Method for efficiently degrading tetracyclic and sulfonamide antibiotics by laccase
A technology of antibiotics and tetracyclics, applied in the field of enzyme engineering and technology and fermentation, can solve the problems of high price, unsatisfactory degradation effect, and difficulty in obtaining intellectual property rights, etc., and achieve the effect of broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0024] The experimental materials involved in the embodiments of the present invention are as follows:
[0025] strain
[0026] Pycnoporus sp.SYBC-L10 has been deposited in China Center for Type Culture Collection in 2015 with the deposit number CCTCC#NO: M2015020, address: Wuhan University, Wuhan, China.
[0027] culture medium
[0028] PDA medium composition: potatoes 200g L -1 , Glucose 20g L -1 , agar powder 20g L -1 , pH natural;
[0029] PDB medium composition: potatoes 200g L -1 , Glucose 20g L -1 , pH natural;
[0030] The composition of the improved basal enzyme production medium: glucose 15g L -1 , soybean meal 5g L -1 , diammonium hydrogen citrate 0.5g L -1 , CuSO 4 ·5H 2 O 0.125g L -1 , KCl 0.5g L -1 , KH 2 PO 4 1g L -1 , MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.5g L -1 , yeast extract 1g L -1 , MnSO4·H 2 O 0.01g L -1 , the initial pH is 4.0;
[0031] main reagent
[0032] Tetracycline (TC, 95%, CAS: 60-54-8) and sulfamethoxazole (SMX, 98%, CAS 723-46-6) were pur...
example 1
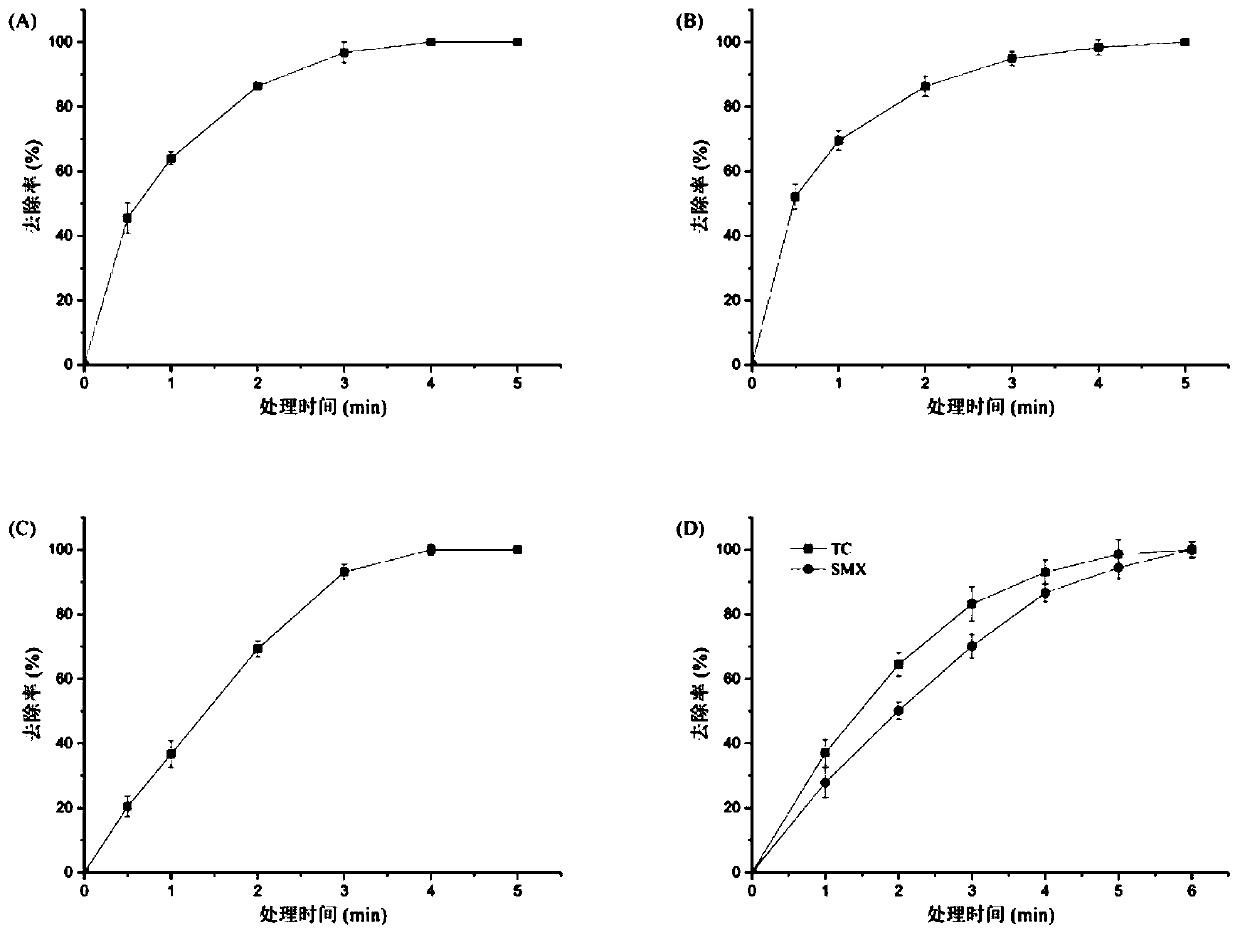
[0035] Application of Example 1 Laccase Mediator System in the Degradation of Tetracyclic Antibiotics
[0036] 1.1 Reaction system
[0037] 1.5mL contains a final concentration of 50mg L -1 TC,5.0U mL -1 Lac-Q, 0.5 mmol L -1 ABTS
[0038] 1.2 Reaction conditions
[0039] 25°C, pH 6.0, static incubation.
[0040] 1.3 Operation steps
[0041] (1) Use a pipette to draw 1.05mL of 0.1mol L -1 Phosphate-sodium hydrogen phosphate buffer solution with pH 6.0 was added to a 1.5 centrifuge tube, 0.15mL tetracycline mother solution was drawn into the centrifuge tube, and 0.15mL ABTS mother solution was added to the centrifuge tube, and incubated at 25°C for 10 minutes.
[0042] (2) Take 0.15mL of pure enzyme solution with a pipette gun, add it to a centrifuge tube, start the reaction, start the timer, and react for 0.5-5 minutes. Sample 0.25 mL at 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 minutes respectively, and immediately add 0.5 mL of methanol to terminate the reaction. Each reaction was perf...
example 2
[0047] Application of example 2 laccase mediator system in the degradation of tetracyclic antibiotics
[0048] 2.1 Reaction system
[0049] 1.5mL contains a final concentration of 50mg L -1 TC,10.0U mL -1 Lac-Q, 1.0 mmol L -1 ABTS
[0050] 2.2 Reaction conditions
[0051] 0°C, pH 6.0, static incubation.
[0052] 2.3 Operation steps
[0053] (1) Use a pipette to draw 0.75mL of 0.1mol L -1 Phosphate-disodium hydrogen phosphate buffer solution with pH 6.0 was added to a 1.5 centrifuge tube, 0.15mL tetracycline mother solution was drawn into the centrifuge tube, and 0.3mL ABTS mother solution was added to the centrifuge tube, and incubated at 0°C for 10 minutes.
[0054] (2) Take 0.3mL of pure enzyme solution with a pipette gun, add it to a centrifuge tube, start the reaction, start the timer, and react for 0.5-5 minutes. Sample 0.25 mL at 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 minutes respectively, and immediately add 0.5 mL of methanol to terminate the reaction. Each reaction was perfo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com