High-temperature phase-change heat storage material, heat storage brick and preparation method of heat storage brick
A heat storage material and high-temperature phase change technology, applied in the field of energy storage materials, can solve the problems such as cracks and deformation of heat storage materials, and achieve the effects of expanding the use temperature range, reducing the preparation cost, and having good adhesion.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
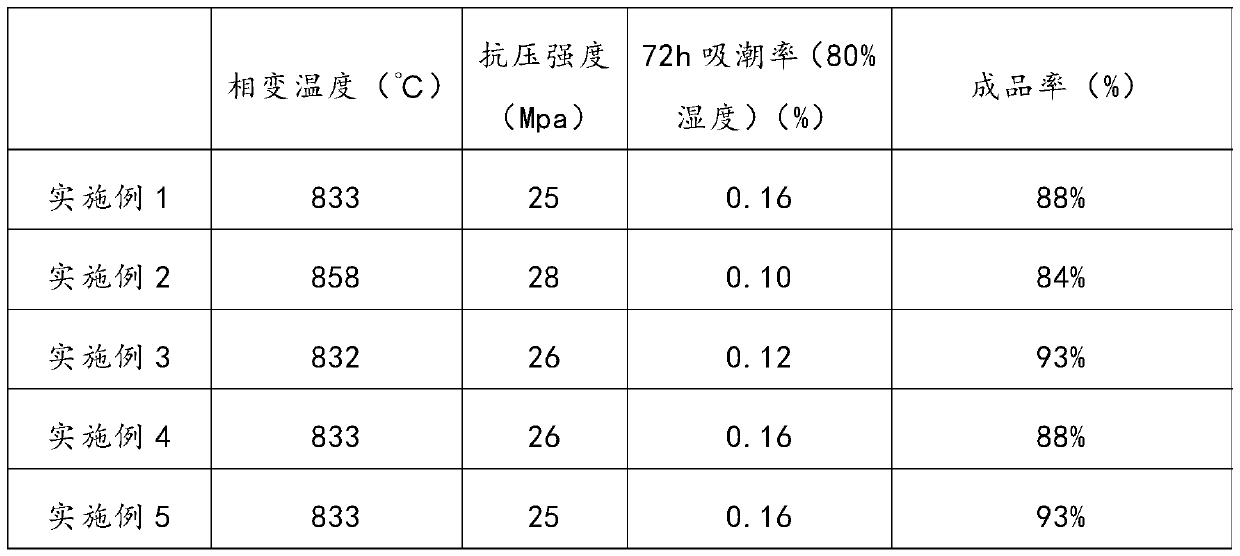
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] (1) the fused magnesia powder and the heavy sodium carbonate with a particle diameter of 60 μm are uniformly mixed to form the first mixture;
[0029] (2) The first mixture is mixed with barium carbonate and sodium silicate to form the second mixture. The mass ratio of fused magnesium oxide powder, heavy sodium carbonate, barium carbonate and sodium silicate is 40:50:6 :0.5;
[0030] (3) Based on the mass of the second mixture, add 12% water to the second mixture, stir and knead for 10 minutes and pass through a 20-mesh sieve to form a mixture;
[0031] (4) Compress the above-mentioned kneaded material at 16Mpa for a holding time of 30s; then dry at 25°C for 4h;
[0032] (5) Sintering at 835° C. for 1 hour to obtain a high temperature phase change heat storage brick.
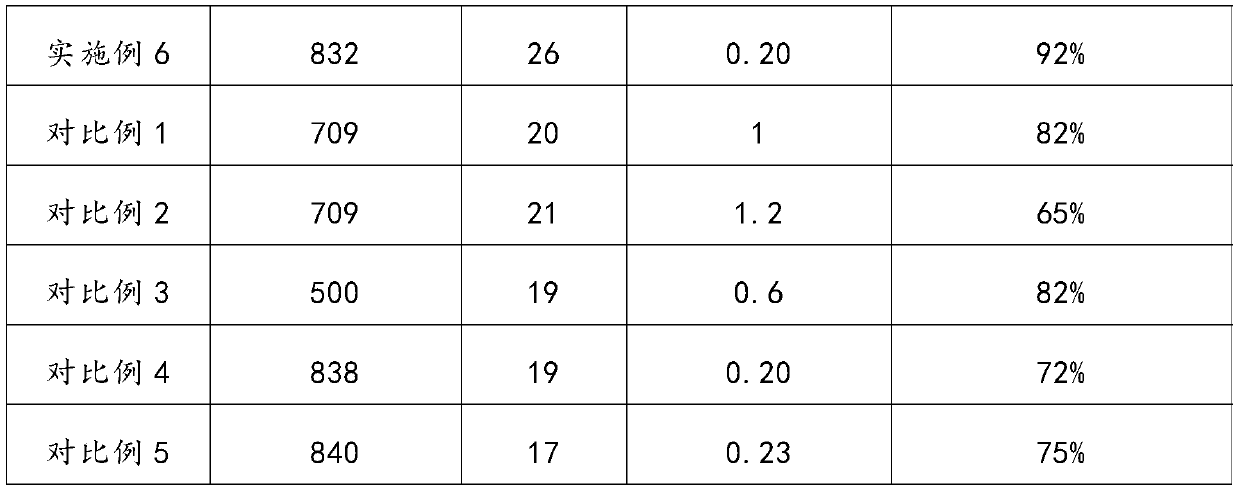
Embodiment 2
[0034] (1) the fused magnesia powder and the heavy sodium carbonate with a particle diameter of 60 μm are uniformly mixed to form the first mixture;
[0035] (2) The first mixture is mixed with bismuth oxide and sodium silicate to form the second mixture. The mass ratio of fused magnesium oxide powder, heavy sodium carbonate, barium carbonate and sodium silicate is 44:50:1 : 5 mix homogeneously, obtain compound;
[0036] (3) Based on the mass of the second mixture, add 10% water to the second mixture, stir and knead for 15 minutes and pass through a 20-mesh sieve to form a mixture;
[0037] (4) Compress the above-mentioned kneaded material at 16Mpa for a holding time of 30s; then dry at 50°C for 5h;
[0038] (5) Sintering at 850° C. for 1 hour to obtain a high temperature phase change heat storage brick.
Embodiment 3
[0040] (1) the fused magnesia powder and the heavy sodium carbonate with a particle diameter of 40 μm are uniformly mixed to form the first mixture;
[0041] (2) The first mixture is mixed with barium carbonate, bismuth oxide and sodium silicate to form the second mixture, and the mass ratio of fused magnesium oxide powder, heavy sodium carbonate, barium carbonate and bismuth oxide is 32:56 :3:2:2;
[0042] (3) Based on the mass of the second mixture, add 10% water to the second mixture, stir and knead for 20 minutes and pass through a 20-mesh sieve to form a mixture;
[0043] (4) Compress the above-mentioned kneaded material at 16Mpa for a holding time of 30s; then dry at 75°C for 5h;
[0044] (4) Sintering at 830° C. for 1 hour to obtain a high temperature phase change heat storage brick.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com