Application of polypeptide compound in preparation of drugs for treating non-alcoholic liver disease, idiopathic pulmonary interstitial fibrosis and arteriosclerosis
A non-alcoholic technology for pulmonary interstitial fibrosis, applied in the field of biochemistry, can solve the problems of NASH and fibrosis, inflammation and cytotoxicity, etc., and achieve the effect of low toxicity, large safety window and small dosage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] The preparation of embodiment 1 compound 1-6:
[0068] Compounds 1-6 were synthesized from the carboxy-terminus to the amino-terminus by the Fmoc solid-phase peptide synthesis method, and the amino acid connection sequence was connected sequentially as described above. Specific steps are as follows:
[0069] ①Conditions: MBHAR (Amide-MBHA-Resin amide-protected MBHA resin) or Wang resin is used to synthesize the Fmoc protecting group by activating lipids.
[0070] ②Indene detection reagent:
[0071] Reagent 1: 20g phenol / 5ml ethanol
[0072] Reagent 2: 0.05 0.001M KCN (water) / 2.5ml pyridine
[0073] Reagent 3: 0.5g ninhydrin / 10ml ethanol
[0074] The use of indene detection reagent, reagent 1: reagent 2: reagent 3 = 1: 2: 1 (drops), heated in boiling water for 3-10min.
[0075] ③Process:
[0076] A. Resin treatment: Weigh a certain amount of MBHA resin (1% degree of cross-linking, 200-400 mesh, substitution value 0.5mmol / g) in the synthesizer, add DCM and stir fo...
Embodiment 2
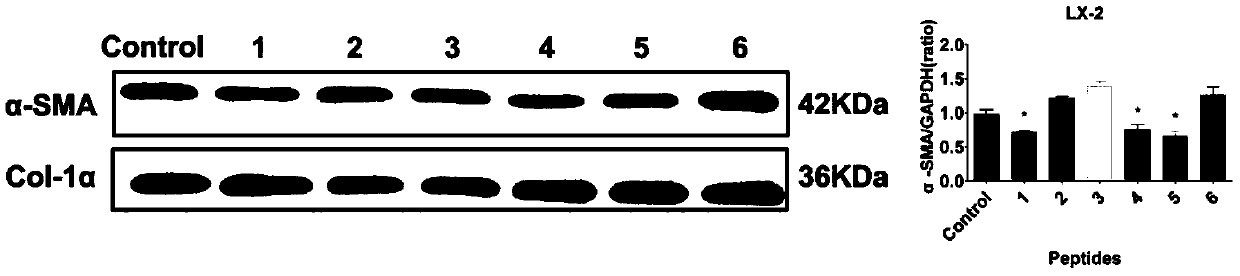
[0095] Example 2 Antioxidant Polypeptide 1-6 Anti-nonalcoholic Hepatitis and Liver Fibrosis Activity
[0096] 2.1 In vitro cell experiments of compounds 1-6:
[0097] By constructing two cell models (palmitic acid (PA)-induced steatosis model of human hepatoma cell (HepG2) and fibrosis model of human hepatic stellate cell (LX-2)), the active ingredients of compounds 1-6 were tested. preliminary determination.
[0098] 2.1.1 Compounds 1-6 improve PA-induced fatty degeneration of HepG2 cells:
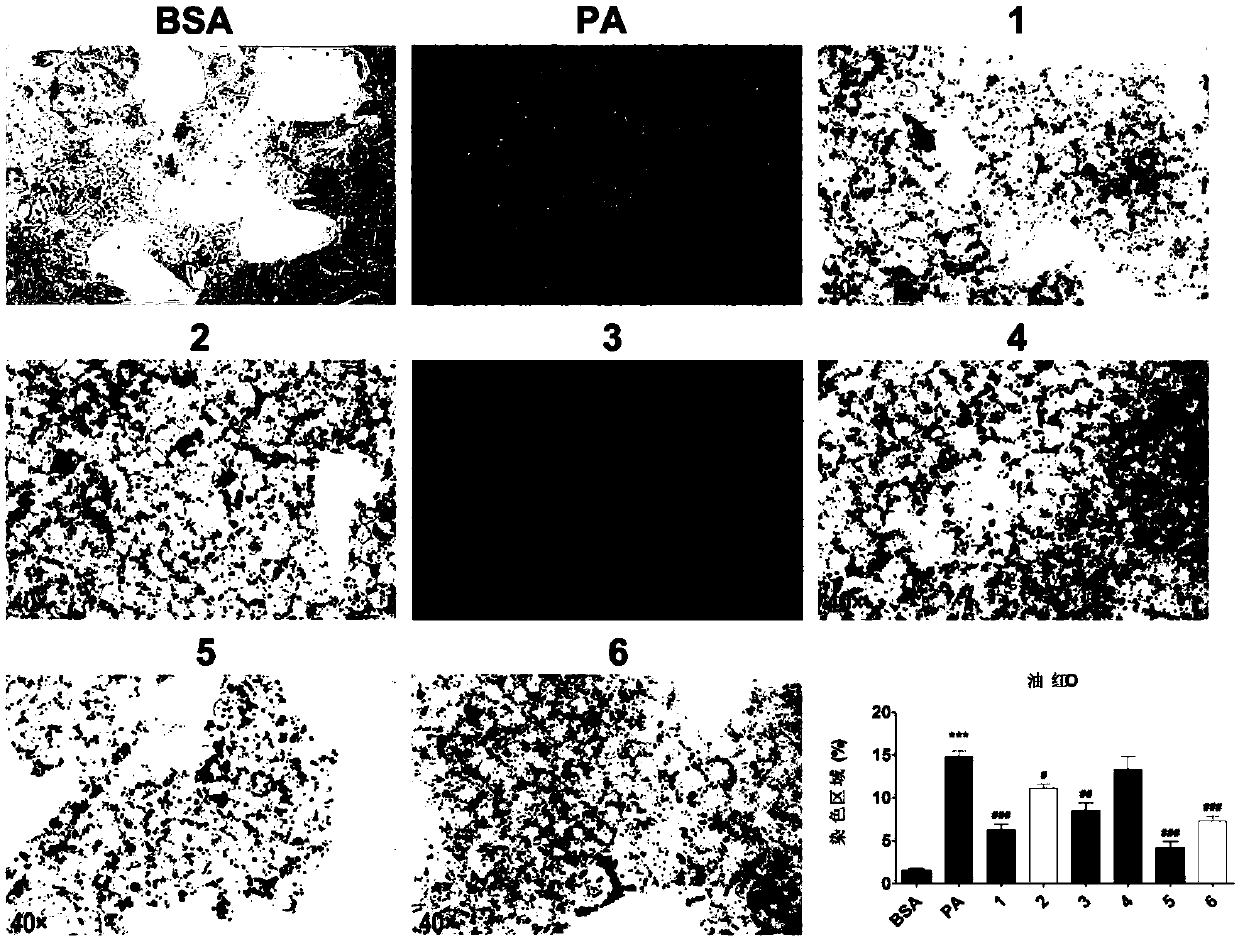
[0099] After the HepG2 cells adhered to the wall for 24 hours, and the degree of fusion reached 70-80%, the HepG2 cells were induced with PA (final concentration of 24 hours) for 24 hours, and then 100 uM compound 1-6 was added to the experimental group, and the same dose of PBS was added to the control group. After 24 hours of action , Oil red O staining was performed to detect the effect of drugs on fatty degeneration cells. figure 1 In the middle, the red area is the oil red O stain...
Embodiment 3
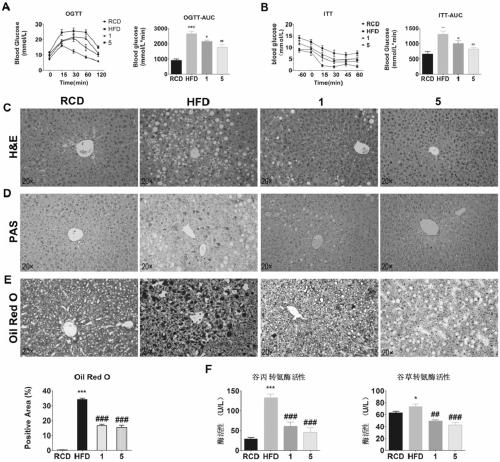
[0147] Example 3 Compound 5's Therapeutic Efficacy Study on Pulmonary Fibrosis
[0148] (1) Materials and methods
[0149] animal:
[0150] 8-week-old SPF-grade female C57BL / 6 mice, 20-25g, were provided by the Guangdong Provincial Experimental Animal Center, and experiments were carried out in the SPF-grade laboratory of the Experimental Animal Center of the School of Pharmacy, Sun Yat-sen University. Adaptive feeding for 1 week. Breeding environment: a room with a temperature of 20-25°C, a humidity of 70%, and a controlled light-dark cycle of 12 hours, with free access to food and water.
[0151] Drugs and reagents:
[0152] Bleomycin (BLM, purchased from TCI); pentobarbital sodium, bleomycin hydrochloride for injection, hydroxyproline (HYP) standard (purchased from Sigma, USA).
[0153] (2) Establishment of an animal model of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis:
[0154] Twenty-four SPF female C57BL / 6 mice were randomly divided into 3 groups (n=8), 3 groups in total: ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com