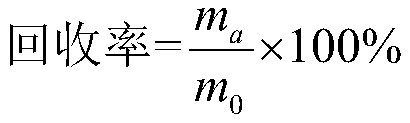Method for assisting recovery of lithium and cobalt in waste electrode material through microwave roasting
A technology of microwave roasting and electrode materials, applied in battery recycling, recycling technology, recycling by waste collectors, etc., can solve the problems of low wet leaching efficiency, affecting acid leaching behavior, and hindering leaching reaction, and achieves omitting the need for pre-treatment. Treatment process, simplify the pretreatment process, and improve the effect of solubility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
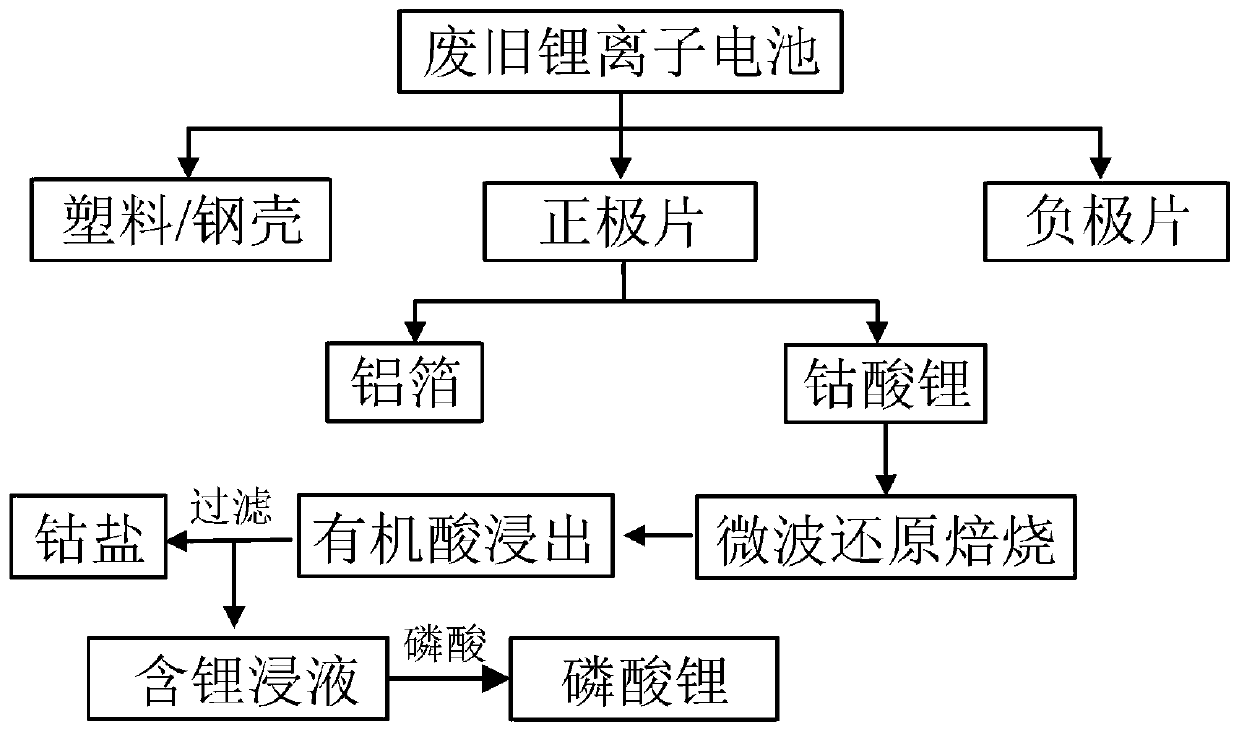
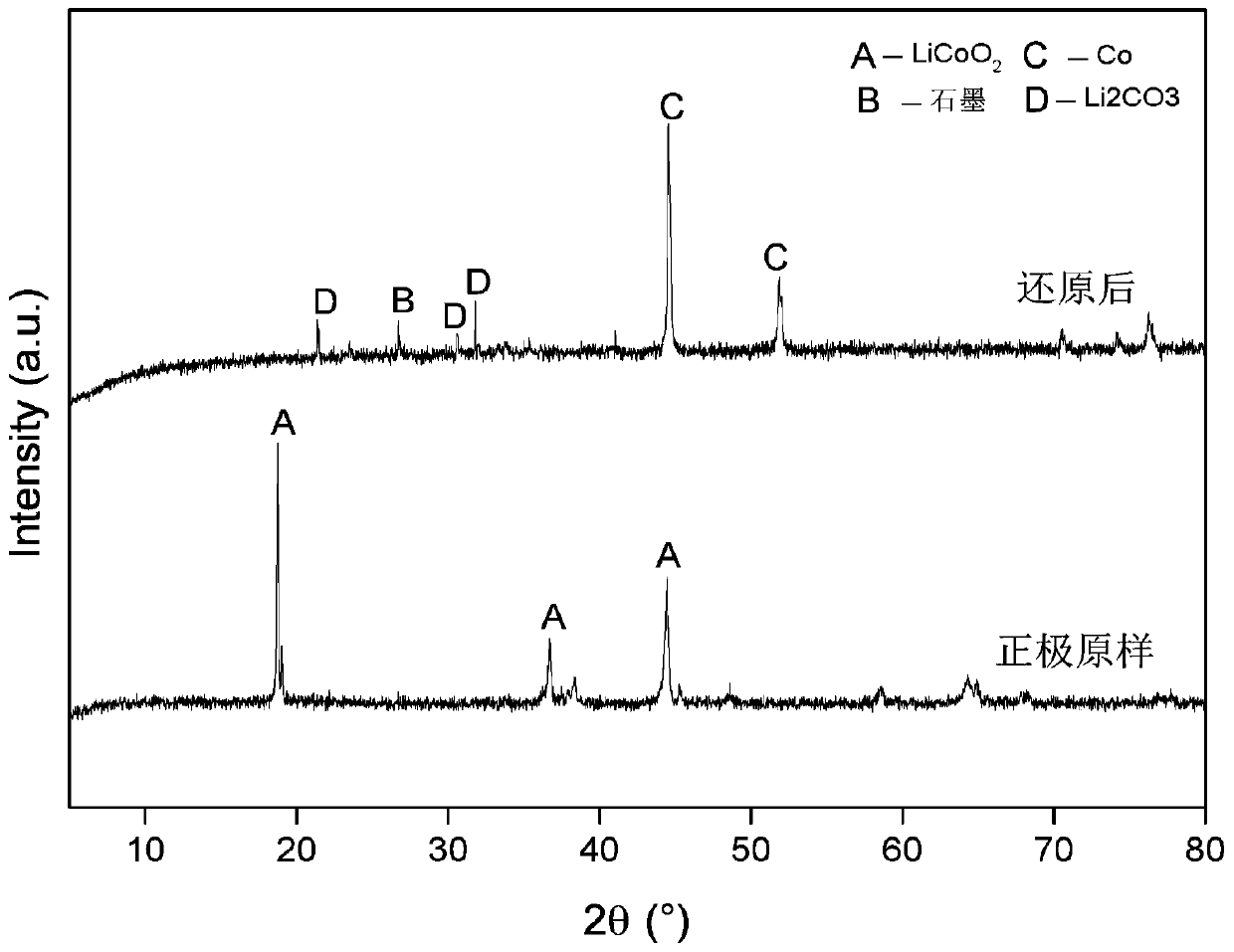
[0031] Disassemble the positive and negative electrode sheets after discharging and air-drying the waste lithium cobalt oxide battery, crush and sieve the positive electrode sheet, take materials smaller than 74 microns, and put them into a microwave tube furnace protected by argon gas. Roasted for 20 min under 200W microwave power, and collected the roasted solid phase product. The reduced roasted product was mixed with 1.5mol / L benzenesulfonic acid, the solid-to-liquid ratio was 30g / L, and stirred in a constant temperature water bath at a speed of 500rpm for 60min to prepare an acid leaching solution for waste electrode materials, and the cobalt element was directly recovered in the form of precipitation. Phosphoric acid is added to the filtered leaching solution, lithium ions are precipitated from the solution in the form of precipitation, and the precipitated product of lithium is recovered. The recoveries of cobalt and lithium in this embodiment are 90.5% and 92.8% respec...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Disassemble the positive and negative electrode sheets after discharging and air-drying the waste lithium cobaltate batteries, crush and sieve the positive electrode sheets, take -74 micron materials, and put them into a microwave tube furnace protected by argon gas. Roast for 20 min under 500W microwave power, and collect the solid phase product of roasting. The reduced roasted product was mixed with 1.5mol / L benzenesulfonic acid, the solid-to-liquid ratio was 30g / L, and stirred in a constant temperature water bath at a speed of 500rpm for 60min to prepare an acid leaching solution for waste electrode materials, and the cobalt element was directly recovered in the form of precipitation. Phosphoric acid is added to the filtered leaching solution, lithium ions are precipitated from the solution in the form of precipitation, and the precipitated product of lithium is recovered. The difference between the implementation conditions of this example and Example 1 is that the ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Disassemble the positive and negative electrode sheets after discharging and air-drying the waste lithium cobaltate batteries, crush and sieve the positive electrode sheets, take -74 micron materials, and put them into a microwave tube furnace protected by argon gas. Roasted at 800W microwave power for 20min, and collected the roasted solid phase product. The reduced roasted product was mixed with 1.5mol / L benzenesulfonic acid, the solid-to-liquid ratio was 30g / L, and stirred in a constant temperature water bath at a speed of 500rpm for 60min to prepare an acid leaching solution for waste electrode materials, and the cobalt element was directly recovered in the form of precipitation. Phosphoric acid is added to the filtered leaching solution, lithium ions are precipitated from the solution in the form of precipitation, and the precipitated product of lithium is recovered. The difference between the implementation conditions of this example and Example 1 and Example 2 is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com