Methods for determining potency of adeno-associated virus preparations
A preparation and dosage technology, which is applied in the field of determining the potency of adeno-associated virus preparations, and can solve problems such as wrong dosage of patients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
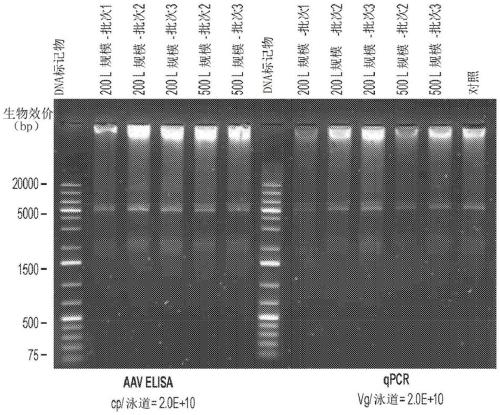
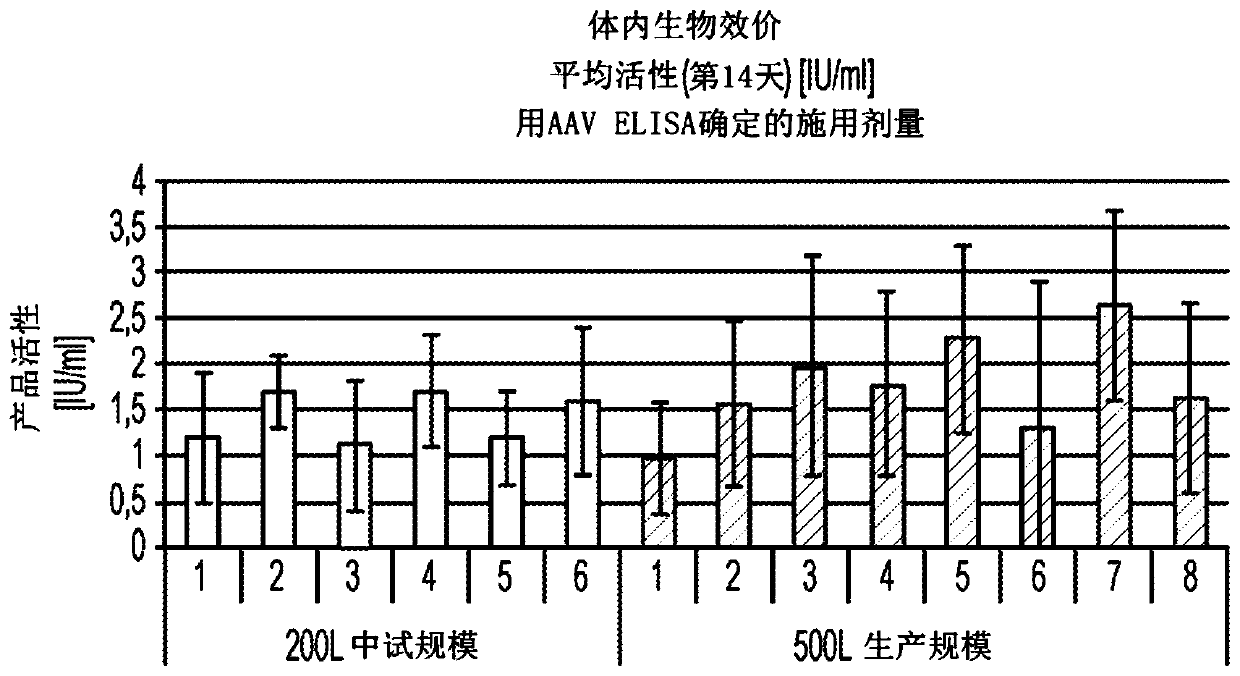
[0121] This example illustrates an AAV-specific ELISA. ELISA determines the amount of AAV8 particles present in assay fractions or preparations.
[0122] An AAV-specific ELISA was performed to identify AAV-containing fractions. Conformation-specific monoclonal antibodies were used to detect epitopes repeatedly expressed on assembled AAV-8 particles.
[0123] AAV8 ELISA was performed on a TECAN Roboter system with the AAV-8 titration ELISA kit (Cat. No. PRAAV8; Progen (Heidelberg, Germany)). Briefly, monoclonal antibodies specific for conformational epitopes on the assembled AAV8 capsid (ADK8) were coated on microtiter strips and used to capture AAV8 particles from AAV fractions. Captured AAV8 particles were detected by two steps. In the first step, a biotin-conjugated monoclonal antibody (specific for ADK8 antibody) binds to the immune complex (ADK8 and ADK8 antibody). Add streptavidin peroxidase conjugate to the immune complex bound to biotin-conjugated monoclonal antibod...
Embodiment 2
[0126] This example demonstrates cryogenic transmission electron microscopy (CryoTEM).
[0127] CryoTEM enables visualization of nanoparticles such as AAV. The technique involves depositing AAV formulations on thin supported carbon films in a temperature and humidity controlled environment. After removing excess AAV formulation (leaving some adhered AAV formulation), grids were vitrified in liquid ethane and then stored in liquid nitrogen. CryoTEM analysis of AAV capsid particles was used to assess overall sample morphology, i.e., the presence of various AAV morphologies (often including spherical and deformed AAV particles, subunit structures, and larger structurally less defined morphologies) by automated image analysis methods. ), and the packing level of the pellets.
[0128] AAV fractions or formulations are kept close to their native state by embedding them in amorphous amorphous ice on an inert carrier by flash freezing under cryogenic conditions. Image-based analysi...
Embodiment 3
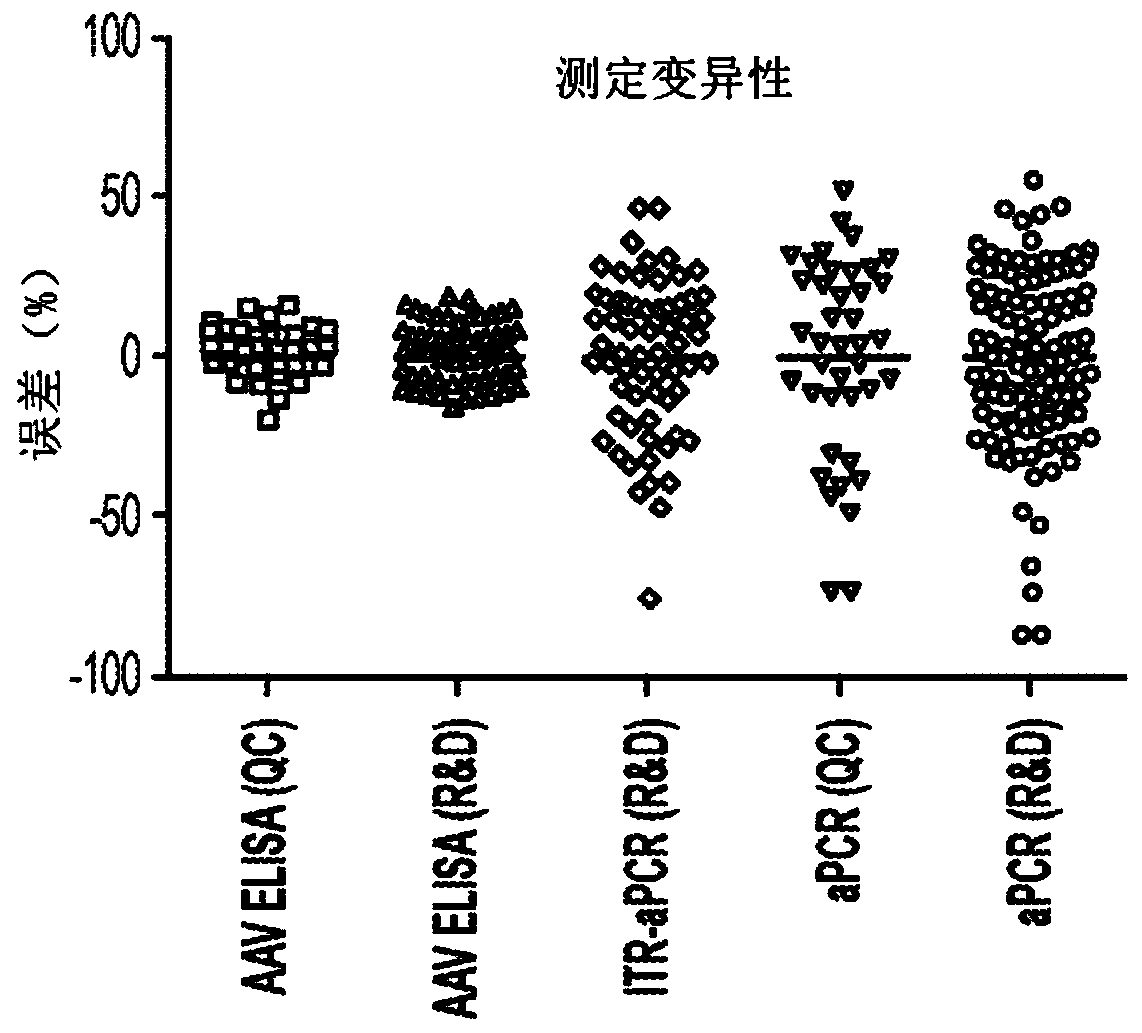
[0132] This example demonstrates that using an AAV-specific ELISA results in less variability than using qPCR technology.
[0133] AAV8 ELISA: Total AAV8 capsid particle titers were measured using a commercial kit (Progen) calibrated to capsid particle (cp) concentration as described in Example 1. AAV8 reference standard material.
[0134] qPCR: developed based on Chemical quantitative PCR assay to measure vector genome copy concentration of transgenic DNA. For ITR-qPCR of FVIII, the vector genome titer (vg) per milliliter (ml) was determined using TaqMan-based qPCR (using primers and fluorescently labeled probes to detect sequences within the ITR sequence of the vector genome). To detect ITR-specific sequences in AAV particles, samples were treated with DNAse I, and after a subsequent proteinase K step, the scAAV genome was released from the capsid. Finally, restriction enzyme digestion was performed to resolve the AAV ITR T-type structure.
[0135] A plasmid used as a ...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap