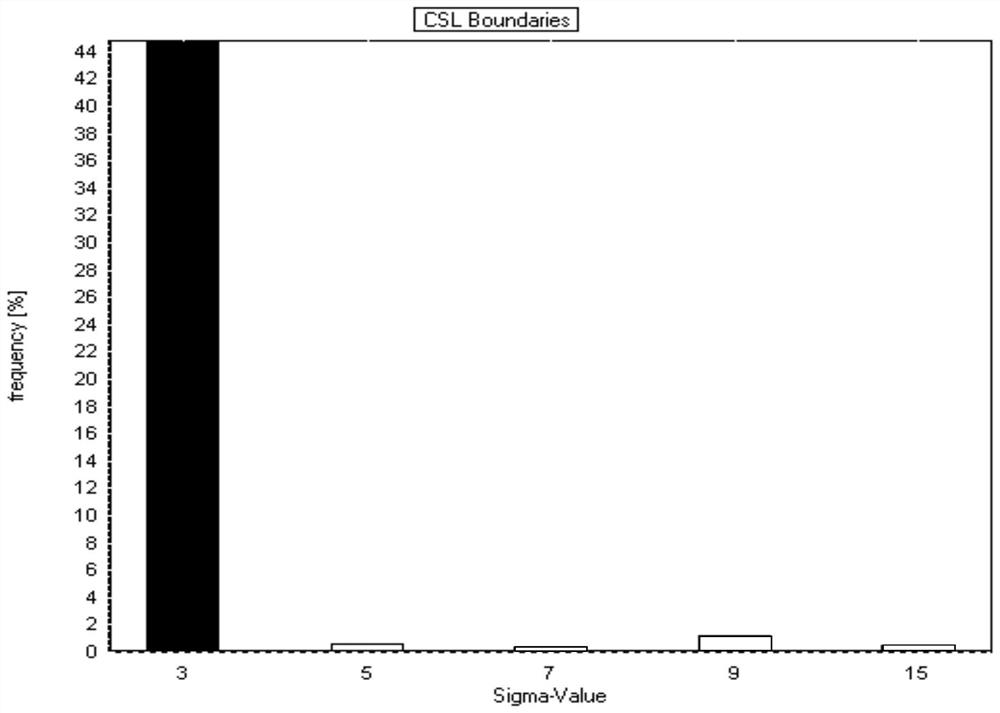
[0051] (4) The hot-rolled sheet is subjected to solution treatment at 1100°C, time t=1.2h=60min; after intergranular corrosion detection, observe the metallographic structure, such as Figure 5 As shown, there is no obvious grain shedding and corrosion tendency; the proportion of CSL grain boundary is 46%. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com