A kind of bio-based polyester polyurethane film and preparation method thereof
A polyester polyurethane, bio-based technology, applied in the field of bio-based polyester polyurethane film and its preparation, can solve the problems of lack of biodegradability, insufficient utilization of crop straw waste, etc., to achieve expanded utilization, excellent mechanical performance, the effect of expanding the scope of application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
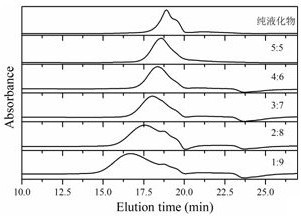
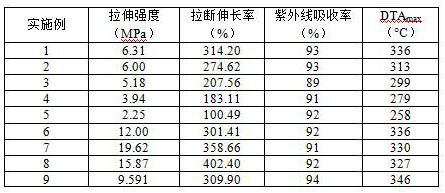
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] (1) Put 20 g of polyethylene glycol (molecular weight 400) and 5 g of glycerin into a three-necked flask and mix them, place them in an oil bath at 140 °C, add 1.75 g of concentrated sulfuric acid (98%) and 5 g of straw powder ( 50 mesh), stirred and reacted for 120 min. After the reaction, the reaction mixture was diluted with absolute ethanol, washed, filtered through a Buchner funnel to remove the residue, and the filtrate was removed by rotary evaporation (0.5 mbar, 65 ℃, 1 h). water ethanol to obtain straw liquefaction;
[0032] (2) Under a nitrogen atmosphere, take 2 g of straw liquefaction, 18 g ε -caprolactone and 0.4g stannous isooctanoate (40% mixed in a closed reaction flask, stirred and reacted at 120 °C for 8 h, after the reaction was completed, the reaction solution was transferred to 65 °C oven for overnight placement after rotary steaming under reduced pressure, To remove unreacted volatile components to obtain bio-based polycaprolactone polyols;
[0...
Embodiment 2
[0035] (1) Put 20 g of polyethylene glycol (molecular weight 400) and 5 g of glycerin into a three-necked flask and mix them, place them in an oil bath at 140 °C, add 1.75 g of concentrated sulfuric acid (98%) and 5 g of straw powder ( 50 mesh), stirred and reacted for 120 min. After the reaction, the reaction mixture was diluted with absolute ethanol, washed, filtered through a Buchner funnel to remove the residue, and the filtrate was removed by rotary evaporation (0.5 mbar, 65 ℃, 1 h). water ethanol to obtain straw liquefaction;
[0036] (2) Under a nitrogen atmosphere, take 4 g of straw liquefaction, 16 g ε -Caprolactone and 0.4g stannous isooctanoate are mixed in a closed reaction flask, stirred and reacted at 120°C for 8 h, after the reaction, the reaction solution is decompressed and rotary evaporated and then transferred to a 65°C oven for overnight placement to remove Unreacted volatile components to obtain bio-based polycaprolactone polyols;
[0037] (3) Take 2 g ...
Embodiment 3
[0039] (1) Put 20 g of polyethylene glycol (molecular weight 400) and 5 g of glycerin into a three-necked flask and mix them, place them in an oil bath at 140 °C, add 1.75 g of concentrated sulfuric acid (98%) and 5 g of straw powder ( 50 mesh), stirred and reacted for 120 min. After the reaction, the reaction mixture was diluted with absolute ethanol, washed, filtered through a Buchner funnel to remove the residue, and the filtrate was removed by rotary evaporation (0.5 mbar, 65 ℃, 1 h). water ethanol to obtain straw liquefaction;
[0040] (2) Under a nitrogen atmosphere, take 6 g of straw liquefaction, 14 g ε -Caprolactone and 0.4g stannous isooctanoate are mixed in a closed reaction flask, stirred and reacted at 120°C for 8 h, after the reaction, the reaction solution is decompressed and rotary evaporated and then transferred to a 65°C oven for overnight placement to remove Unreacted volatile components to obtain bio-based polycaprolactone polyols;
[0041] (3) Take 2 g of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com