StSCI protein for changing self-incompatibility of diploid potato material
A potato and diploid technology, applied in the field of genetics and breeding, can solve the problems of time-consuming and human resources, distant kinship, self-incompatibility of diploid potatoes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
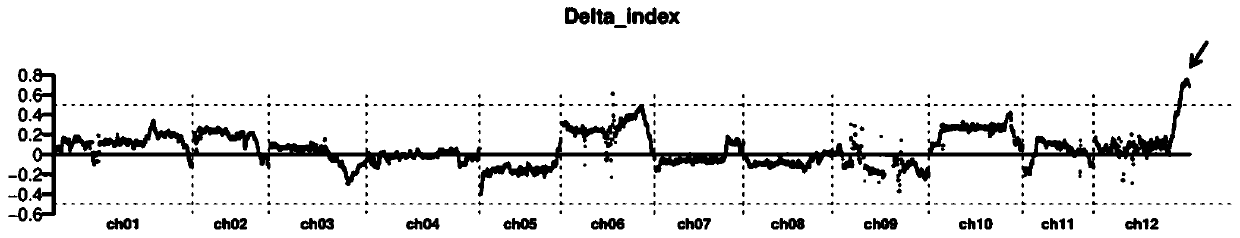
[0092] Example 1 StSCI gene mapping
[0093] The self-incompatible diploid material PI225689 was pollinated with the pollen of the diploid potato material RH89-039-16, and the seeds were harvested as the F1 generation. The self-compatibility traits of the F1 generation plants were investigated, and half of the plants were self-compatible and self-incompatible, indicating that the self-compatibility gene in RH89-039-16 was in a heterozygous state, while RH89- 039-16 showed self-compatibility traits, which indicated that the gene controlling the self-compatibility of RH89-039-16 was dominant, and this dominant gene was named StSCI gene. The leaves of 40 self-compatible plants and 40 self-incompatible plants were selected from the F1 generation and mixed to extract genomic DNA, and the genomic DNA of the two groups of mixed pools was sequenced.
[0094] The sequencing results were analyzed, and the StSCI gene was preliminarily located in the 2.5Mb interval at the end of chromoso...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Example 2 StSCI gene verification
[0100] In order to verify that the PGSC0003DMG400016861 gene is the self-compatibility-induced gene in RH89-039-16, pCAMBIA1301 was used as the backbone vector to construct a promoter region containing 1245 bp upstream of the start codon of the PGSC0003DMG400016861 gene in RH89-039-16 and a 3352 bp The plant binary vector containing the full-length region of the gene, with the help of the Agrobacterium transformation system, transferred the PGSC0003DMG400016861 gene in RH89-039-16 together with its promoter into the original self-incompatible diploid potato material S15 In -65, complementary transgenic plants were obtained. At the same time, an overexpression vector with CaMV35S as the promoter linked to the coding region of the PGSC0003DMG400016861 gene was constructed, and transferred into the self-incompatibility material PI 225689 by the same method.
[0101] At the same time, using CRISP / Cas9 technology, a gene knockout vector o...
Embodiment 3
[0102] Example 3 A method for producing self-compatible diploid potatoes
[0103] Using Agrobacterium LBA440, the pCAMBIA1301 vector carrying the nucleotide sequence encoding the StSCI protein (SEQ ID NO.2) and the promoter (SEQ ID NO.3) was transferred into a self-incompatible of diploid potatoes. It was found that the introduction of the above-mentioned pCAMBIA1301 vector made the StSCI gene in the diploid potato express the StSCI protein, and then transformed the self-incompatible diploid potato into self-compatible.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com