Method for identifying base modification
A base, non-modification technology, applied in the field of identifying single-base methylation modification, can solve the problems of low repetition rate, no single-base precision method, and low resolution, so as to reduce false positives and save antibodies The effect of the enrichment step
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
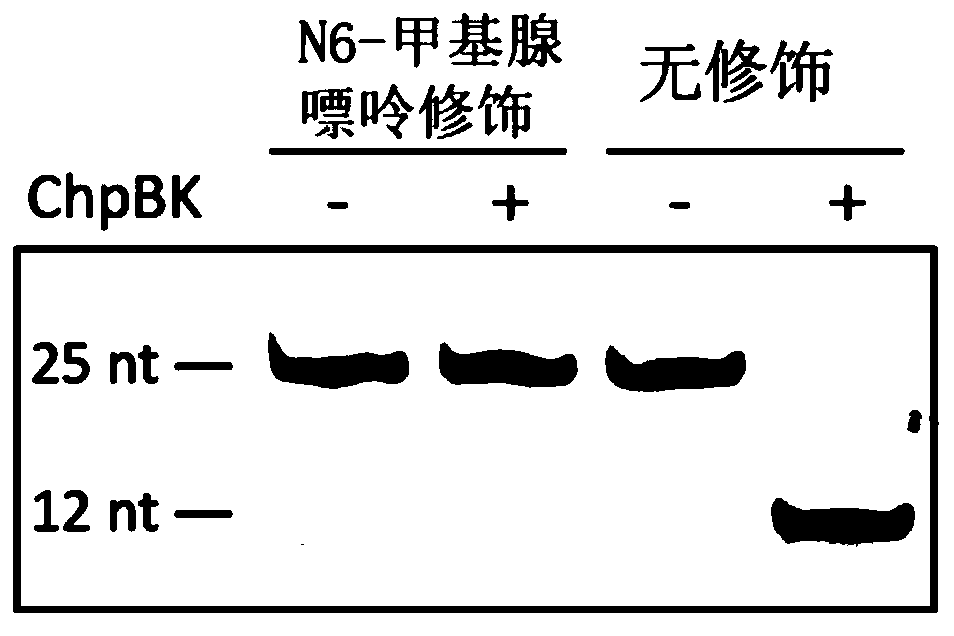
[0052] Example 1 RNA endonucleases MazF and ChpBK cut RNA oligonucleotides
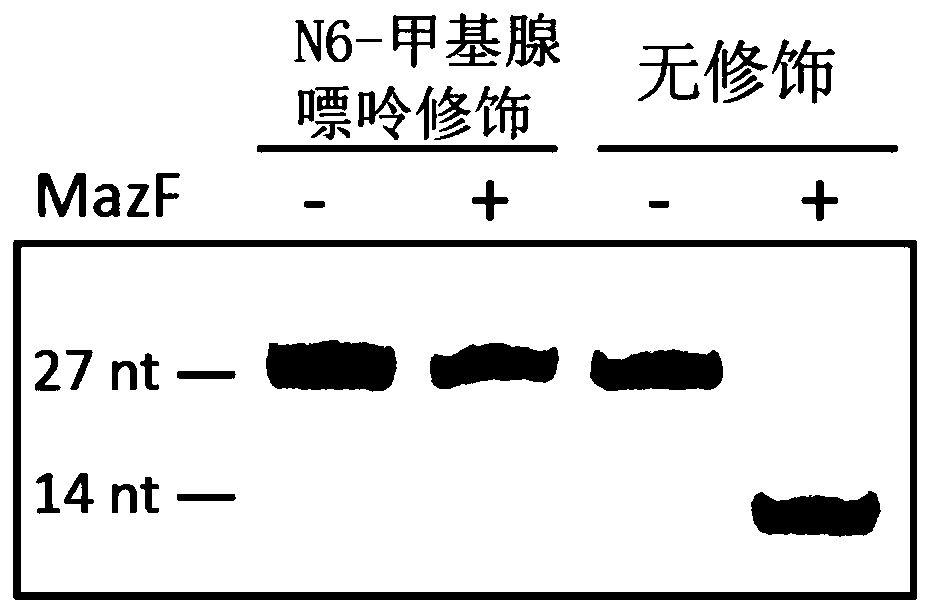
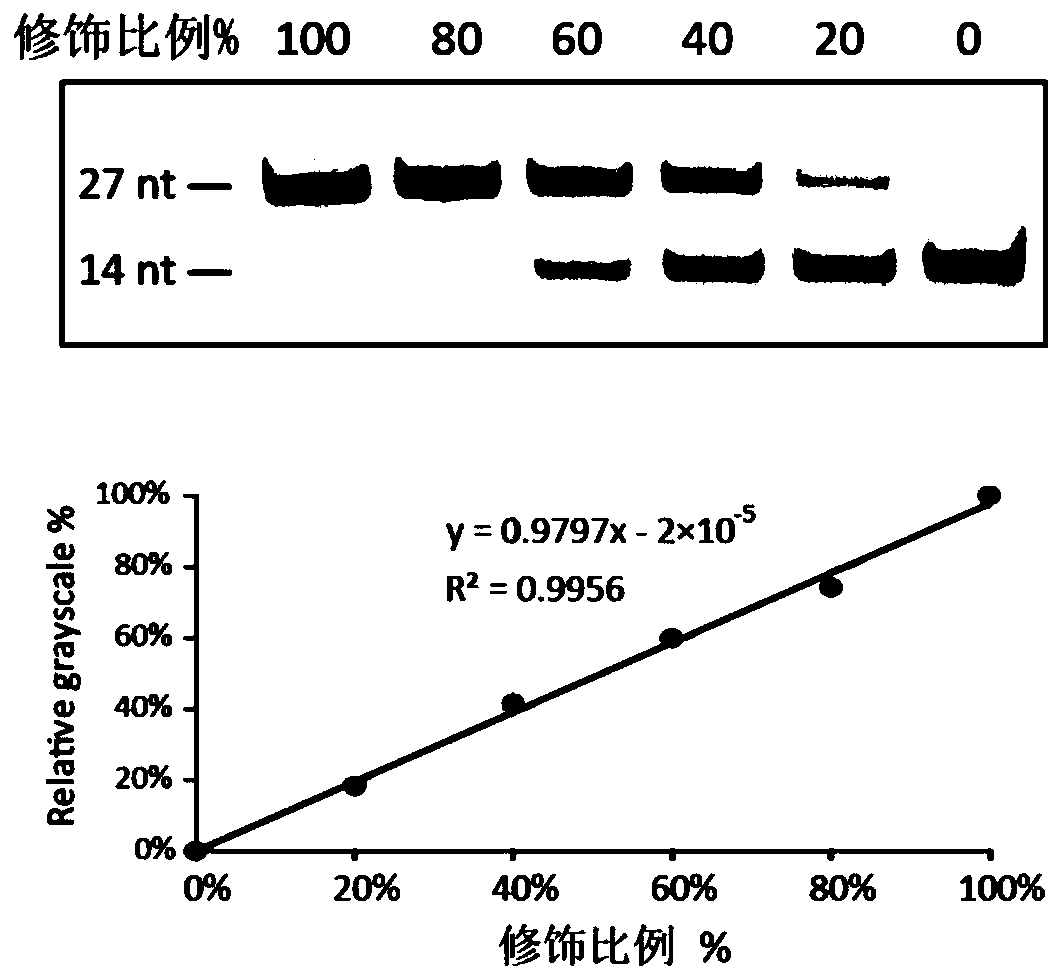
[0053] Using RNA oligonucleotide sequences synthesized in vitro for verification, it was found that MazF could only digest the ACA sequence without methylation modification, and cut at the 5' end of ACA, but could not digest the methylation modification ACA sequence ( figure 1 ). We mixed RNA oligonucleotide sequences with and without methyl groups so that the ratios of modification sites were 0%, 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, 100%, respectively, using To simulate the situation of partial methylation in vivo, and use MazF enzyme to carry out enzyme digestion, it is found that the degree of enzyme digestion is directly proportional to the proportion of methylation contained in it ( figure 2 ), indicating that the ratio of N6-methyladenine can be estimated using this enzyme. The MazF of the present invention comes from Baoriyi Biotechnology (Beijing) Co., Ltd., and its product number is 2415A. The RNA oligon...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Example 2 Small RNA library construction process
[0060] use as Figure 5 The way to build a small RNA library, the specific operation is as follows:
[0061] 1) Demethylation treatment: mRNA was treated with N6-methyladenine modified demethylase FTO as a negative control. Before the reaction, the mRNA must be heated in a PCR machine at 85°C for 5 minutes, and then placed on ice for 2 minutes immediately to remove the secondary structure of the mRNA. The demethylation reaction system is as follows:
[0062] final concentration or total mRNA ~200ng N6-methyladenine modified demethylase FTO 2.5ug α-Ketoglutarate (α-KG) 300uM Ammonium Ferrous Sulfate (Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2) 283uM Ascorbic acid (L-ascorbic acid) 2mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH7.5) 50mM RNase inhibitor 20U Enzyme-free water (RNase-free H2O) To 20ul
[0063] React at room temperature (25°C) for 3 hours, add 1ul 40mM EDTA to terminate the reaction, or ...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Example 3 High-throughput sequencing data analysis
[0081] use Figure 6 The flow process carries out sequencing analysis to the small RNA library that embodiment 2 obtains, and specific steps are as follows:
[0082] First, perform quality control on the sequencing data, remove the sequencing adapters, and retain the remaining fragments larger than 15nt sequencing short sequences (reads);
[0083] Use Hisat2 software to compare the sequencing data back to the reference genome to obtain its specific position on the genome.
[0084] The ACA sequence not digested by MazF was located from the alignment results. The specific method is that if an ACA sequence is at the beginning of the sequencing reads, it is a normal unmethylated A, because it is the site cut by the MazF enzyme; and when the ACA sequence appears in the middle of the reads, it is not Not cut by MazF enzyme, its first A is the methylation site. Since only reads above 15nt are retained when the data is de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com