A method and device for strengthening electro-Fenton water treatment
A technology of water treatment and Fenton reaction, which is applied in the direction of oxidized water/sewage treatment, special compound water treatment, water/sewage treatment, etc., to achieve the effects of good stability, improved degradation efficiency, and low dosage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Degradation of four typical organic pollutants by adding different oxalate concentrations
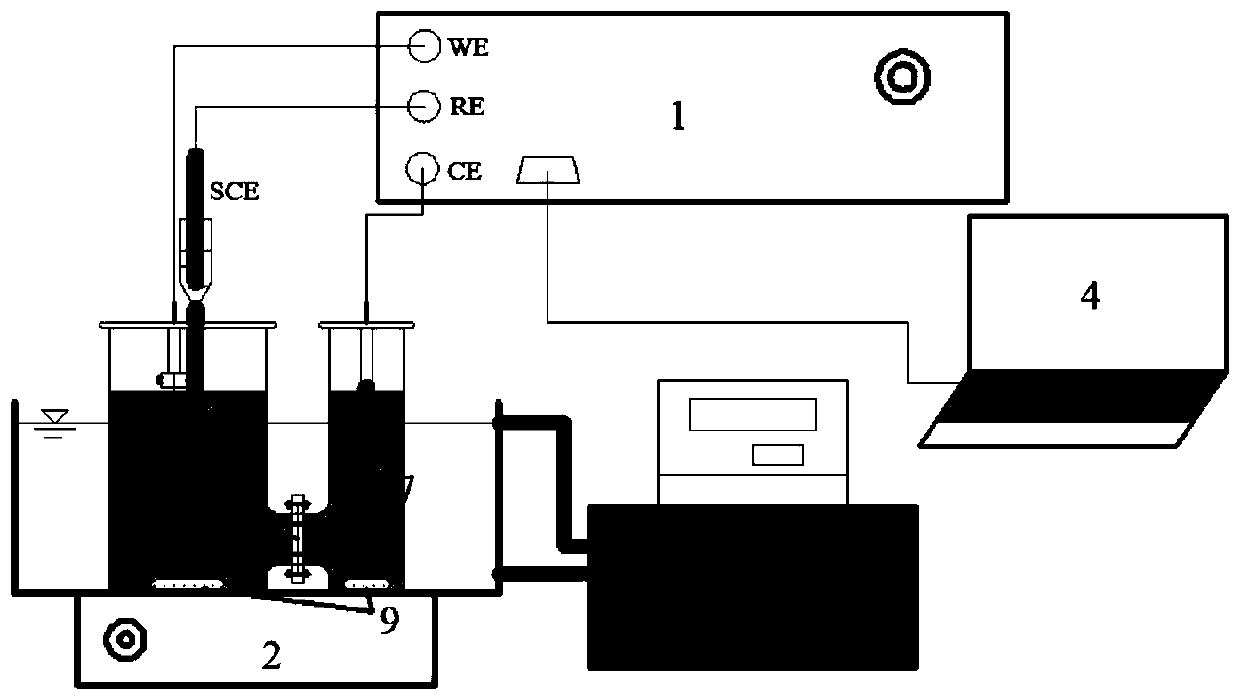
[0059] use figure 1 For the shown setup, 0.5 mM Fe was added to the cathode reaction solution 3+ and H 2 o 2 , compared to the sulfamethoxazole (SMX) of 20mg / L when the concentration of oxalate was 0mM, 0.15mM, 0.3mM, 0.5mM and 0.75mM in the medicament bag with oxalate added as the main component, The degradation enhancement of 4-DCP, phenol (Ph) and benzoic acid (BA), the multiples of the enhancement of the degradation rate of pollutants by the concentration of different drug packages are as follows Figure 4 shown.
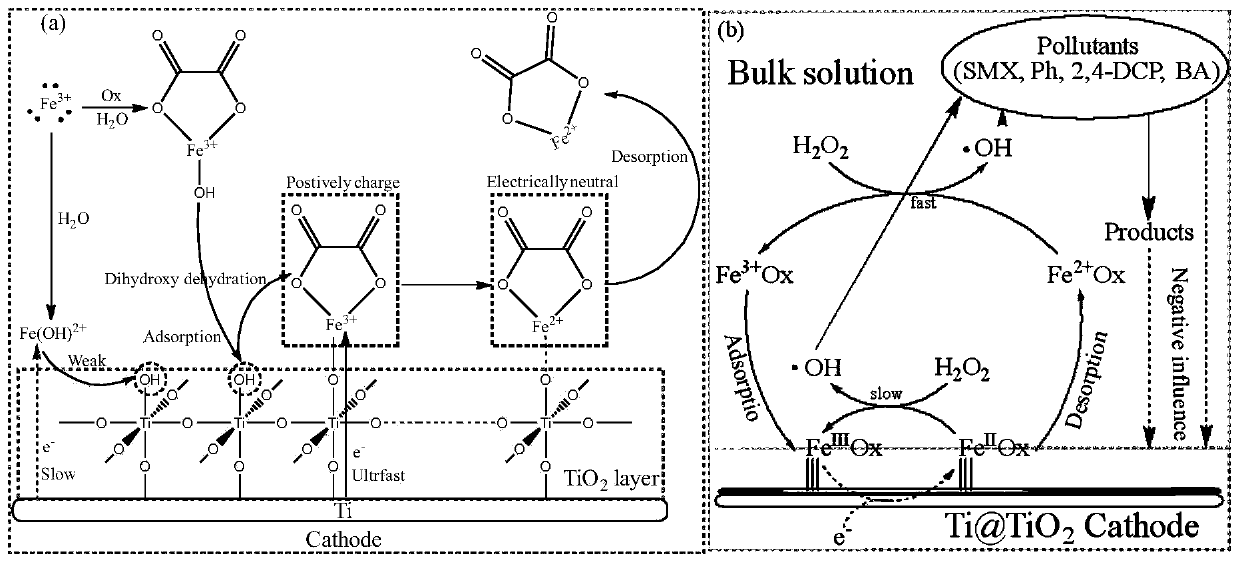
[0060] Result analysis: From the results of Example 1, it can be seen that the use of anodized pretreated Ti@TiO 2 The electrode, after adding a low concentration of oxalate as the main component of the agent package, can effectively enhance the degradation rate of typical organic pollutants by electroreduction Fenton, and the oxalate and Fe 3+ The strengthen...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Ti@TiO 2 Electrode surface oxide layer on Fe 3+ Intensification of electroreduction
[0063] use figure 1 The shown device, using Ti@TiO pretreated by anodization for different times 2 Electrode, comparing different TiO2 when adding a low concentration of oxalate-based pharmaceutical package 2 Oxide layer thickness vs. Fe 3+ Influenced by the electrochemical reduction, the results are as follows Figure 5 shown.
[0064] Result analysis: From the results of Example 2, it can be seen that when a low-concentration pharmaceutical package is added, the uniform TiO on the Ti sheet electrode 2 layer can significantly accelerate the Fe 3+ Electrochemical reduction of Ti@TiO after anodic oxidation 2 Compared with ordinary commercial Ti sheet electrodes, the electrode can reduce Fe per unit power consumption 2+ The amount increased by 2.3 to 2.8 times.
Embodiment 3
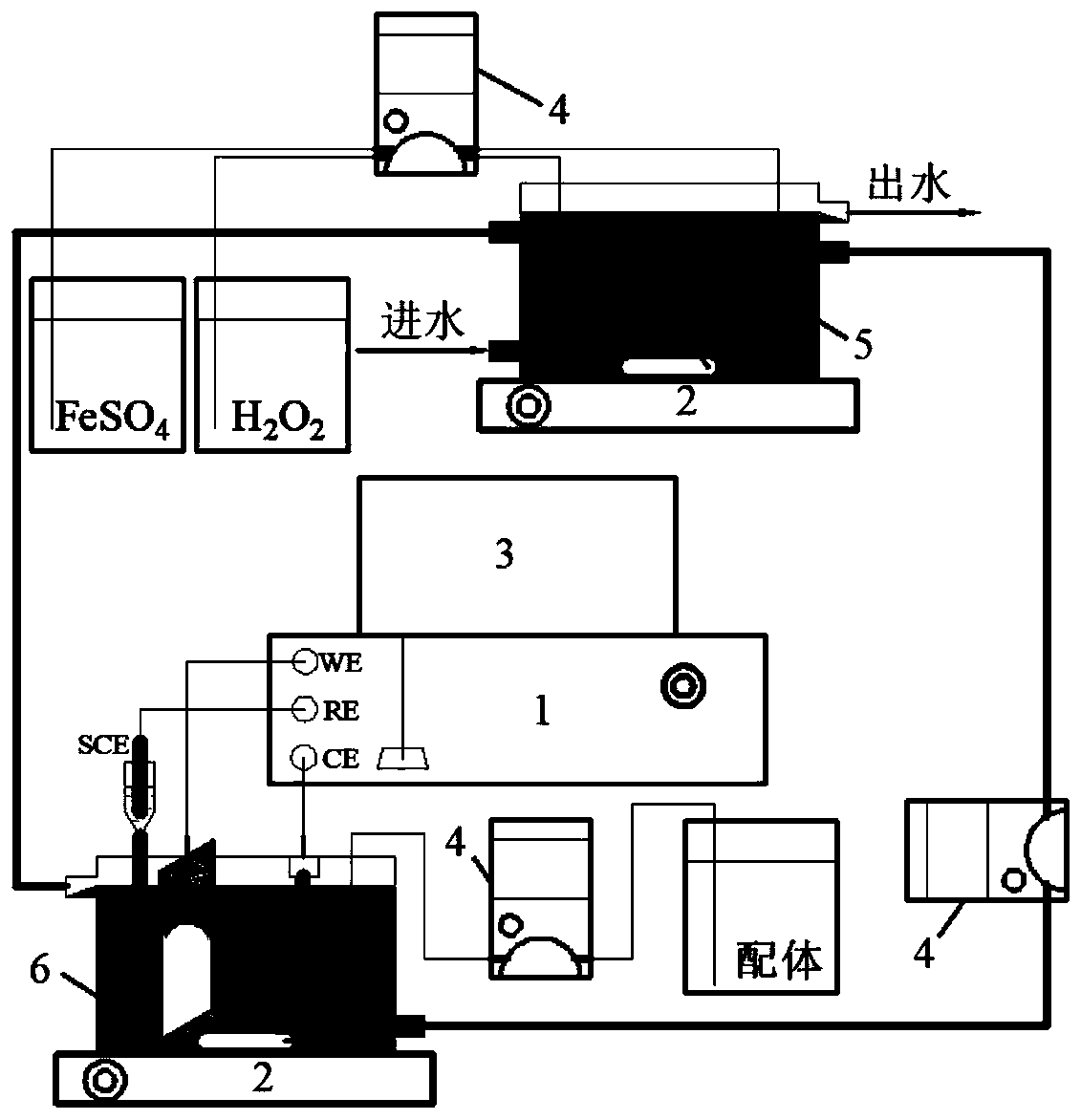
[0066] use figure 2 The shown device continuously pumps the actual printing and dyeing wastewater whose initial pH is adjusted to 3.5 with concentrated sulfuric acid, and continuously pumps 1.0mM FeSO into (5) Fenton reaction tank 4 and 3.0mM H 2 o 2 , (6) The reflux ratio of the electrochemical reduction tank is 200%. (1) When the electrochemical workstation is not powered on, the simulation is the traditional Fenton technology. When the terminal voltage of (1) the electrochemical workstation is 0.5V, the simulation is the ordinary The electro-Fenton technology of electro-reduction, when continuously pumping an appropriate concentration of oxalate-based reagent packs into the electrochemical reduction tank (6), simulates the enhanced electro-Fenton water treatment process. The effects of the three different technologies on printing and dyeing wastewater COD removal rate and Fe in effluent 2+ The proportion of Figure 6 shown.
[0067] At the same time, under the conditi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com