Real-time fluorescent PCR method for detecting mycobacterium avium and application of primer pairs
A technology of Mycobacterium avium and bacteria, which is applied in the field of real-time fluorescent PCR detection of Mycobacterium avium, can solve the problems of infrequent use, poor accuracy and complicated operation, and achieves the effects of reducing the probability of errors, high accuracy and low price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] Embodiment 1, strain and its accuracy analysis
[0071] 1. Strains
[0072] 21 standard strains of mycobacteria: Mycobacterium avium (ATCC25291), Mycobacterium intracellulare (ATCC13950), Mycobacterium abscessus (ATCC19977), Mycobacterium chelonis (ATCC14472), Mycobacterium kansasii (ATCC12478), Ge Mycobacterium aureus (ATCC14470), Mycobacterium fortuitum (ATCC6481), Mycobacterium phlei (ATCC11758), Mycobacterium aureus (ATCC23366), Mycobacterium scrofula (ATCC19981), Mycobacterium light yellow (ATCC43909), stigmata Mycobacterium smegmatis (ATCC19420), Mycobacterium tuberculosis (ATCC27294), Mycobacterium malmosa (ATCC29571), Mycobacterium simianum (ATCC25275), Mycobacterium suja (ATCC35799), Mycobacterium suis (ATCC33776), Mycobacterium terrae (ATCC15755), Mycobacterium flavinum (ATCC14474), Mycobacterium disidei (ATCC19340), Mycobacterium stutzeri (ATCC27962).
[0073] Five common pathogenic bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC29213), Escherichia coli (ATCC25922), ...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Embodiment 2, the acquisition of the primer that is used to detect Mycobacterium avium
[0080] 1. Primer design, screening and preparation
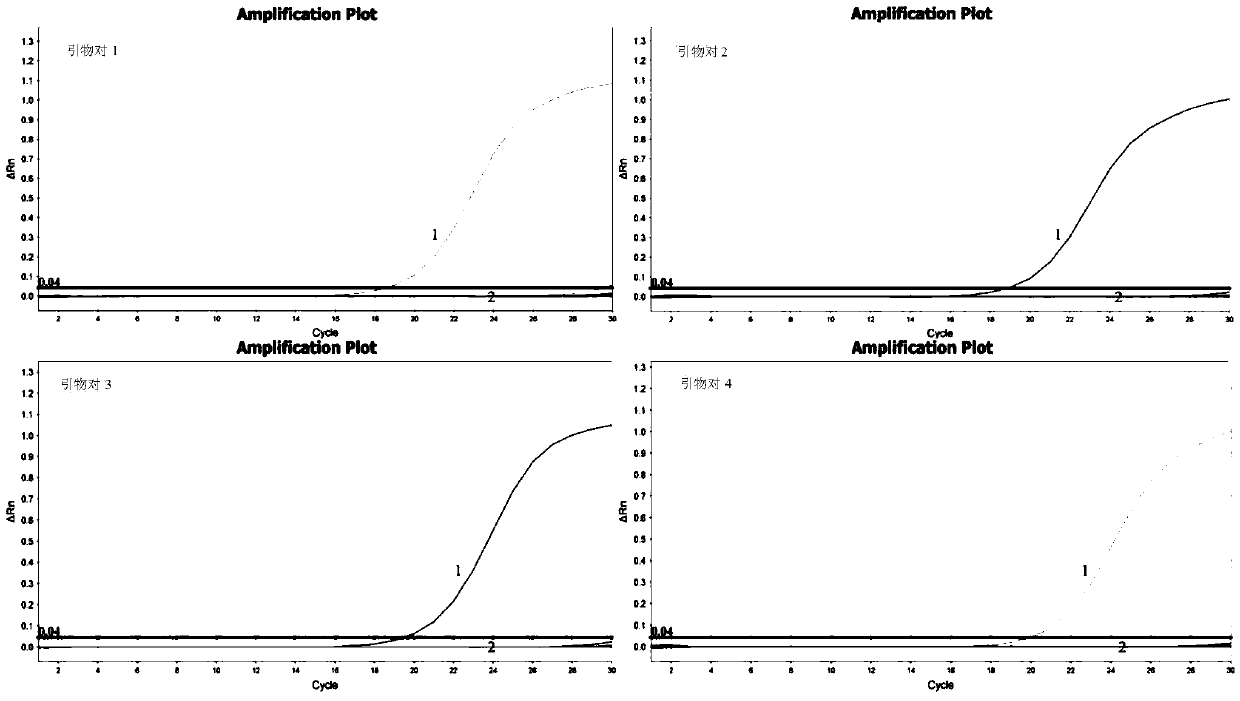
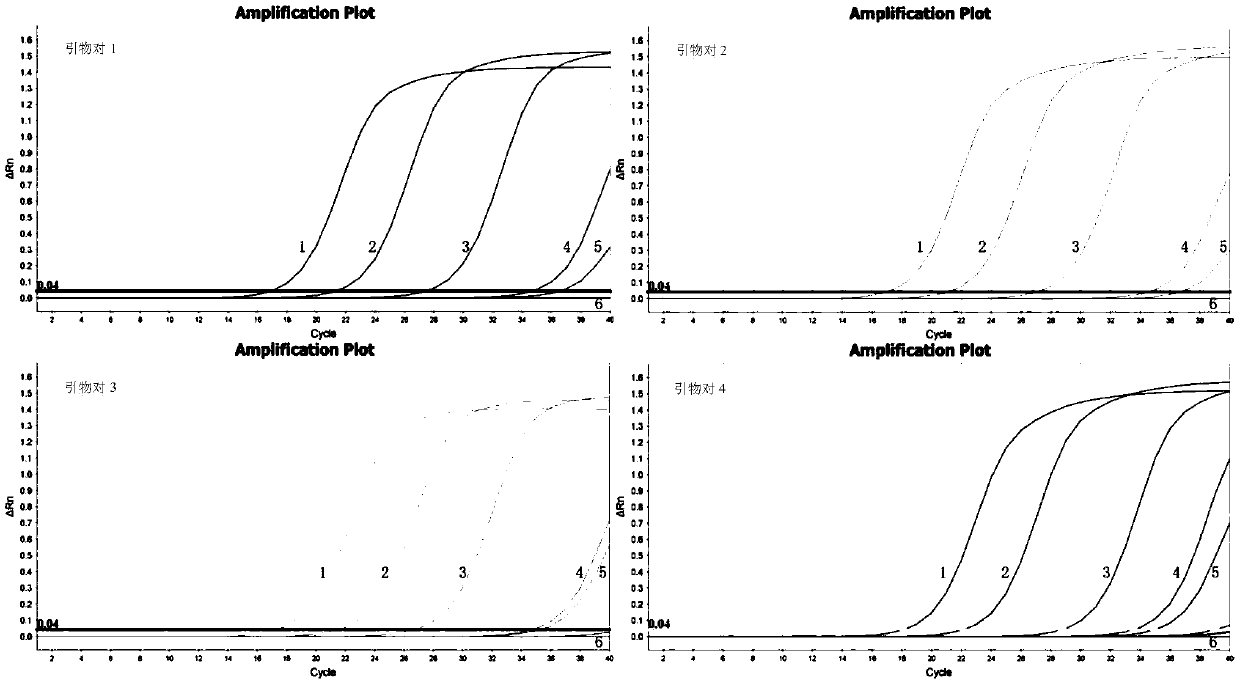
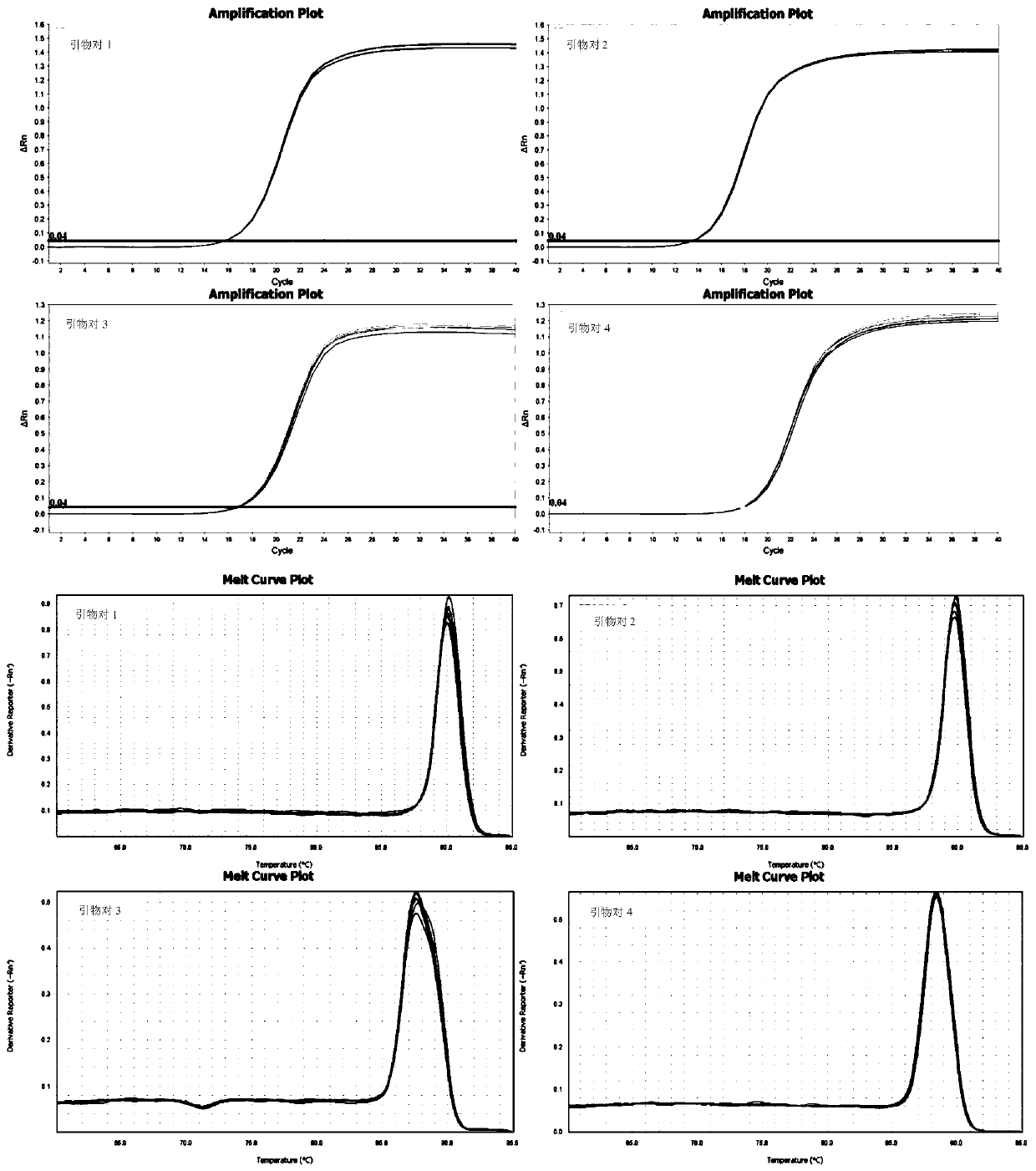
[0081] A large number of sequence analyzes and comparisons were carried out to obtain several primers for identifying Mycobacterium avium. Preliminary experiments were performed on each primer to compare performances such as sensitivity, specificity, and repeatability, and finally four pairs of primers for identifying Mycobacterium avium were obtained, as shown in Table 1.
[0082] Table 1 is used to identify four pairs of primers of Mycobacterium avium
[0083]
[0084] Note: F indicates the forward primer, R indicates the reverse primer.
Embodiment 3
[0085] Embodiment 3, accuracy
[0086] Four pairs of primers in Table 1 were used to amplify the genomic DNA of the Mycobacterium avium standard strain respectively; 10 μl of the amplified product was carried out on a 2% agarose gel, and the amplified product was sequenced at the same time, and the sequencing results were used in BLAST and GenBank databases. The amplified sequences of each standard bacteria gene were compared to analyze and evaluate the accuracy of the mycobacterium standard bacteria used in this study.
[0087] The results showed that the sequencing results of the amplified products of primer pairs 1, 2, 3 and 4 were aligned with the target gene sequences in the GenBank database, and the concordances were 100%, 100%, 100%, and 99.32%, respectively. It shows that the four pairs of primers for Mycobacterium avium designed in the present invention all have higher diagnostic accuracy for Mycobacterium avium.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com