Method for detecting three potato pathogenic bacteria by multiple PCR (polymerase chain reaction) techniques
A technical detection and pathogenic bacteria technology, which is applied in the field of detecting three potato pathogenic bacteria using multiplex PCR technology, can solve the problems of not meeting the detection requirements, increasing the detection complexity, and inaccurate detection results, achieving fast detection speed, no potential safety hazards, The effect of high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
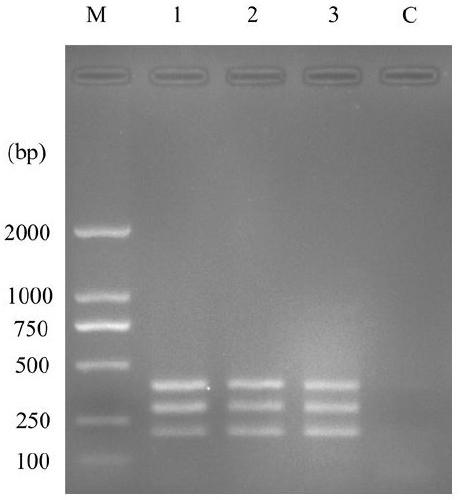
[0045] Embodiment 1 The establishment of detection method
[0046] (1) Genomic DNA extraction: HP Fungal DNA kit was used to extract the genomic DNA of Phytophthora infestans, Alternaria solani and Rhizoctonia solani (AG3 fusion group) respectively.
[0047] (2) Primer design: According to the specific gene INF1 gene of Phytophthora infestans (GenBank: AY830094.1), the specific gene histone H3 gene of Alternaria solani (GenBank: KF308960.1) and Rhizoctonia solani (AG3 The primers were designed for the gene sequence of the specific gene RSENDO1 gene (GenBank: KM522918.1), which were Pi-F / R, As-F / R and Rs-F / R in sequence. The nucleotide sequences of the primers used are shown in Table 1:
[0048] Table 1 Nucleotide sequence list of primers
[0049]
[0050] (3) Multiplex PCR reaction:
[0051] The 25μL amplification system is shown in Table 2:
[0052] Table 2 The concentration of each component in the multiplex PCR system
[0053]
[0054] Reaction program: react at ...
Embodiment 2
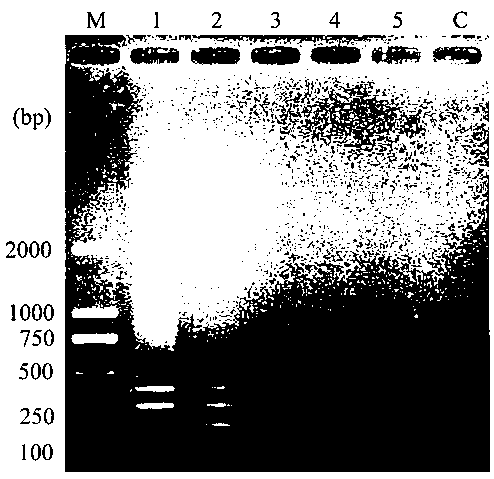
[0057] Example 2 Pathogen Detection Sensitivity Experiment
[0058] The template DNA concentrations of the three pathogenic bacteria were diluted to five concentration gradients of 1 ng / μL, 100 pg / μL, 10 pg / μL, 1 pg / μL and 0.1 pg / μL, and obtained according to the method established in Example 1 For test results, see figure 2 As shown (1: 1ng / μL; 2: 100 pg / μL; 3: 10 pg / μL; 4: 1 pg / μL; 5: 0.1 pg / μL; C: blank control), by figure 2 It is known that when the template concentration is 10 pg / μL, all three pathogens can be detected; when the template concentration is 1 pg / μL, except Phytophthora infestans, the other two pathogens can be detected. When the template concentration was 0.1 pg / μL, none of the three pathogenic bacteria could be detected. Therefore, the detection limits of Phytophthora infestans, Alternaria solani and Rhizoctonia solani (AG3 fusion group) are successively 10 pg / μL, 1 pg / μL and 1 pg / μL, so it can be judged that the established The multiplex PCR detection...
Embodiment 3
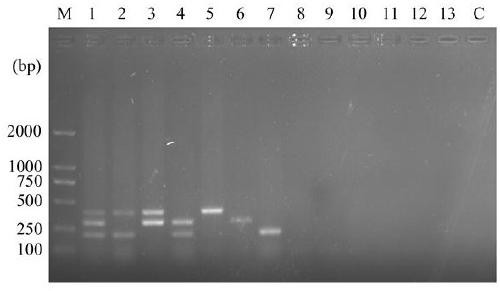
[0059] Example 3 Pathogen Detection Specificity Experiment
[0060] According to the method established in Example 1, three kinds of potato pathogenic bacterium genomic DNAs are used as the positive control of the template, and sterile deionized water is used as the negative control of the template. Alternaria solani, Rhizoctonia solani (AG3 fusion group), Phytophthora sojae, Phytophthora capsici, Alternaria, Alternaria adenocarp, Rhizoctonia solani (AG1 fusion group) and Phytophthora solani Genomic DNA of Rhizoctonia sp. (AG4 fusion group) was amplified by PCR. See the test results image 3 , when adding one, two or three DNA templates of the bacteria to be detected in the present invention, the electrophoresis results of the PCR product correspondingly only appear the target bands (1-7 swimming lanes) of the added bacteria, while adding the DNA of other bacteria The electrophoresis results of the multiple PCR products of the template have no bands (lane 8-13), thus indicat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com