Near-infrared light-emitting binuclear ruthenium complex as tumor cell recognition and imaging reagent
A technology of binuclear ruthenium complexes and tumor cells, which is applied in the field of fluorescent biomolecular probes, can solve the problems of few reports on near-infrared luminescent ruthenium complexes, and achieve good near-infrared phosphorescence emission performance, great development potential, and no cytotoxicity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] Embodiment 1: cell culture and the cytotoxicity experiment of binuclear ruthenium (II) complex
[0016] Human cervical cancer HeLa cells in CO at 37°C 2 cultured in an incubator (relative humidity 95%, CO 2 Content 5%), the cell culture medium is DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% double antibody.
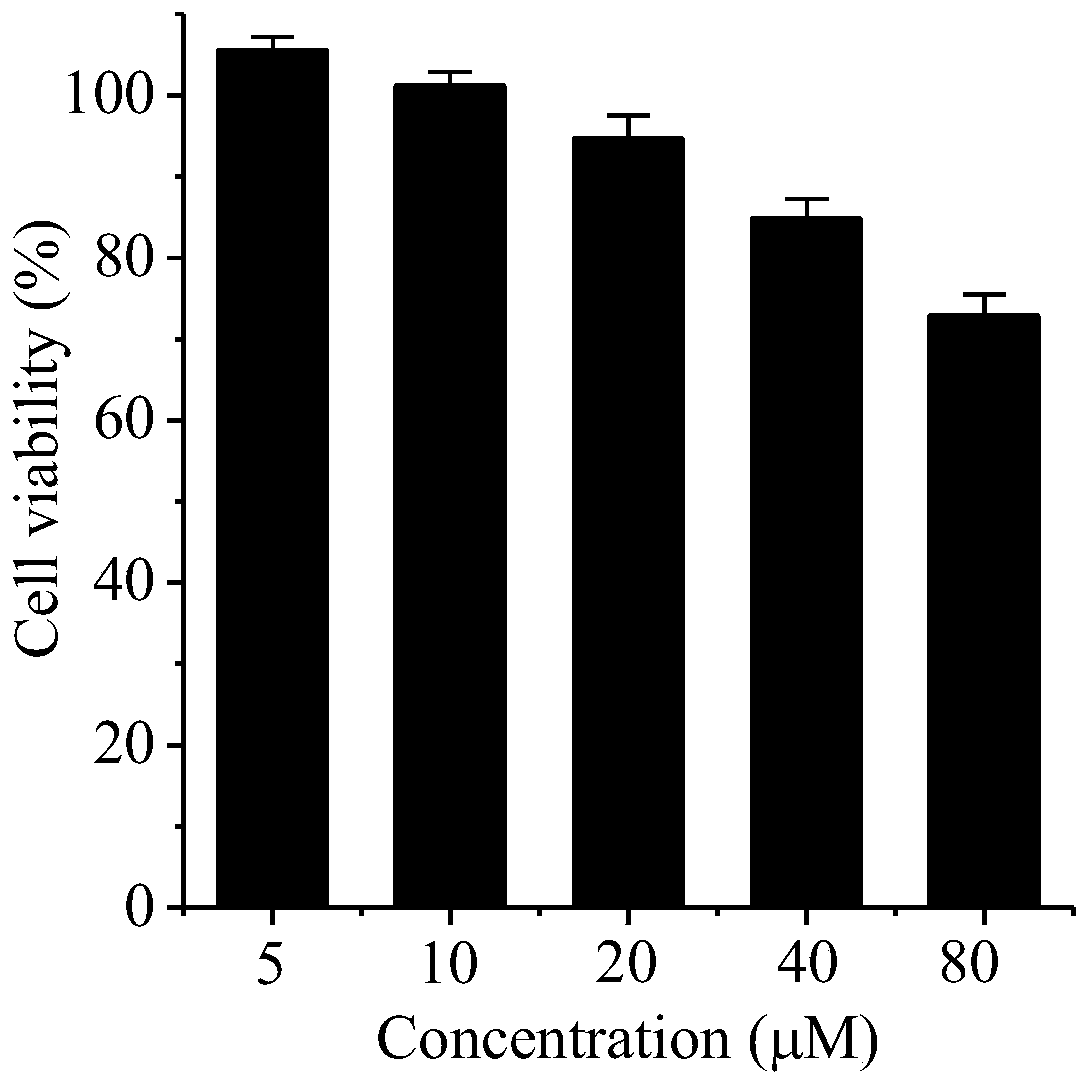
[0017] The effect of complexes on cell viability was detected by MTT assay. Take tumor cells in the logarithmic growth phase, and use a cell concentration of 1×10 4 Inoculate each well in a 96-well plate, 100 μL per well, add cell-free medium to the blank control wells, and fill the peripheral wells with sterile PBS. Cultivate in an incubator for 24 hours, discard the medium in each well, add 100 μL of binuclear ruthenium complexes of different concentrations prepared in fresh medium, set up 5-6 replicate wells, and add fresh medium without ruthenium complexes in the control group. After culturing for 48 hours, 10 μL of 5 mg / mL MTT solution was added to...
Embodiment 2
[0020] Example 2: Binuclear ruthenium (II) complex recognizes tumor cells
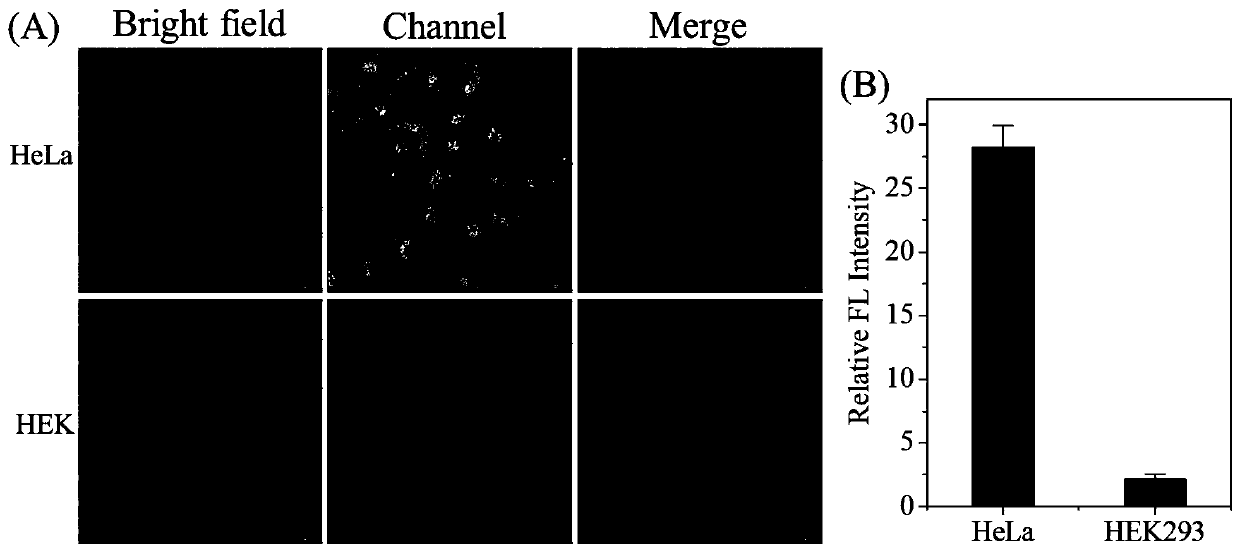
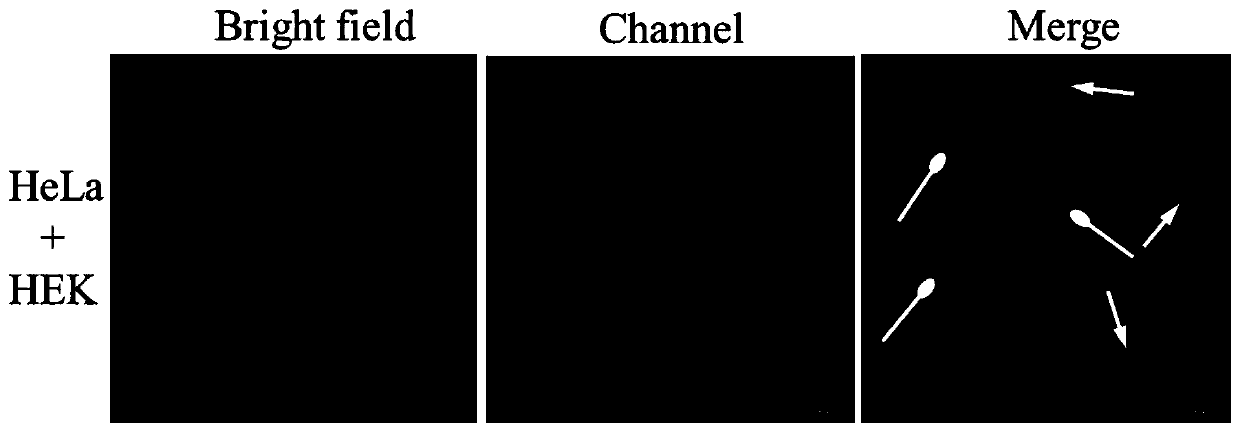
[0021] At a cell density of 1×10 4 Inoculate human cervical cancer HeLa cells and human embryonic kidney HEK293 cells into 20mm confocal small dishes respectively. After culturing in the incubator for 24 hours, discard the old culture medium and replace it with 40μM binuclear ruthenium complex. The culture medium was freshly cultured for 8 hours, washed three times with phosphate buffer solution of pH=7.4, excited at 562nm with a Nikon A1R laser confocal fluorescence microscope, and imaged in the red channel of 640-720nm. figure 2 The results shown show that the binuclear ruthenium complex can be effectively taken up by tumor HeLa cells, while the uptake rate of normal human HEK293 cells is low. Under the same experimental conditions, the fluorescence intensity of tumor cells is 13 times that of normal cells. In order to further confirm the target recognition ability of ruthenium complexes on tumor c...
Embodiment 3
[0022] Example 3: Subcellular localization of binuclear ruthenium complexes in HeLa cells
[0023] HeLa cells were treated with 1×10 4 Cells / well were seeded in a 20mm confocal small dish, and after 24 hours of culture, fresh medium containing 40 μM binuclear ruthenium complex was added and incubated in an incubator for 8 hours. The culture solution in the small dish was discarded, washed twice with phosphate buffer solution of pH=7.4, lysoTracker Green at a concentration of 200nM, mitochondrial dye MitoTracker Green at 200nM and nuclear dye Hoechst33342 at a concentration of 5μg / mL were added for staining After 30 minutes, washed with phosphate buffer three times, the subcellular localization of the binuclear ruthenium complex was observed with a Nikon A1R laser confocal fluorescence microscope. Binuclear ruthenium(II) complexes (λ ex =562nm,λ em =640-720nm), LysoTracker Green and MitoTrackerGreen (λ ex =488nm,λ em =505-530nm), Hoechst33342 (λ ex =405nm,λ em = 430-460n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com