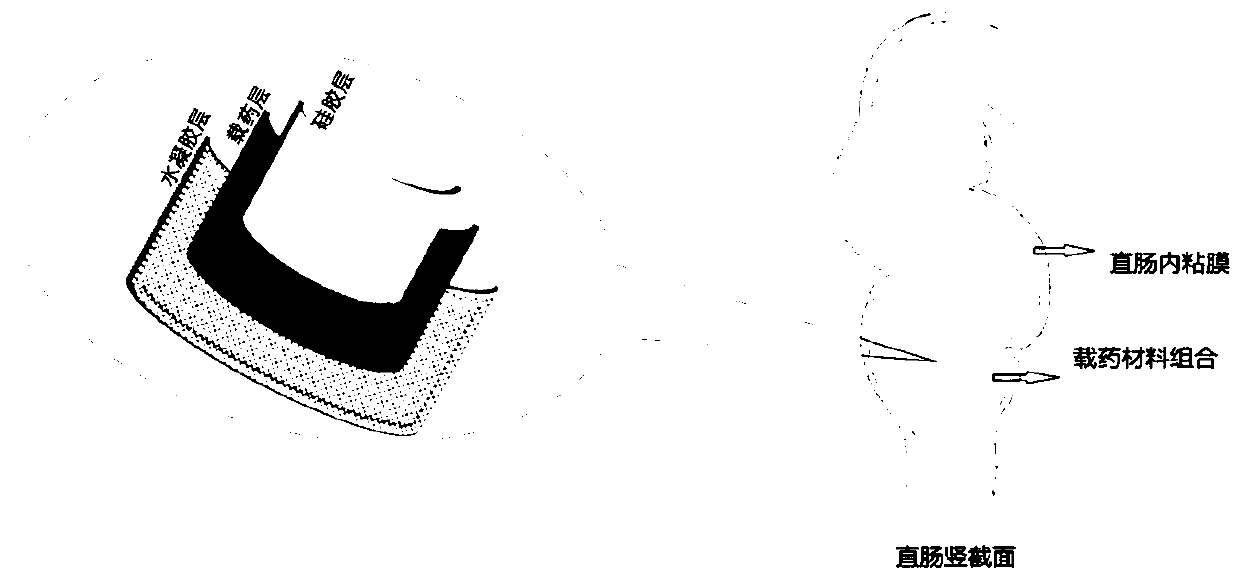
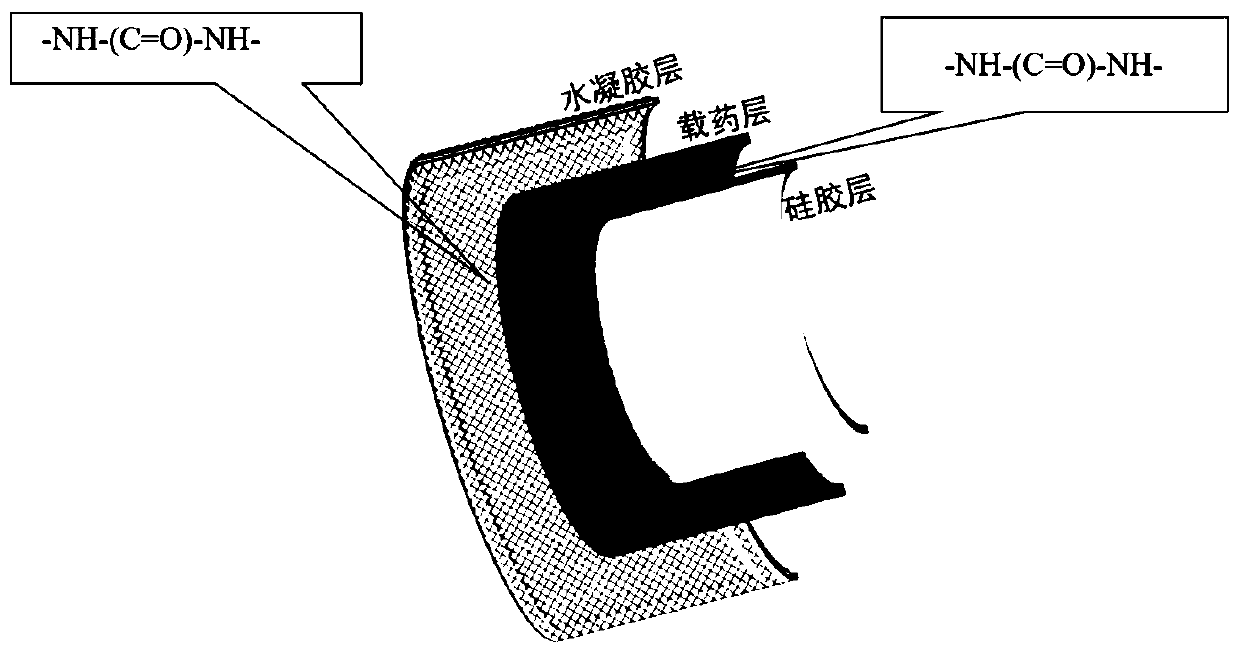
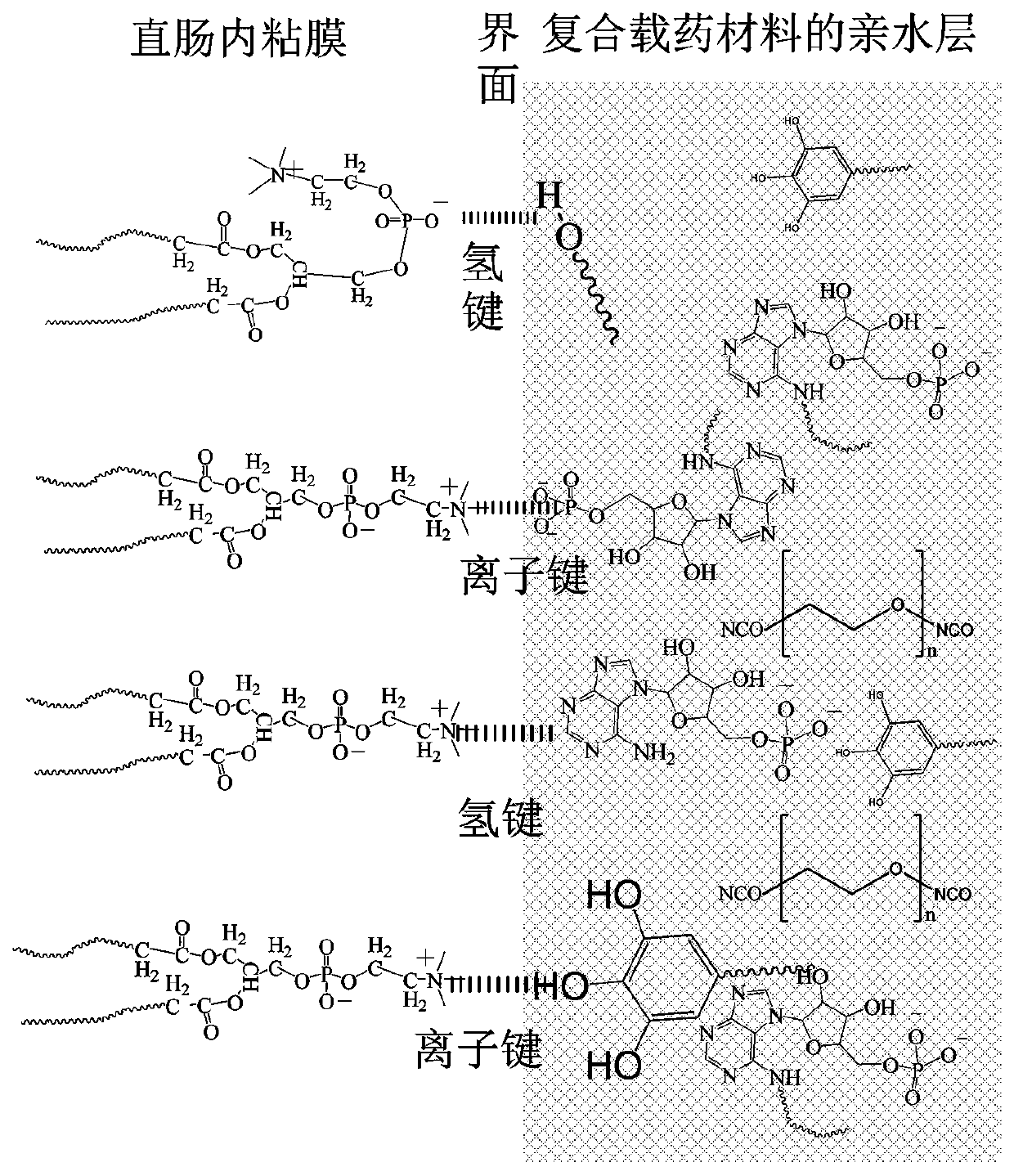
Drug sustained-release material and application thereof in sustained-release material for treating proctitis
A technology for slow-release materials and drugs, which can be used in plant raw materials, drug combinations, drug delivery, etc., and can solve problems such as high patient compliance requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] (1) Hydrogel layer preparation:
[0044] React polyethylene glycol (molecular weight 2000, the same below) with IPDI at a molar ratio of 1:2 to obtain NCO-capped polyethylene glycol (PEG-2NCO). Take 100 g of PEG-2NCO and dissolve it in an appropriate amount of water at 40°C. Add 1.5 g of 2'-deoxyadenosine-5'-monophosphate, 20 g of sodium chloride, 10 g of PVA (degree of polymerization 1700, degree of hydrolysis 99%), and 1.5 g of vitamin C, and set aside.
[0045] (2) Preparation of the drug-loaded layer: 38.8 g of ε-caprolactone, 1.80 g of 1,4-butanediol, and 0.08 g of dibutyltin dilaurate. Put ε-caprolactone into the reaction flask, dissolve 1,4-butanediol in 10ml of DMF, add it to the reaction flask, vacuumize for 30min, and pass nitrogen to make ring-opening polymerization under nitrogen environment; 140 Stir the reaction for 4 hours at ℃, and stir for 3 hours under vacuum at 180℃; put it into a vacuum drying oven to evaporate the solvent.
[0046] Weigh 10 g of t...
Embodiment 2
[0055] The preparation of the hydrogel layer and the hydrophobic layer is the same as in Example 1.
[0056] Preparation of the drug-loaded layer: (1) Weigh 10 g of PCL (number average molecular weight 2000) and dissolve it in 10 g of DMF by heating, and vacuumize at 100° C. for 30 min. (2) After cooling to 40°C, add 2.2g of IPDI to react for 2 hours, raise the temperature to 80°C and react for 2 hours, then cool to room temperature. (3) 1.2g of paclitaxel and 1.2g of 5-aminosalicylic acid were dissolved in 1g of DMF and added therein, stirred evenly, and set aside.
[0057] The assembly of the drug-carrier composite membrane is similar to Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0059] Preparation of the hydrogel layer:
[0060] (1) Copolymerize vinyl acetate and acrylic acid at a molar ratio of 10:1: dissolve 30 g of vinyl acetate and acrylic acid monomers in DMF, add 0.15 g of azobisisobutyronitrile AIBN initiator to initiate polymerization, and react for 10 hours. A polyvinyl acetate-acrylic acid copolymer was obtained. (2) adding 10% NaOH solution to carry out hydrolysis reaction to obtain polyvinyl alcohol-acrylic acid copolymer. (3) Add 1.5g of tannic acid, 3.5g of deoxyadenosine acid, 10g of gelatin, 20g of NaCl, and add 100g of water to dilute, mix well, then add 5g of trifunctional aziridine crosslinking agent (SC100) and mix Evenly; add 50g of Panax notoginseng extract, Sophora japonica extract, and ginseng extract for later use.
[0061] The drug-loaded layer is the same as Example 2, and the preparation of the hydrophobic layer is the same as Example 1.
[0062] The assembly of the drug-carrier composite membrane was similar to Example ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of grafting | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com