A tumor microenvironment-responsive nuclear-targeted platinum nanoparticle and its preparation method and application
A tumor microenvironment, platinum nanotechnology, applied in antitumor drugs, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of poor targeting of small molecule drugs and limited efficacy in advanced HCC
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
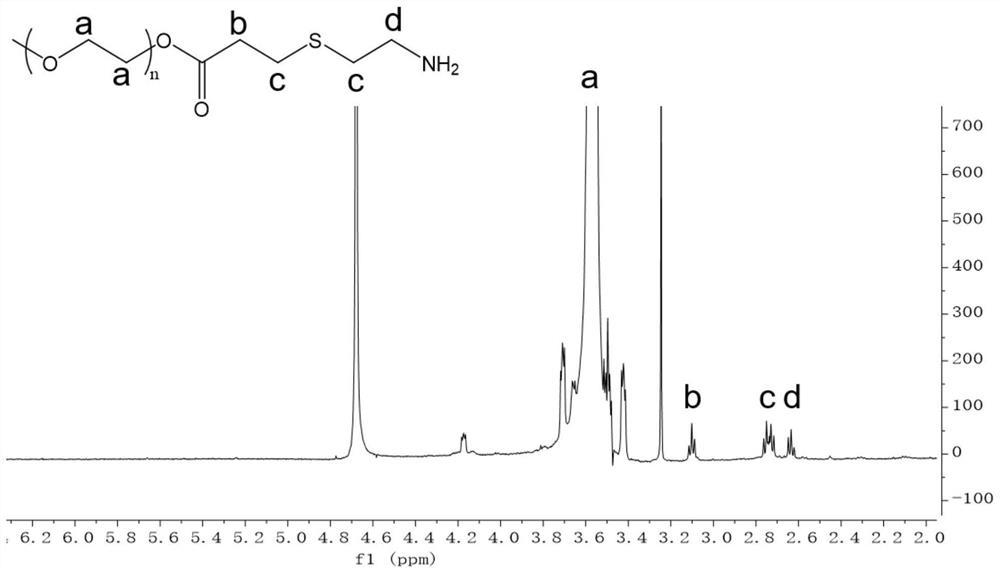
[0041] 1) Synthesis of a pH-sensitive amphiphilic polymer: 0.5 g of ethylene glycol acrylate copolymer and 0.05 g of mercaptoethylamine were dissolved in 5 ml of dimethyl sulfoxide, and under the protection of argon, drop Add 460 μl of triethylamine and stir at room temperature for 24 hours. After the reaction, the solution was dialyzed in water and freeze-dried to obtain a β-mercapto-modified ethylene glycol acrylate copolymer (a pH-sensitive amphiphilic polymer). NMR structural characterization of the prepared pH-sensitive amphiphilic polymer, such as figure 1 shown.
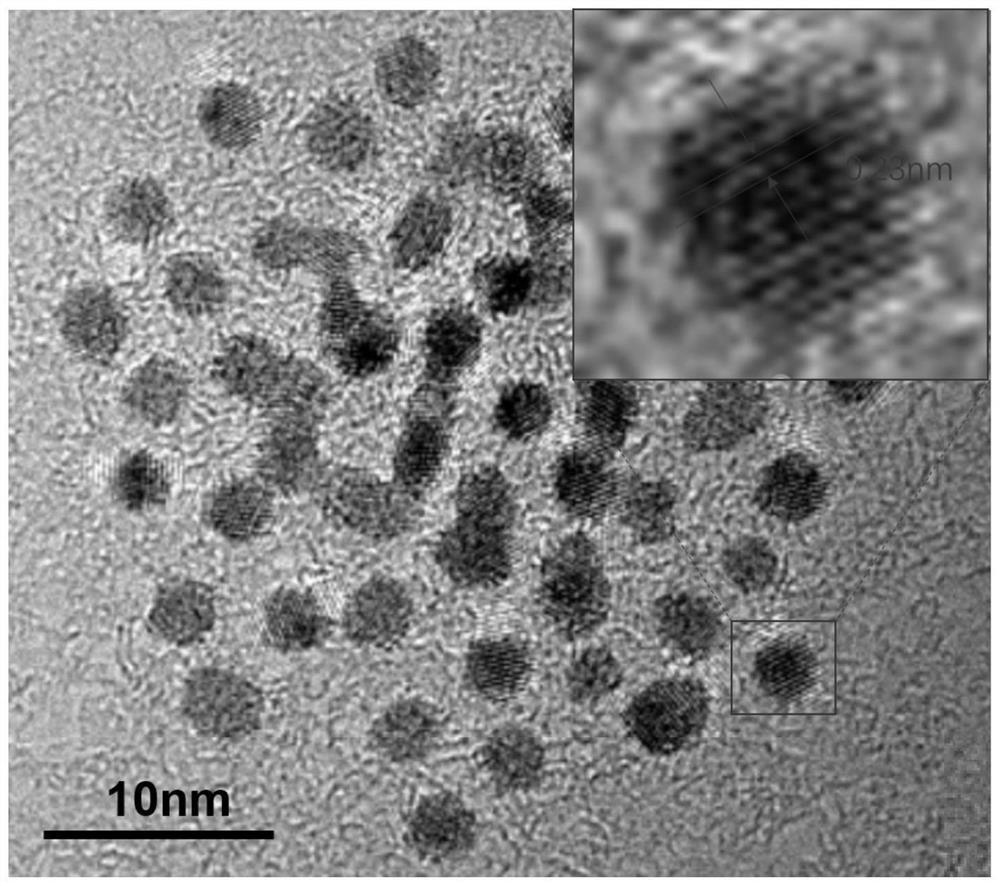
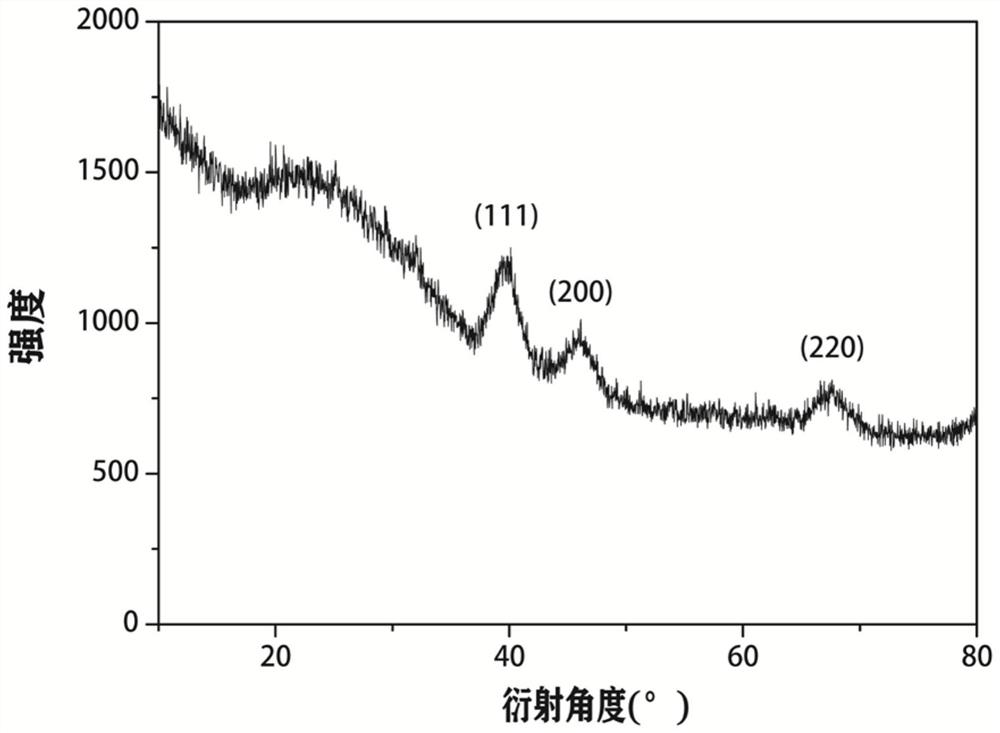
[0042]2) Synthesis of ultra-small platinum nanoparticles: 72 mg of chloroplatinic acid and 0.8 g of polyacrylic acid were dissolved in 38 ml of water, and stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes. Add 5 mg of sodium borohydride and continue stirring for 1 hour, dialyze the reaction solution in water to obtain ultra-small platinum nanoparticles. The prepared ultra-small platinum nanoparticles were characte...
Embodiment 2
[0045] 1) Synthesis of a pH-sensitive amphiphilic polymer: 0.5 g of ethylene glycol acrylate copolymer and 0.05 g of mercaptoethylamine were dissolved in 5 ml of dimethyl sulfoxide, and under the protection of argon, drop Add 460 μl of triethylamine and stir at room temperature for 24 hours. After the reaction, the solution was dialyzed in water and freeze-dried to obtain a β-mercapto-modified ethylene glycol acrylate copolymer. NMR structural characterization of the prepared pH-sensitive amphiphilic polymer, such as figure 1 shown.
[0046] 2) Synthesis of ultra-small platinum nanoparticles: 72 mg of chloroplatinic acid and 0.8 g of polyacrylic acid were dissolved in 38 ml of water, and stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes. Add 5 mg of sodium borohydride and continue stirring for 1 hour, dialyze the reaction solution in water to obtain ultra-small platinum nanoparticles. The prepared ultra-small platinum nanoparticles were characterized by TEM and XRD, as shown in ...
Embodiment 3
[0049] 1) Synthesis of a pH-sensitive amphiphilic polymer: 0.5 g of ethylene glycol acrylate copolymer and 0.05 g of mercaptoethylamine were dissolved in 5 ml of dimethyl sulfoxide, and under the protection of argon, drop Add 460 μl of triethylamine and stir at room temperature for 24 hours. After the reaction, the solution was dialyzed in water and freeze-dried to obtain a β-mercapto-modified ethylene glycol acrylate copolymer. NMR structural characterization of the prepared pH-sensitive amphiphilic polymer, such as figure 1 shown.
[0050] 2) Synthesis of ultra-small platinum nanoparticles: 72 mg of chloroplatinic acid and 0.8 g of polyacrylic acid were dissolved in 38 ml of water, and stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes. Add 5 mg of sodium borohydride and continue stirring for 1 hour, dialyze the reaction solution in water to obtain ultra-small platinum nanoparticles. The prepared ultra-small platinum nanoparticles were characterized by TEM and XRD, as shown in ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com