Method for preparing macroporous quick-response polyacrylamide hydrogel by adopting frontal polymerization of acrylamide deep-eutectic solvent
A low eutectic solvent, acrylamide-based technology, applied in the field of functional polymer material preparation, can solve the problems of slow polymerization speed, reduced production energy consumption, easy residues, etc., to shorten the reaction time, reduce production energy consumption, and achieve no The effect of pollutant emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
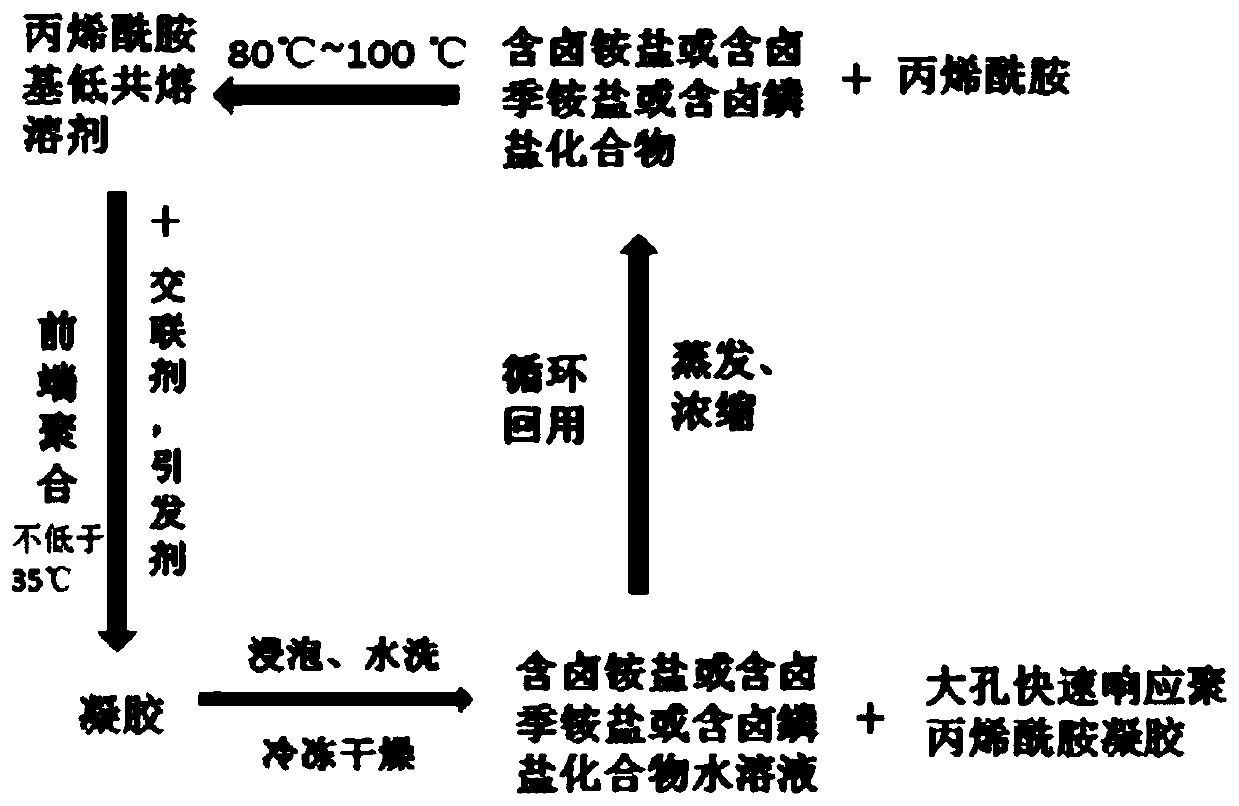
[0024] (1) Mix 7.1g of acrylamide and 27.6g of triethylamine hydrochloride and stir at 80°C until a transparent and clear liquid is formed, then cool to obtain an acrylamide-based deep eutectic solvent;
[0025] (2) Add 0.694g of N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide and 0.347g of potassium persulfate to the acrylamide-based deep eutectic solvent obtained in step (1) at 35°C to form a mixture solution, and then form Transfer the mixed solution of the mixture into the reactor test tube, heat the upper end of the reactor with an electric soldering iron, and cause the initiator to decompose under heat to initiate the reaction. After the thermal initiation reaction begins, remove the heat source until all the raw materials in the reactor are converted into polymers. gel;
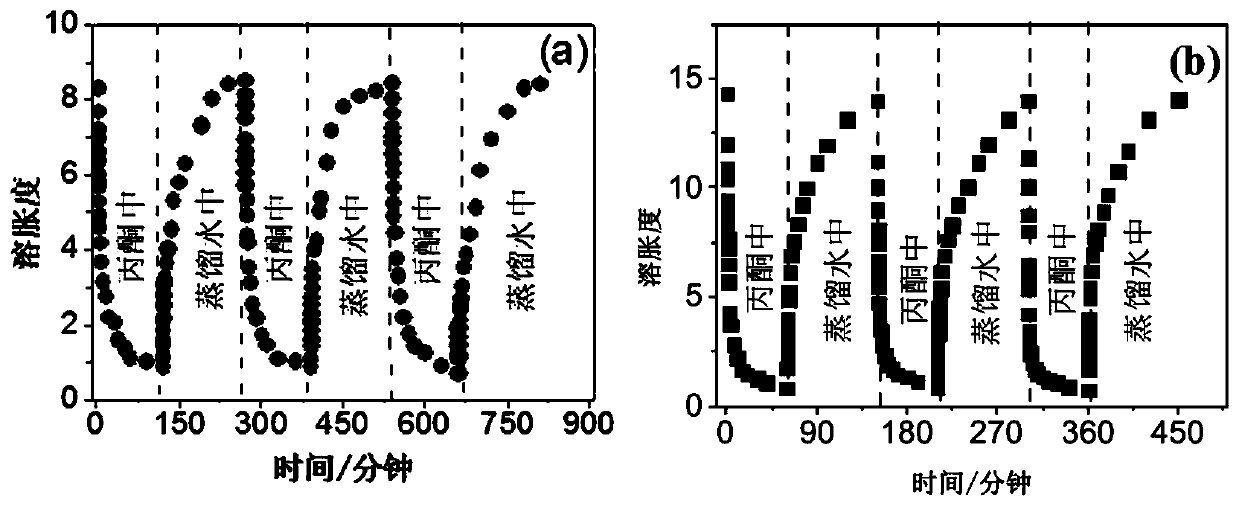
[0026] (3) Soak and wash the polymer gel obtained in step (2) with distilled water to remove triethylamine hydrochloride, and freeze-dry the polymer gel after soaking and washing to obtain the target macroporous fast-resp...
Embodiment 2
[0029] (1) Mix 7.1g of acrylamide and 28g of hydroxyethyltrimethylammonium chloride and stir at 80°C until a transparent and clear liquid is formed, then cool to obtain an acrylamide-based deep eutectic solvent;
[0030] (2) Add 0.702g of N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide and 0.351g of potassium persulfate to the acrylamide-based deep eutectic solvent obtained in step (1) at 35°C to form a mixture solution, and then form Transfer the mixed solution of the mixture into the reactor test tube, heat the upper end of the reactor with an electric soldering iron, and cause the initiator to decompose under heat to initiate the reaction. After the thermal initiation reaction begins, remove the heat source until all the raw materials in the reactor are converted into polymers. gel;
[0031](3) The polymer gel obtained in step (2) is soaked and washed with distilled water to remove hydroxyethyltrimethylammonium chloride, and the polymer gel after soaking and washing is freeze-dried to obtain t...
Embodiment 3
[0034] (1) Mix 7.1g of acrylamide and 59g of tetrabutylphosphonium chloride and stir at 80°C until a transparent and clear liquid is formed, then cool to obtain an acrylamide-based deep eutectic solvent;
[0035] (2) Add 1.322g of N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide and 0.661g of potassium persulfate to the acrylamide-based deep eutectic solvent obtained in step (1) at 35°C to form a mixture solution, and then form Transfer the mixed solution of the mixture into the reactor test tube, heat the upper end of the reactor with an electric soldering iron, and cause the initiator to decompose under heat to initiate the reaction. After the thermal initiation reaction begins, remove the heat source until all the raw materials in the reactor are converted into polymers. gel;
[0036] (3) Soak and wash the polymer gel obtained in step (2) with distilled water to remove tetrabutylphosphonium chloride, and freeze-dry the polymer gel after soaking and washing to obtain the target macroporous fast-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com