Salt-tolerant xylosidase mutant K321D as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of xylosidase and wild xylosidase, which is applied in the field of salt-tolerant xylosidase mutant K321D and its preparation, and can solve problems such as lack of stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
[0031] Construction and Transformation of Experimental Example 1 Expression Vector
[0032] According to the xylosidase nucleotide sequence KY391885 (SEQ ID NO.4) recorded in GenBank, the coding gene hJ14GH43 of the wild xylosidase HJ14GH43 was synthesized; the coding gene k321d (SEQ ID NO.2) of the mutant enzyme K321D was synthesized;
[0033] The synthetic coding gene hJ14GH43 and coding gene k321d sequences were respectively connected with the expression vector pEasy-E1 to obtain the expression vector containing hJ14GH43 and k321d, and the ligation products were respectively transformed into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), and the wild enzymes HJ14GH43 and Recombinant strain of mutant enzyme K321D.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2 Preparation of wild enzyme HJ14GH43 and mutant enzyme K321D
[0035] The recombinant strains containing hJ14GH43 and k321d were inoculated in LB (containing 100 μg mL - 1 Amp) medium, shake rapidly at 37°C for 16h.
[0036] Then, the activated bacterial solution was inoculated into fresh LB (containing 100 μg mL -1 Amp) culture medium, rapid shaking culture for about 2 ~ 3h, OD 600 After reaching 0.6-1.0, add IPTG (isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside) with a final concentration of 0.1 mM for induction, and continue shaking culture at 20° C. for about 20 h.
[0037] Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 5 minutes to collect the bacteria, suspend the bacteria with an appropriate amount of Tris-HCl buffer solution with a pH of 7.0, and then ultrasonically disrupt the bacteria in a low-temperature water bath.
[0038] After the crude enzyme solution concentrated in the cells was centrifuged at 12,000rpm for 10min, the supernatant was aspirated and the target protein...
Embodiment 3
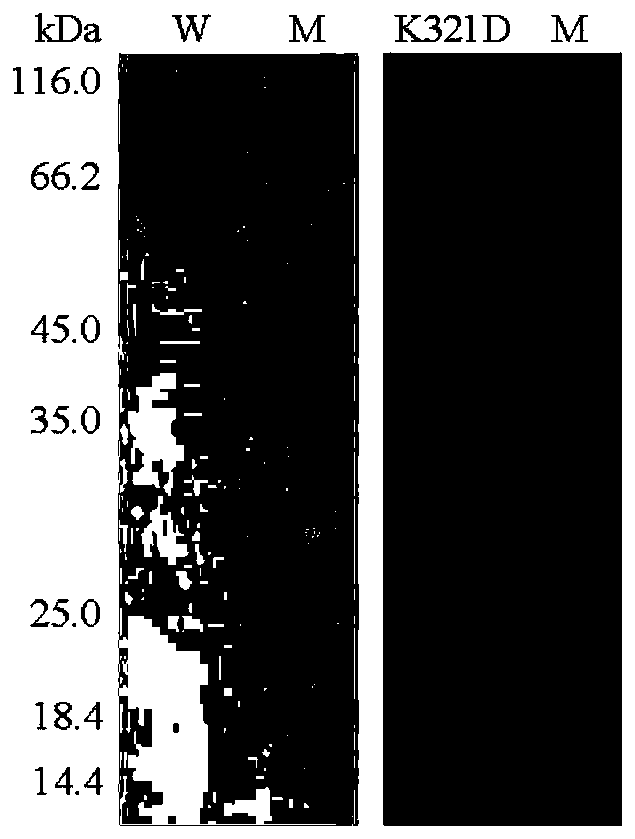
[0040] The property determination of the wild enzyme HJ14GH43 of embodiment 3 purification and mutant enzyme K321D
[0041] The activities of the purified wild enzyme HJ14GH43 and the mutant enzyme K321D were determined by the pNP method, as follows:
[0042] Dissolve pNPX in buffer so that the final concentration is 2mM; the reaction system contains 50μL of appropriate enzyme solution and 450μL of 2mM substrate; 2mL 1M Na 2 CO 3 The reaction was terminated, and the released pNP was measured at a wavelength of 405 nm after cooling to room temperature; 1 enzyme activity unit (U) was defined as the amount of enzyme required to decompose the substrate to produce 1 μmol pNP per minute.
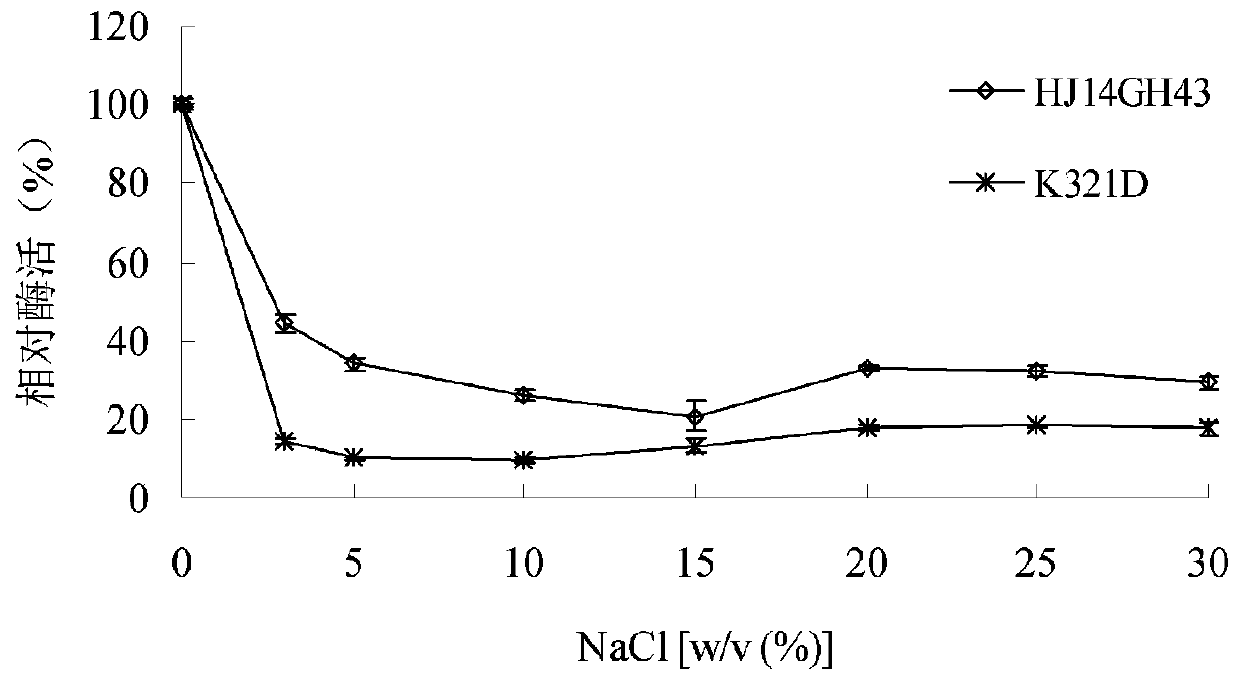
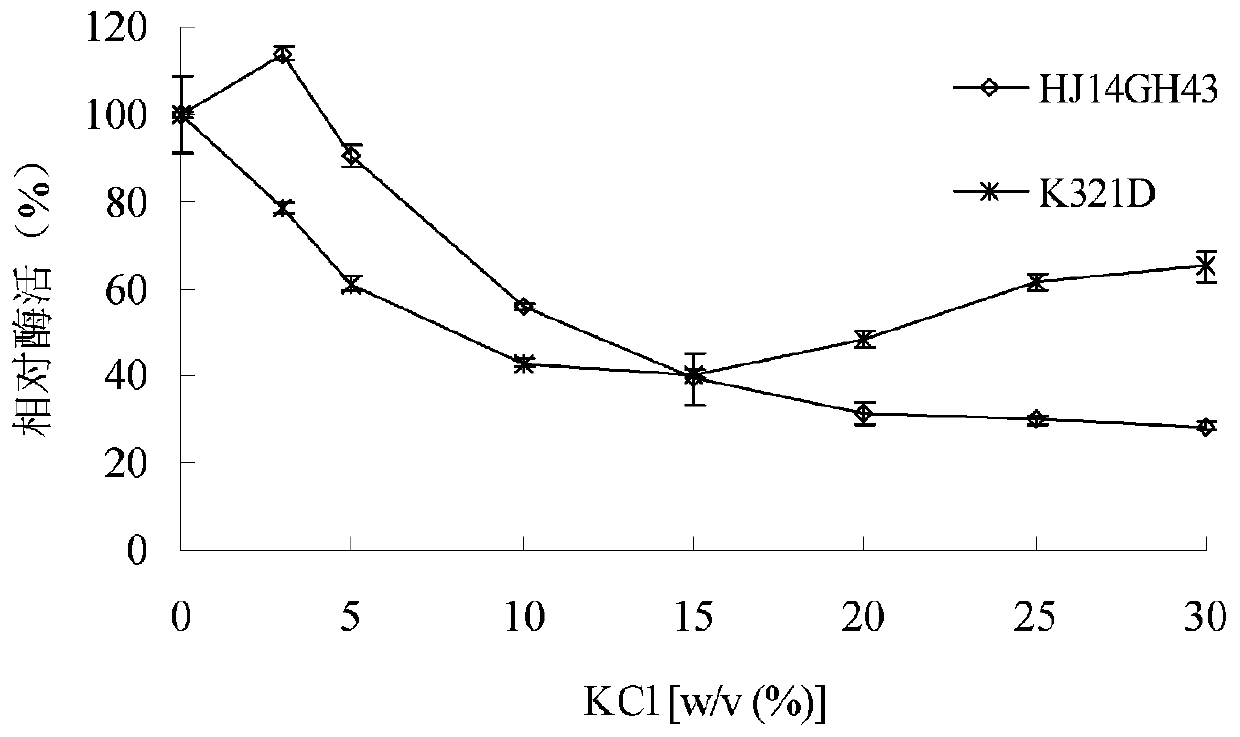
[0043] 1. Stability of purified wild enzyme HJ14GH43 and mutant enzyme K321D in NaCl
[0044] The purified enzyme solution was placed in 3.0-30.0% (w / v) NaCl aqueous solution, treated at 20°C for 60 minutes, and then the enzymatic reaction was carried out at pH 7.0 and 20°C, and the untreated e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com