Low-on-resistance trench silicon carbide power device and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of low on-resistance and power devices, applied in the field of new trench silicon carbide power devices and their manufacturing, can solve the problem that the channel electron mobility of silicon carbide power devices is reduced, the device off current is increased, and the process is difficult. and other problems, to achieve the effect of fast electron saturation drift speed, improved current transmission capacity, and reduced on-resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
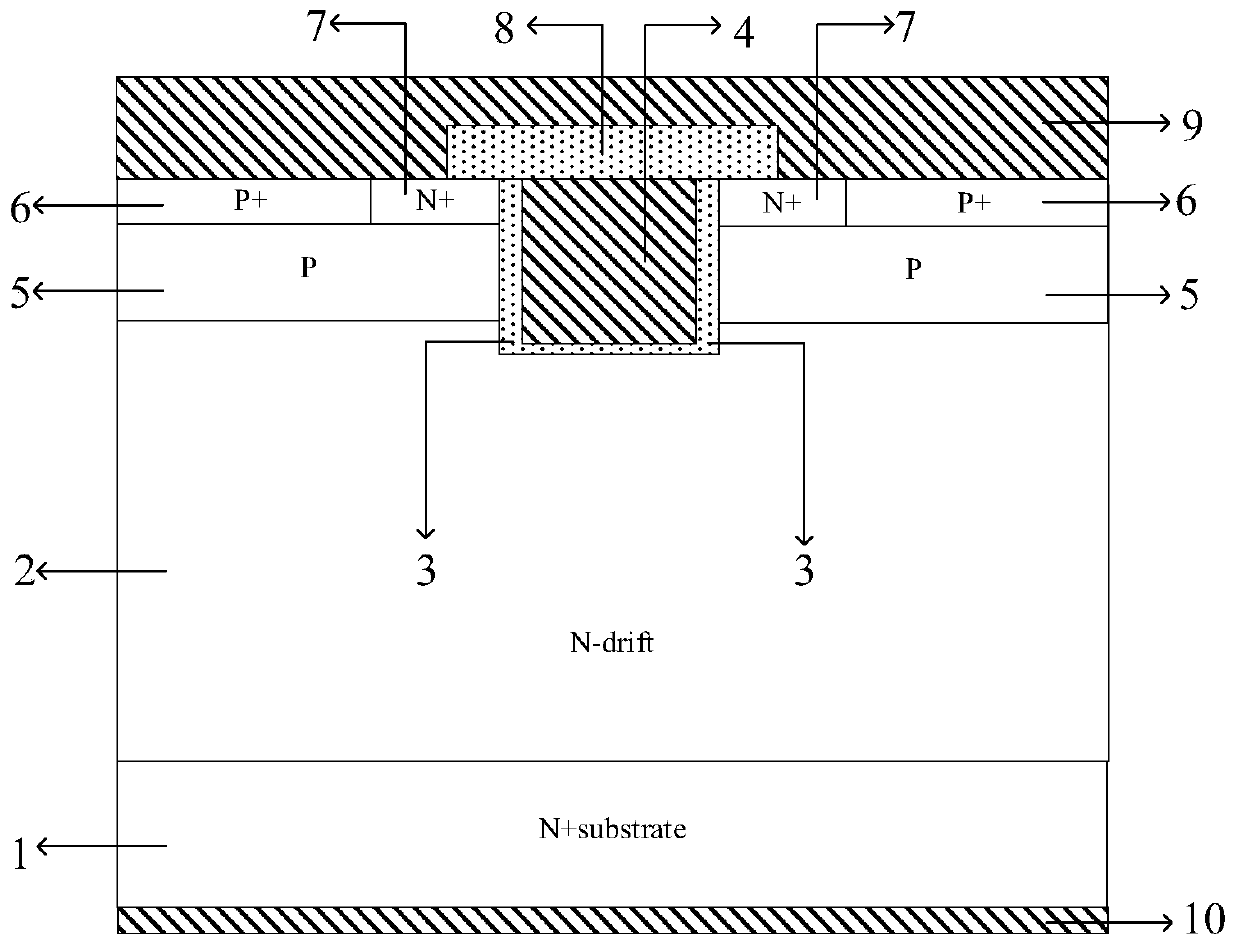
[0032] A trenched SiC power device with low on-resistance, such as figure 2 As shown, it includes: an N-type substrate 1, a drain metal 10 is arranged on one surface of the N-type substrate 1, an N-type epitaxial layer 2 is arranged on the other surface of the N-type substrate 1, and an N-type epitaxial layer 2 is arranged on the N-type substrate 1. The epitaxial layer 2 is provided with a P-type body region 5, an N-type source region 7 and a P-type body contact region 6 are arranged on the P-type body region 5, and the P-type body contact region 6 is located outside the N-type source region 7. The N-type source region 7 and the P-type body contact region 6 are connected with a source metal 9, and a trench is provided in the N-type source region 7, and the trench starts from the surface, depth and N-type epitaxial layer of the N-type source region 7 2, a gate oxide layer 3 is provided on the inner wall and bottom of the trench, polysilicon is filled in the gate oxide layer 3 ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] A method for manufacturing a trench silicon carbide power device with low on-resistance,
[0035] Step 1 as Figure 6 As shown, take an N-type substrate 1, attach silicon carbide on the other surface of the N-type substrate 1 to form an N-type epitaxial layer 2, and use an etching process to form a groove on the surface of the N-type epitaxial layer 2 ,
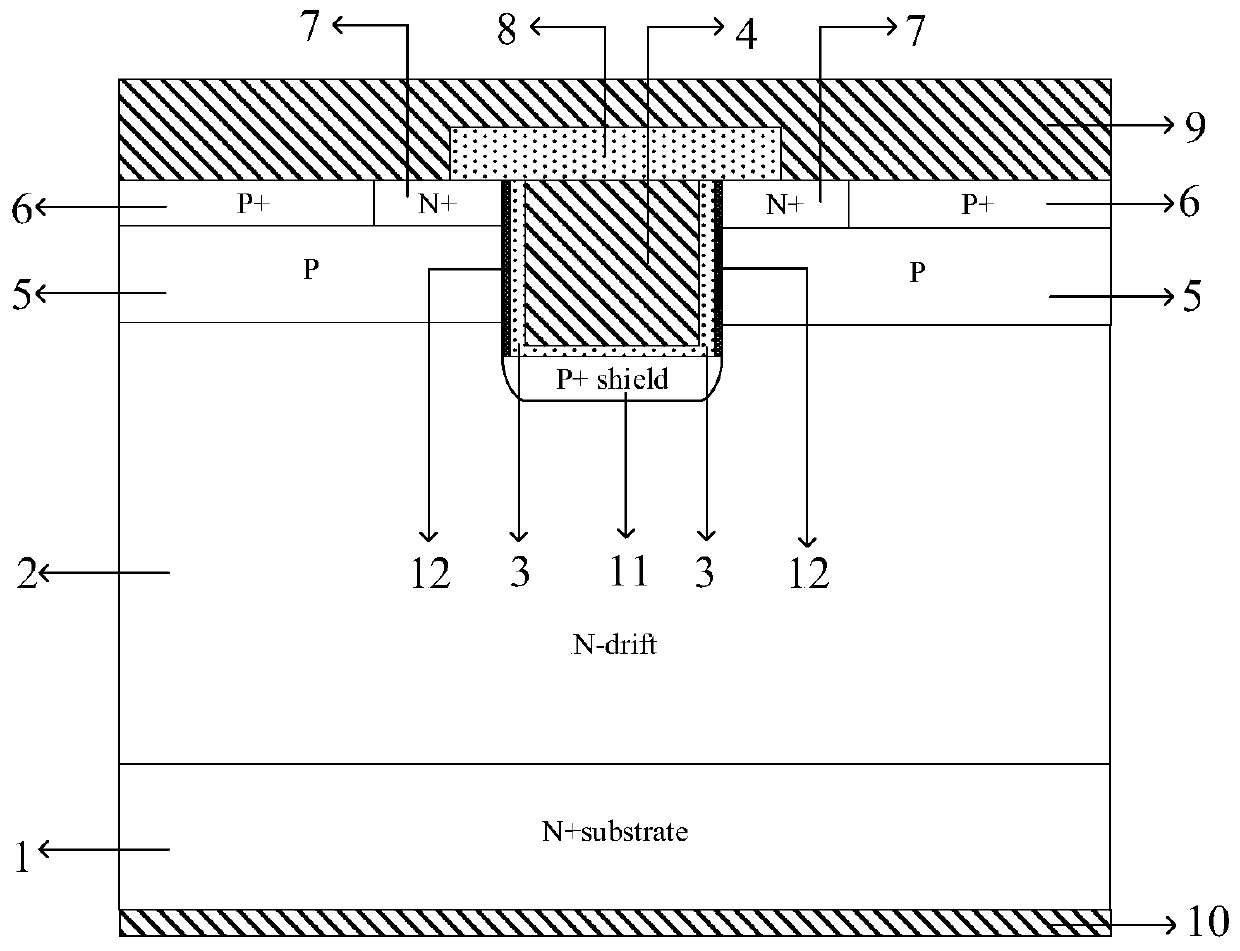
[0036] Step 2 as Figure 7 As shown, using the ion implantation process, a concentration of 10 is formed at the bottom of the trench -4 -10 -6 cm -3 The P-type shielding layer 11,
[0037] Step 3 uses a sputtering process and an etching process to form a layer of metal capable of dissolving carbon on the sidewall of the trench,
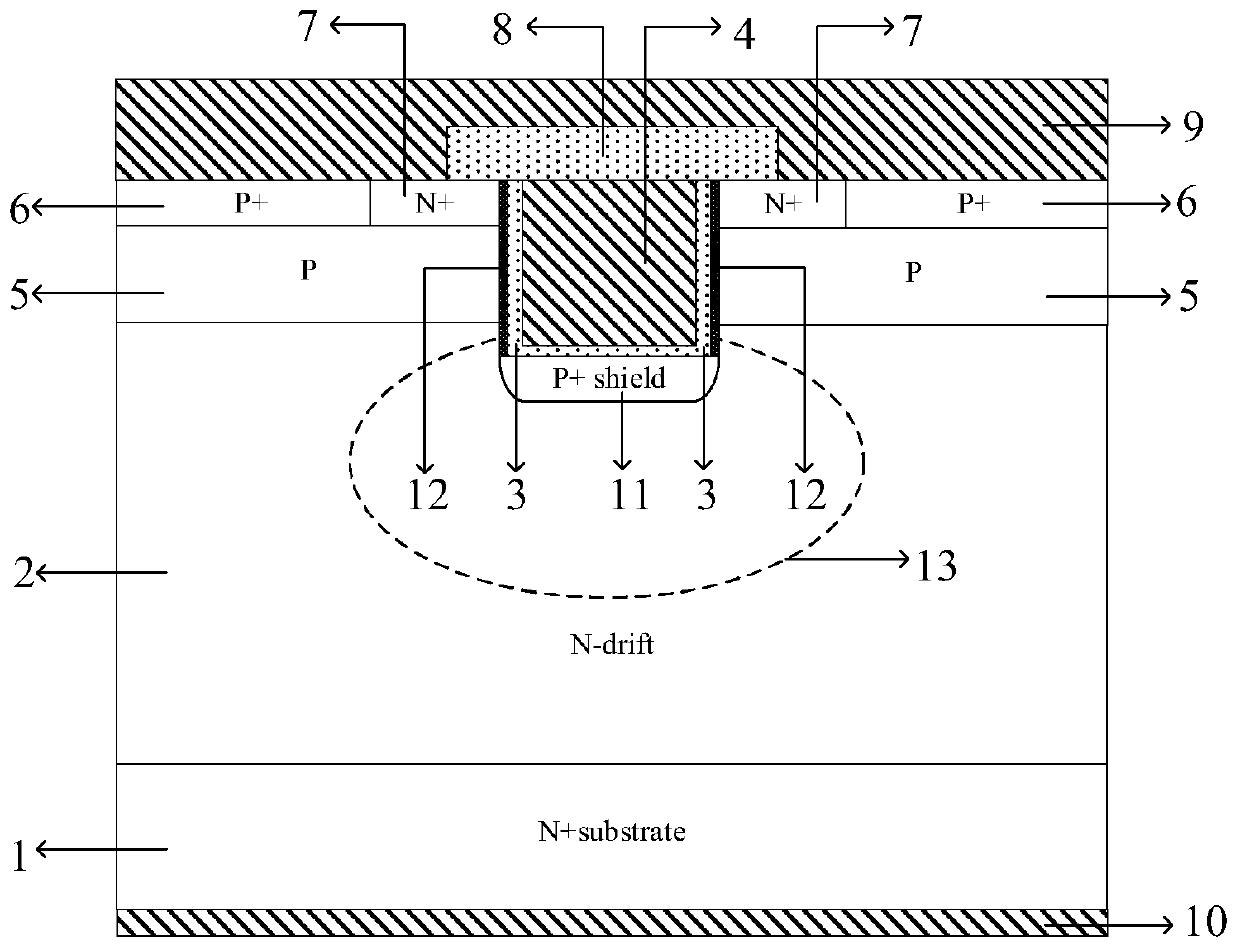
[0038]Step 4 Use a high-energy electron beam to bombard the side wall of the trench to break the silicon-carbon bond on the surface of silicon carbide, and generate a local high temperature of 500°C-1200°C in the metal layer that can dissolve carbon, and the carbon generated by the break...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle of incidence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com