Transaminase mutant, construction method and application thereof
A technology of mutants and transaminases, applied in the field of transaminase mutants and their construction, can solve problems such as poor thermal stability of transaminases, and achieve excellent stereoselectivity, simple culture conditions, and good thermal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
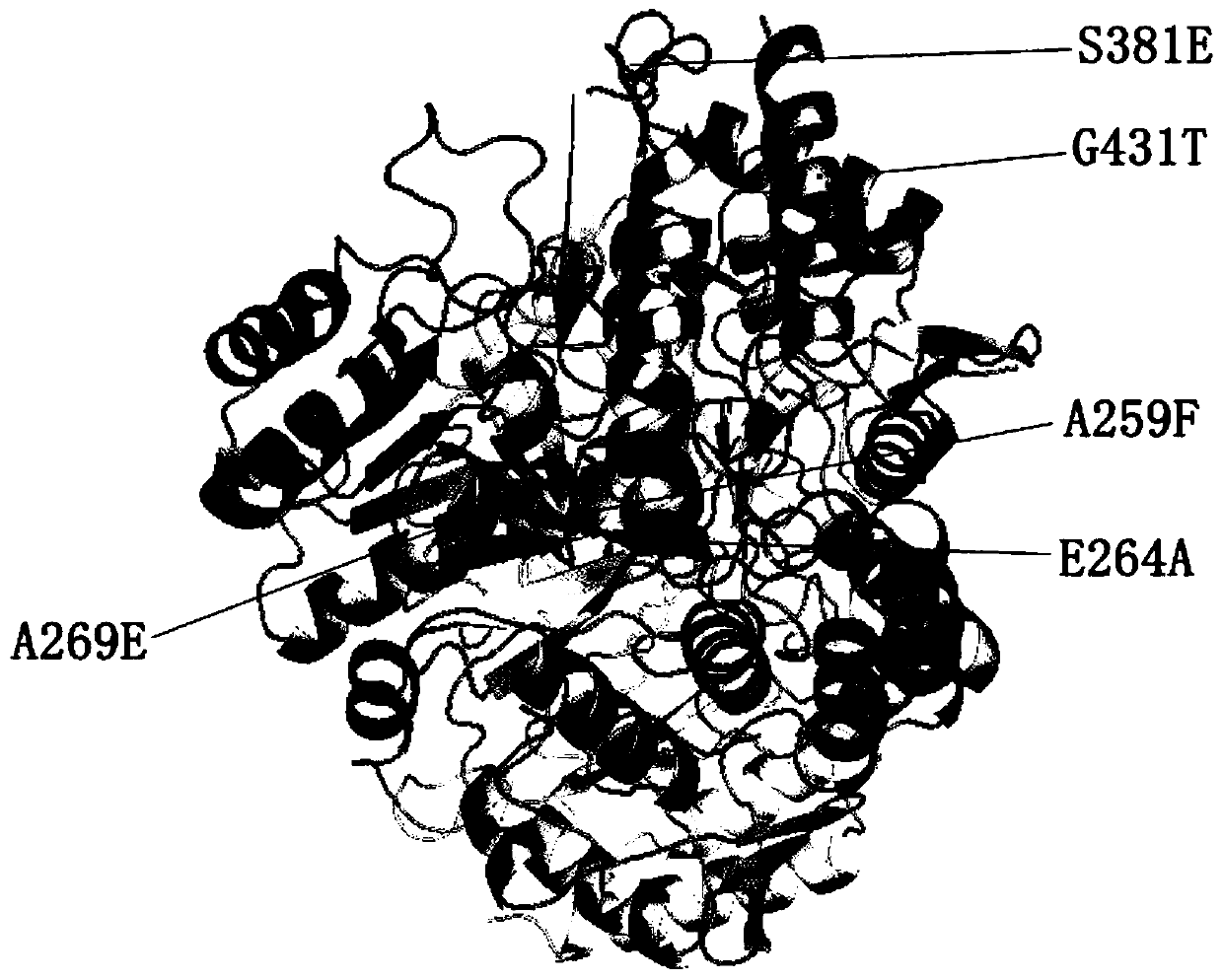
[0037]This embodiment provides a transaminase mutant, which is a molecularly engineered derivative protein based on the amino acid sequence of the wild-type transaminase (WP_0532423951.1), wherein the wild-type transaminase (WP_0532423951.1) is derived from Aspartate aminotransferase (aspartate aminotransferase is a member of the omega transaminase family) gene of the Chromobacter sp.DMS1 strain is expressed after codon optimization, and the nucleic acid sequence encoding the protein is SEQ ID NO .1, the amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO.2.
[0038] The transaminase mutants provided in this embodiment include:
[0039] (a1) a derivative protein having the same function as the protein shown in SEQ ID NO.2 by substituting, deleting or adding one or more amino acids to the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2; or,
[0040] (a2) A derivative protein having at least 92% homology with the protein shown in SEQ ID NO.2 by replacing one or more positions of the amino acid sequence ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The present embodiment provides a gene encoding the transaminase mutant as described in Example 1:
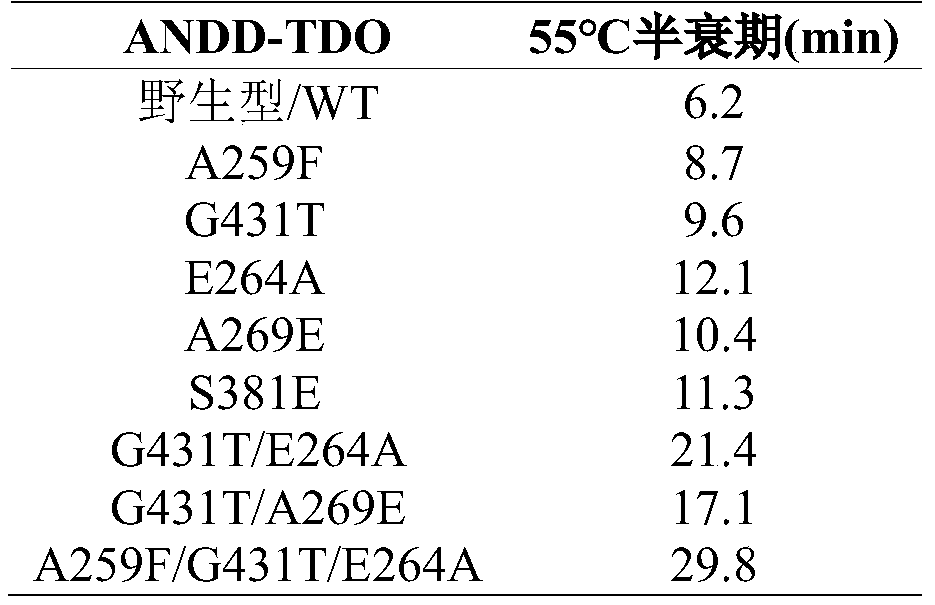
[0050] (1) The nucleic acid sequence encoding the transaminase mutant whose mutation site is A259F is SEQ ID NO.3;
[0051] (2) The nucleic acid sequence encoding the transaminase mutant whose mutation site is G431T is SEQ ID NO.4;
[0052] (3) The nucleic acid sequence encoding the transaminase mutant whose mutation site is E264A is SEQ ID NO.5;
[0053] (4) The nucleic acid sequence encoding the transaminase mutant whose mutation site is A269E is SEQ ID NO.6;
[0054] (5) The nucleic acid sequence encoding the transaminase mutant whose mutation site is S381E is SEQ ID NO.7;
[0055] (6) The nucleic acid sequence encoding the transaminase mutant whose mutation site is G431T / E264A is SEQ ID NO.8;
[0056] (7) The nucleic acid sequence encoding the transaminase mutant whose mutation site is G431T / A269E is SEQ ID NO.9;
[0057] (8) The nucleic acid sequence encoding th...
Embodiment 3
[0059] This example provides a recombinant plasmid comprising the gene provided in Example 2, which is a plasmid vector that can be used to integrate the transaminase gene into a host cell for stable expression, such as pET28a, pUC18, pUC19, pET15b, etc.; the host cell can be selected Gram-invisible bacteria (such as Escherichia coli), Gram-positive bacteria (such as Bacillus subtilis), fungi (such as Aspergillus), yeasts (such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae), actinomycetes (such as Streptomyces), etc., can be used to express transaminase mutant proteins.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com