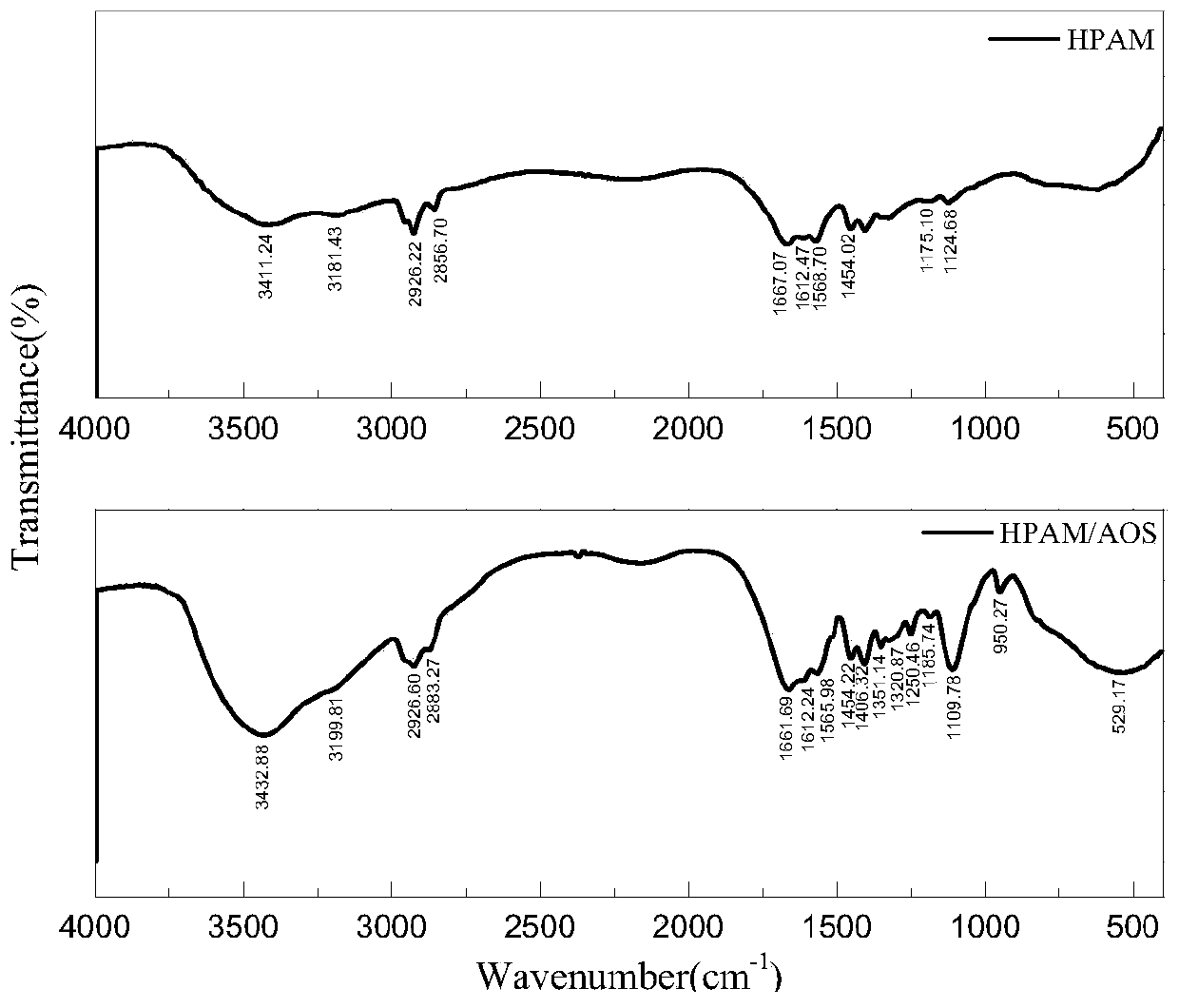
Polymer viscosity reducer for thickened oil and preparation method thereof
A polymer and viscosity reducer technology, which is applied in the field of polymer viscosity reducer for heavy oil and its preparation, can solve the problem of limited viscosity reduction effect of surfactant-based viscosity reduction systems, low heavy oil recovery, and poor surface activity and other problems, to achieve the effects of strong affinity and permeability of heavy oil, enhanced viscosity and mechanical properties, and enhanced flooding performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0041] Another aspect of the present invention provides a preparation method of the polymer viscosity reducer, wherein the method comprises the following steps:
[0042](1) acrylamide and sodium α-olefin sulfonate are dissolved in deionized water to form an aqueous solution,
[0043] (2) At an elevated temperature, for example, 50-70° C., add a redox initiator system to the aqueous solution and keep stirring at a low speed to obtain the polymer viscosity reducer of the formula (I).
[0044] In a preferred embodiment of the method of the present invention, a certain amount of acrylamide and sodium α-olefin sulfonate are mixed in deionized water to form an aqueous solution, and the solution is heated to 50-70°C in a water bath, and then a certain amount of Na 2 S 2 o 8 and Na 2 SO 3 Add it into the solution and keep stirring at a low speed for 8-16h to obtain the amphiphilic polymer HPAM / AOS.
[0045] In a preferred embodiment of the method of the present invention, the con...
Embodiment 1
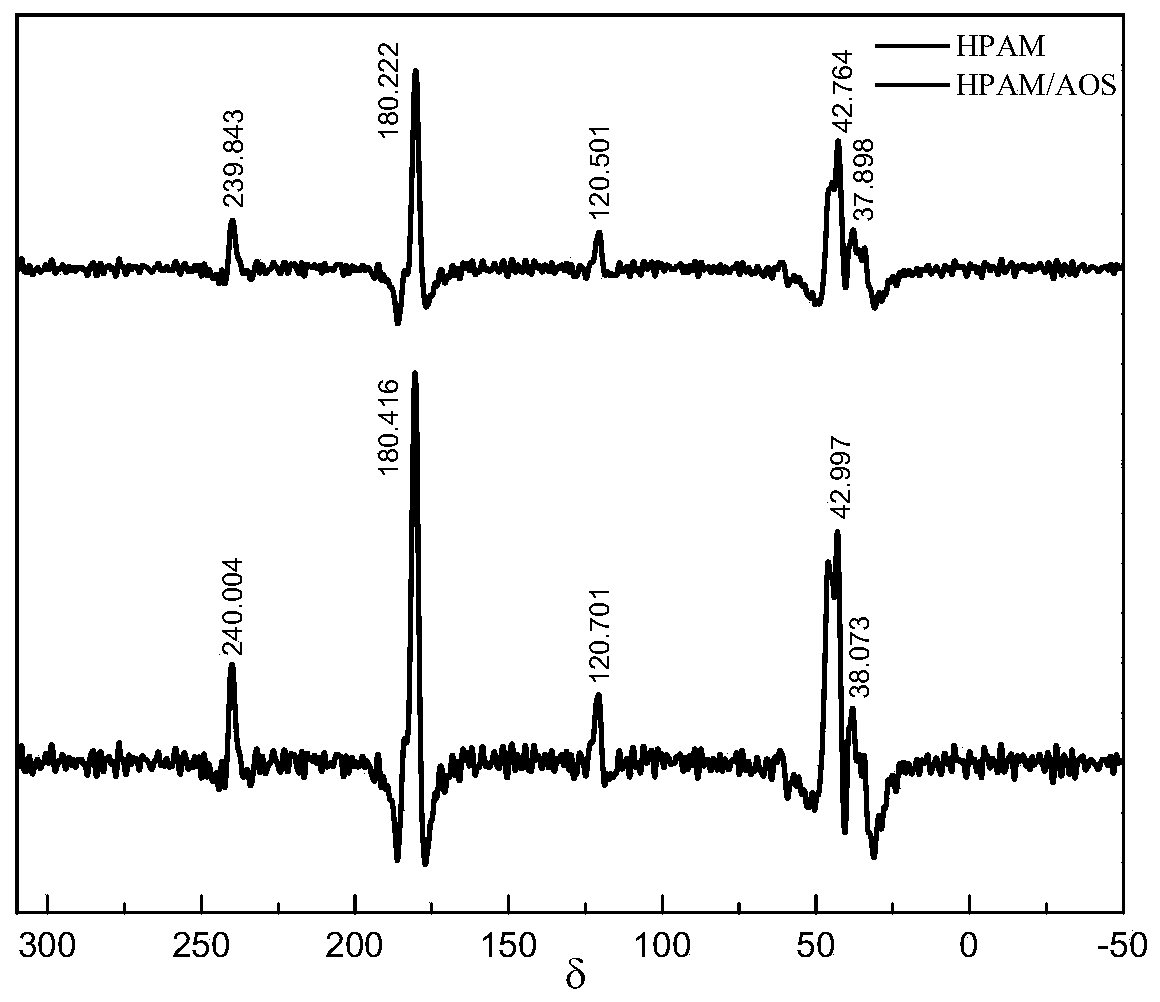
[0067] See Tables 1 and 2 for the elemental analysis of the polymer viscosity reducer (which is the preferred hydrolyzed polymer viscosity reducer) for heavy oil.
[0068] Table 1 Mass ratio of elements in HPAM / AOS and HPAM solid samples
[0069]
[0070] Table 2 The molar ratio of each element in HPAM / AOS and HPAM solid samples
[0071]
[0072] The elemental analysis results are shown in Tables 1 and 2. According to Tables 1 and 2, it is found that the mass fractions and mole fractions of the elements in HPAM and HPAM / AOS are very close, and the absolute values of the relative deviations of the C, H, and O elements are all 3 %, indicating that the main structures of the two are very similar. Due to the extremely low content of S element, it is approximately considered that HPAM and HPAM / AOS do not contain S element. Comparing the elemental analysis results of HPAM and HPAM / AOS, according to the mole fraction of each element of the two, it is found that the two main...
Embodiment 2
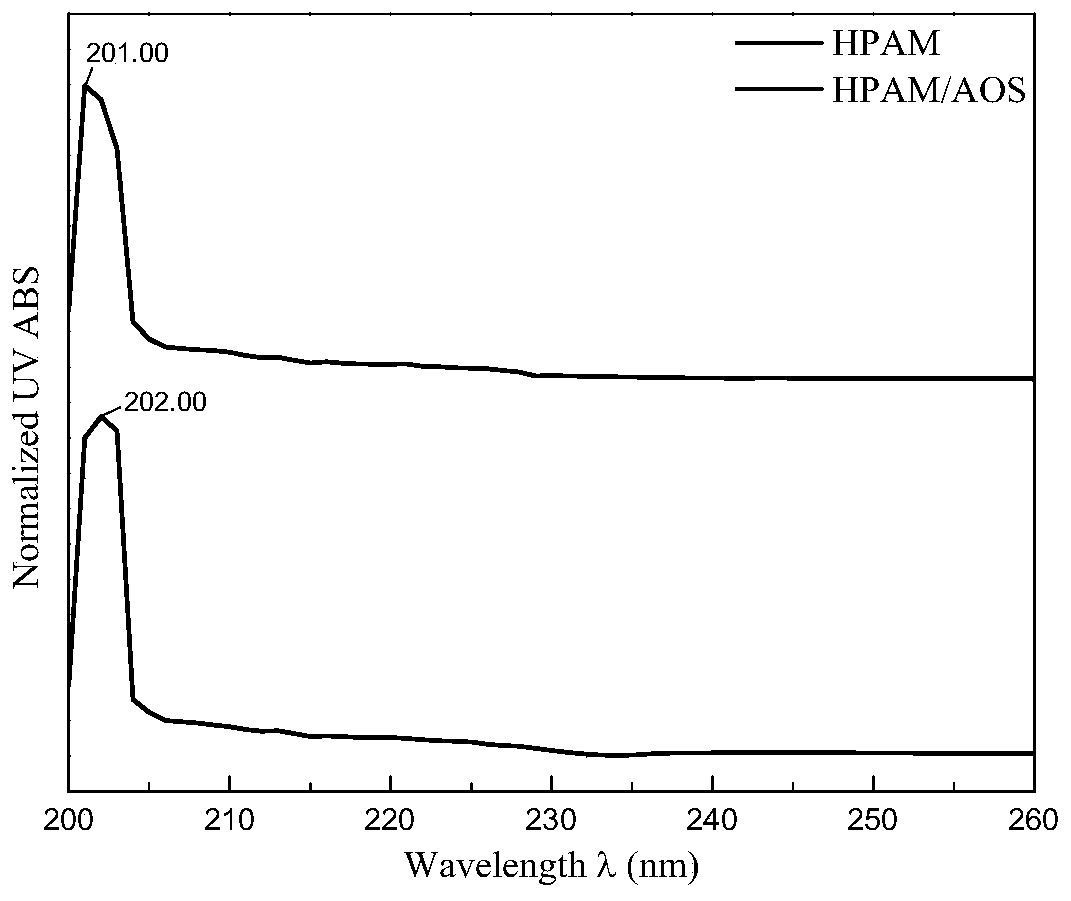
[0074] UV spectroscopic analysis of polymer viscosity reducer for heavy oil, see figure 1 .
[0075] The results of UV spectroscopy were figure 1 shown, according to figure 1 Comparing the UV spectra of HPAM / AOS and HPAM, it can be found that both HPAM / AOS and HPAM have maximum absorption peaks at around 200nm, where λmax of HPAM / AOS=202nm, and λmax of HPAM=201nm. This characteristic absorption band is caused by the n→π* transition of the amide, since the H in the aldehyde group is replaced by -NH 2 Substitution, resulting in a blue shift of the n→π* absorption band. According to this, it can be proved that both HPAM / AOS and HPAM molecules contain "-CONH 2 "Structural unit, HPAM / AOS is similar to HPAM molecular structure, which proves that HPAM / AOS is a polymer modified with HPAM as the matrix.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com