Treatment method for deeply removing thallium and cadmium from smelting wastewater
A treatment method and technology for wastewater are applied in the field of cadmium treatment and deep thallium removal from smelting wastewater, which can solve the problems of difficulty in cadmium and thallium, reversion, and trouble for R&D technicians by cadmium and thallium, and achieves low cost, short reaction time, Safe and convenient to use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
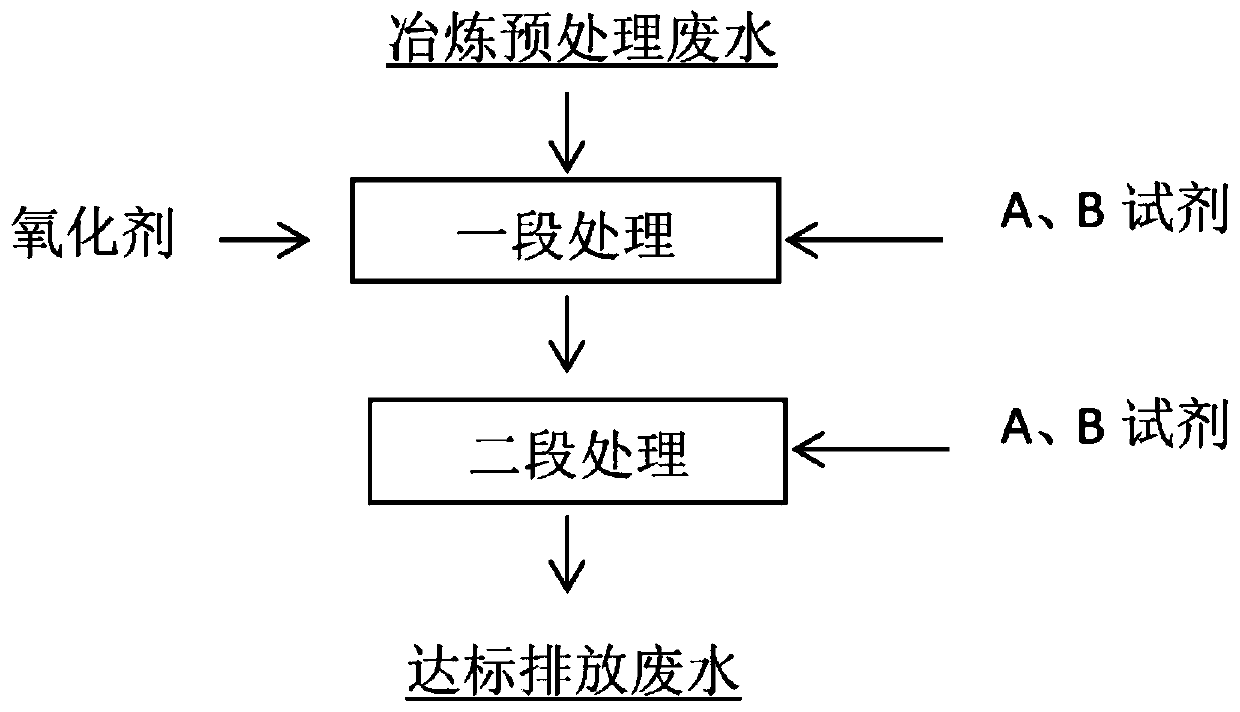
[0029] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a technical solution, a treatment method for deep removal of thallium and cadmium from smelting wastewater, comprising the following steps:
[0030] S1. Reagent A: 12% sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate, 5% sodium tripolyphosphate, 3% sodium sulfide nonahydrate;
[0031] S2. Reagent B: 32% polyferric sulfate, 17% polyaluminum chloride;
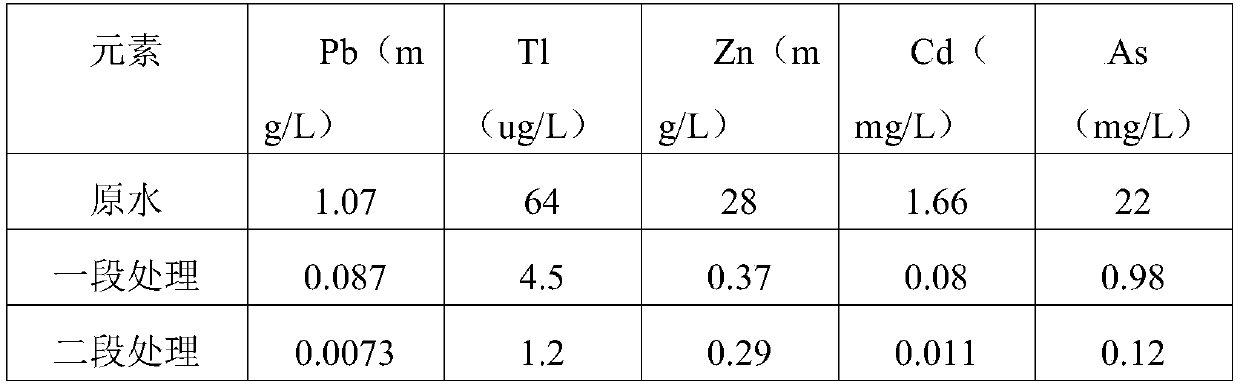
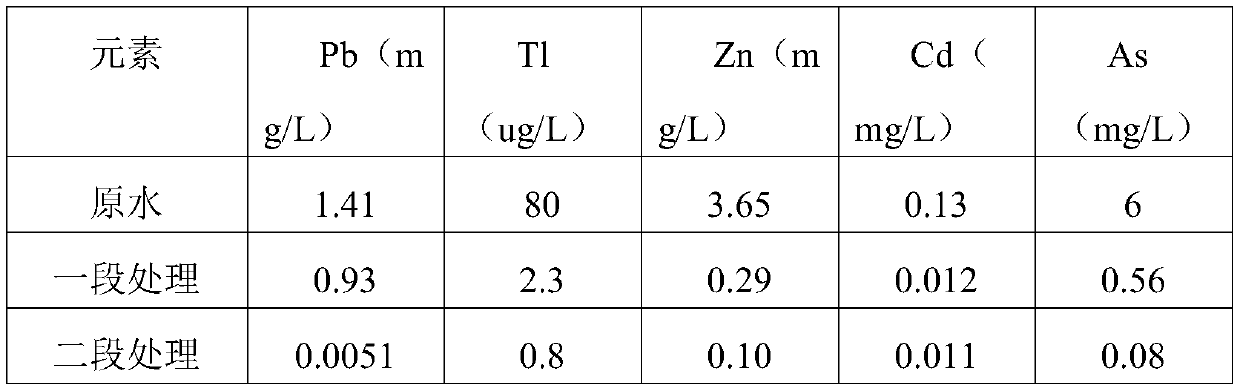
[0032] S3, one-stage treatment: take smelting pretreatment wastewater, add acidic solution, adjust the pH of the wastewater to 10, add an oxidant, then add reagent A to react for 10 minutes, finally add reagent B to react for 5 minutes, and press filter;
[0033] S4. Second-stage treatment: adjust the pH of the liquid after the first-stage filtration to 8, add reagent A to react, then add reagent B to react and let it stand still. After the supernatant is qualified, the waste water is discharged. According to the above technical scheme,
[0034] According to the above tec...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Embodiment 2: as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a technical solution, a treatment method for deep removal of thallium and cadmium from smelting wastewater, comprising the following steps:
[0046] S1. Reagent A: 13% sodium dimethyl dithiocarbamate, 7% sodium tripolyphosphate, 4% sodium sulfide nonahydrate;
[0047] S2. Reagent B: 27% polyferric sulfate, 23% polyaluminum chloride;
[0048] S3, one-stage treatment: take smelting pretreatment wastewater, adjust the pH of the wastewater to 9 with sulfuric acid, add an oxidant, then add reagent A to react for 10 minutes, and finally add reagent B to react for 10 minutes and press filter;
[0049] S4. Second-stage treatment: adjust the pH of the first-stage filtered liquid to 9, add reagent A to react, then add reagent B to react and let it stand still. After the supernatant is qualified, the waste water is discharged. According to the above technical scheme,
[0050] According to the above technical sch...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Embodiment 3: as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a technical solution, a treatment method for deep removal of thallium and cadmium from smelting wastewater, comprising the following steps:
[0062] S1. Reagent A: 5% sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate, 14% sodium tripolyphosphate, 3% sodium sulfide nonahydrate;
[0063] S2. Reagent B: 26% polyferric sulfate, 17% polyaluminum chloride;
[0064] S3, one-stage treatment: take smelting pretreatment wastewater, adjust the pH of the wastewater to 9, add an oxidant, then add reagent A to react for 10 minutes, and finally add reagent B to react for 15 minutes and press filter;
[0065] S4. Second-stage treatment: adjust the pH of the first-stage filtered liquid to 9, add reagent A to react, then add reagent B to react and let it stand still. After the supernatant is qualified, the waste water is discharged. According to the above technical scheme,
[0066] According to the above technical scheme, the heavy metal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com