Method for preparing low-pressure high-selectivity nanofiltration membrane
A selective and nanofiltration membrane technology, applied in the field of nanofiltration, can solve the problems of decreased desalination rate, failure to achieve complete separation of divalent salts and monovalent salts, low water flux of nanofiltration membranes, etc., to achieve high water flux, The effect of excellent ion selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] (1) The polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane supported by the non-woven fabric is fixed, and the prepared aqueous solution containing 1.0wt% piperazine and 2.0wt% trisodium phosphate is poured on the surface of the ultrafiltration membrane, and the immersion time is 2min. After removing the aqueous phase solution, use a rubber roller to remove the residual solution on the surface of the ultrafiltration membrane;
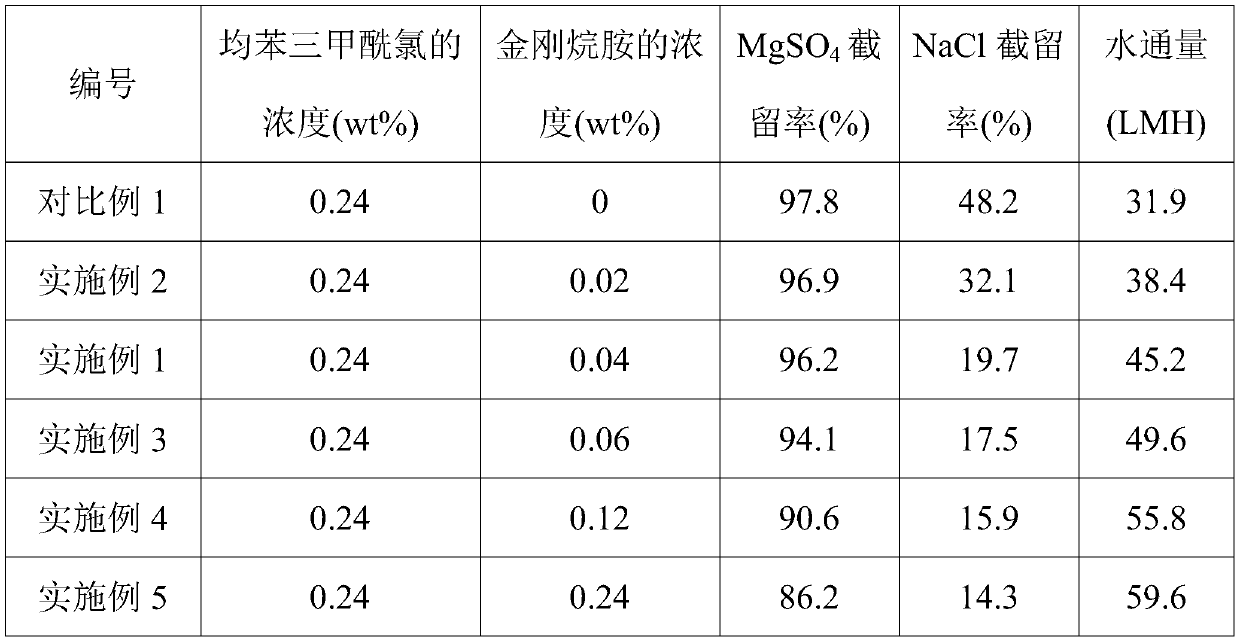
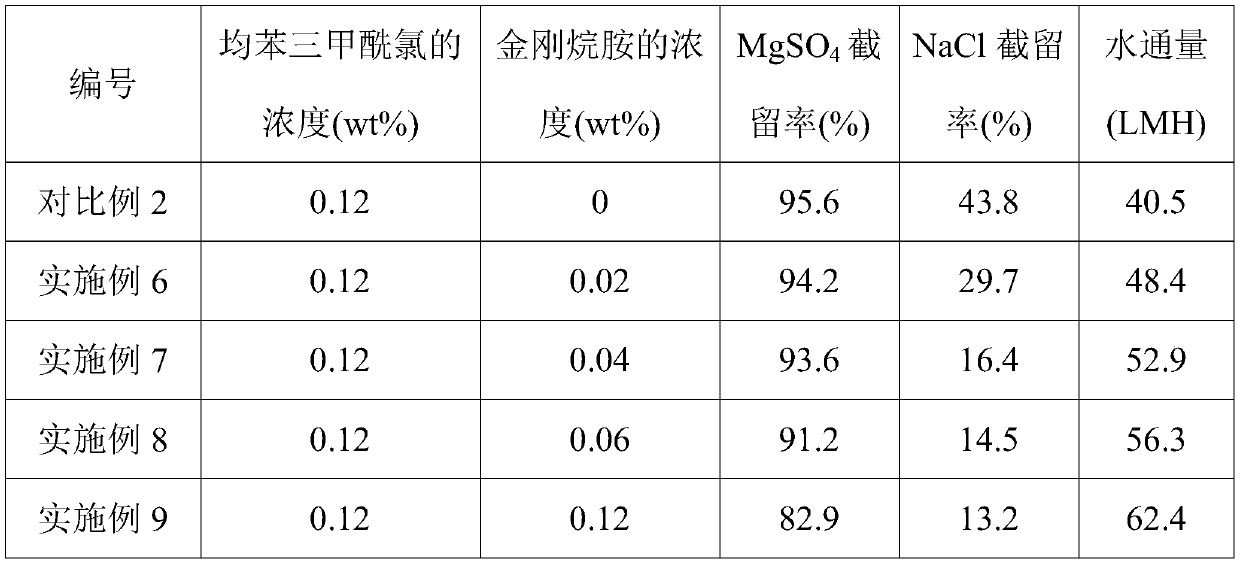
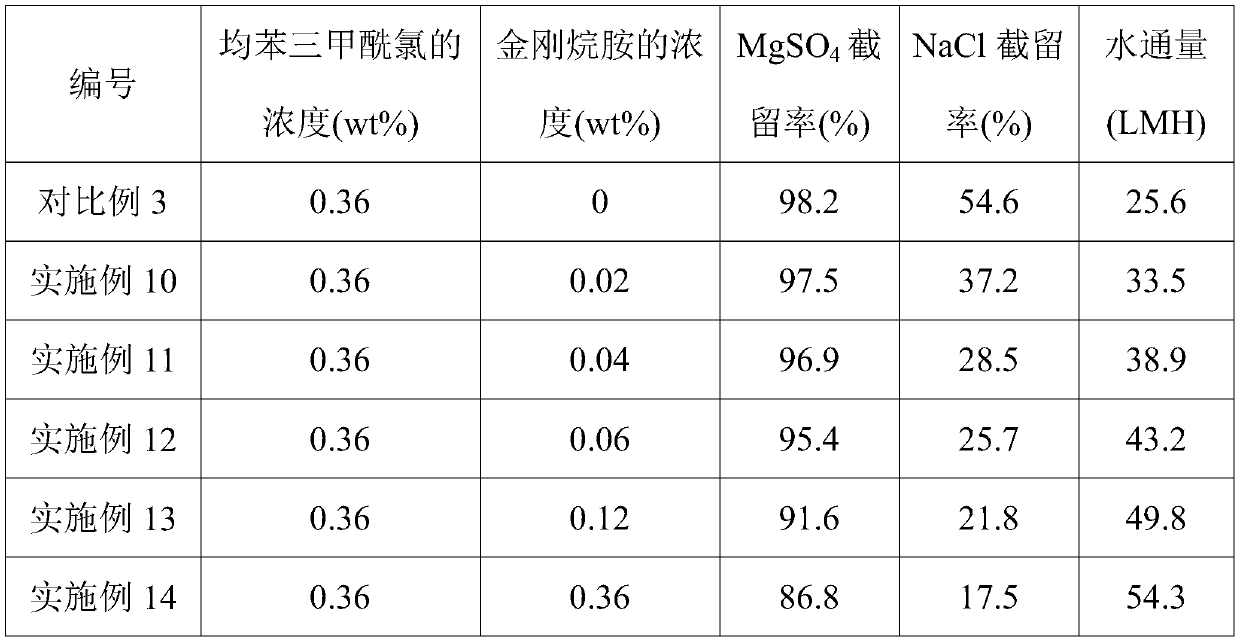
[0027] (2) pour the cyclohexane solution containing 0.24wt% trimesoyl chloride and 0.04wt% amantadine prepared on the surface of the ultrafiltration membrane to carry out interfacial polymerization reaction, and the reaction time is 50s, wherein the oil phase solution The preparation process is as follows: first dissolve trimesoyl chloride and amantadine in cyclohexane respectively, then slowly add amantadine solution dropwise while stirring the trimesoyl chloride solution, and obtain an oil phase solution after mixing evenly;
[0028] (3) After the interfacia...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The main difference between this example and Example 1 is that the concentration of amantadine in the oil phase solution in the step (2) is 0.02wt%.
Embodiment 3
[0032] The main difference between this example and Example 1 is that the concentration of amantadine in the oil phase solution in the step (2) is 0.06wt%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com