A kind of senescence-related nap transcription factor of moso bamboo and its coding gene and application
A transgenic plant and gene technology, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant gene improvement and other directions, can solve the problems of lack of regulatory function analysis, specificity and complexity increasing the difficulty of research on the aging mechanism of Phyllostachys edulis, unclear aging regulatory mechanism, etc. Achieve significant effect and promote the effect of aging process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
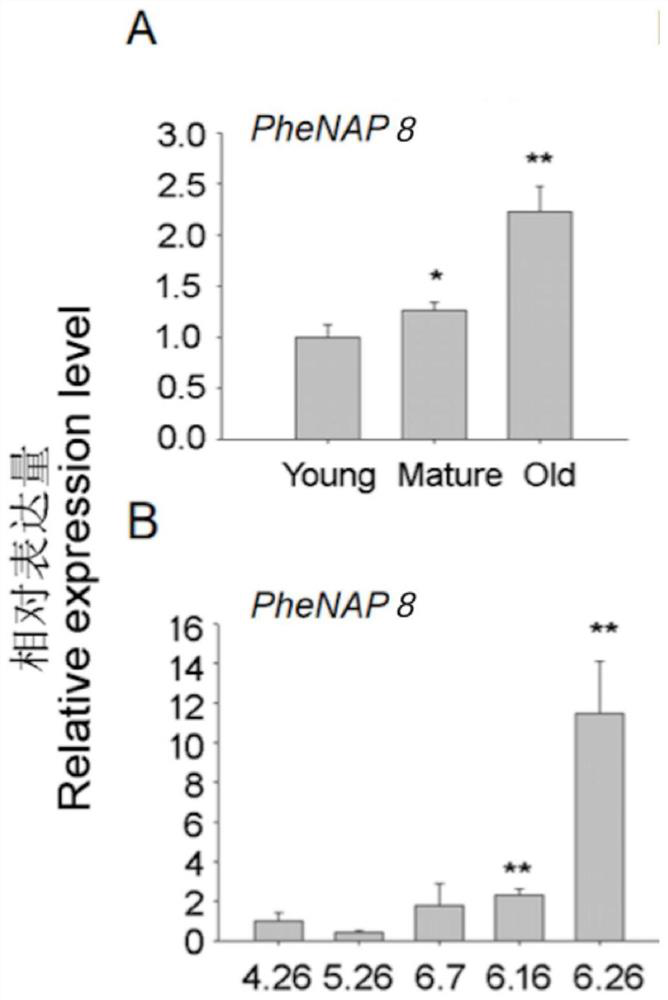
[0053] Example 1 Analysis and identification of the senescence-related gene PheNAP8 in Phyllostachys pubescens
[0054] 1) According to Li (2019) results of postharvest senescence transcriptome sequencing, the number of up-regulated expression among NAC family members was the largest, among which there were 11 PheNAC genes whose expression was basically not detected at 0h postharvest (RPKM<0.3). The expression was significantly upregulated during storage (Table 1). Among them, PheNAP8 has a similar expression pattern, all of which are rapidly up-regulated at 12-24 hours after harvest, and the up-regulation fold (greater than 120) is higher than that of other PheNAC genes, which has an extremely significant or even unexpected up-regulation effect.
[0055] Table 1. Expression analysis of 11 PheNAC genes in Phyllostachys pubescens after harvest (transcriptome sequencing)
[0056]
[0057]
[0058] 2) Expression analysis of PheNAP8 in seedling leaves and flowering leaves o...
Embodiment 2
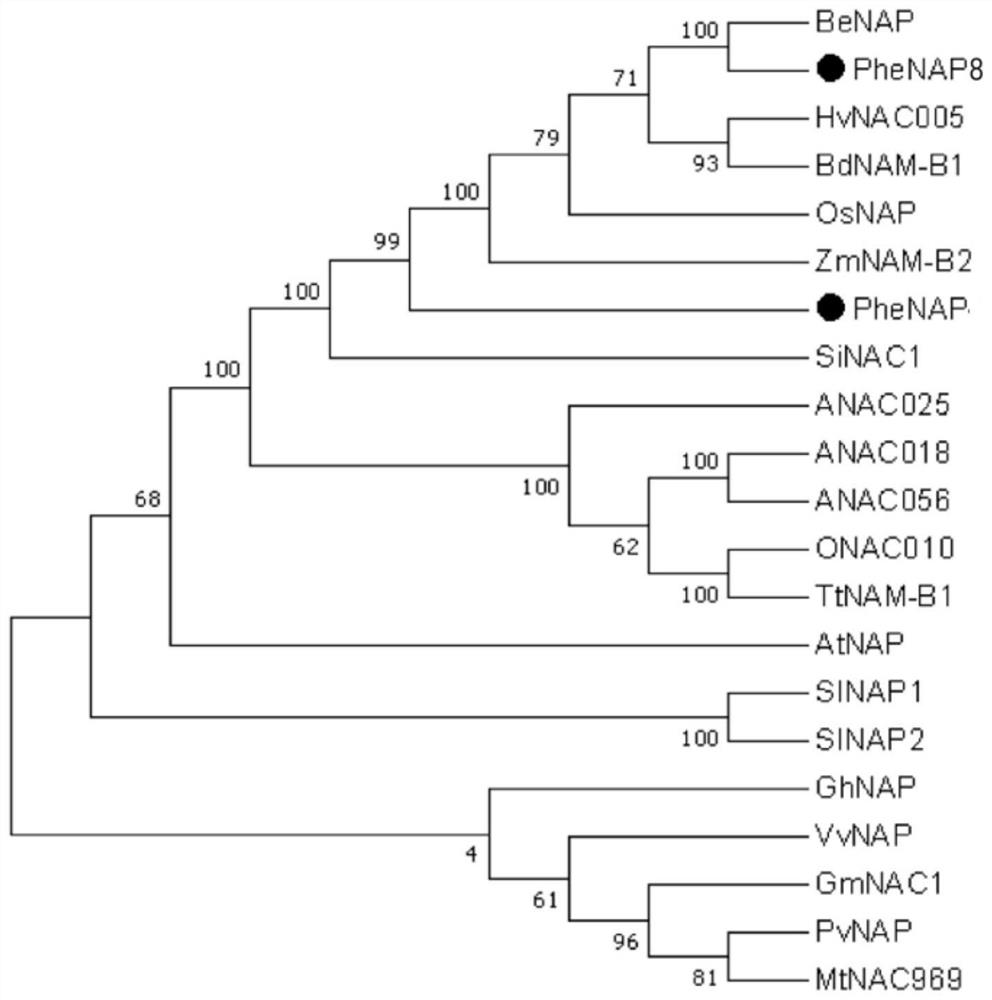
[0067] Example 2 PheNAP8 gene evolution analysis.
[0068] The amino acid sequences of the reported NAP subfamily members were downloaded from the NCBI database, respectively. Through ClustalX1.83 (http: / / www.clustal.org / ), the protein sequence encoded by the PheNAP8 gene of Phyllostachys pubescens was compared with the NAP protein sequences of other species (Thompson et al., 1997), and MEGA 7.0 A rootless phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method (bootstrap value was set to 1000). The results showed that PheNAP8 of Phyllostachys pubescens had high homology with other reported NAP transcription factors, and the sequence similarity between PheNAP8 and BeNAC1 of Bamboo chinensis was the highest ( figure 2 ), but there is no 100% homologous gene, which proves that PheNAP8 is a brand-new gene that has not been reported in the prior art, and is a kind of NAC transcription factor. Members of the NAP subfamily mainly come from Arabidopsis (ANAC018, NP_175...
Embodiment 3
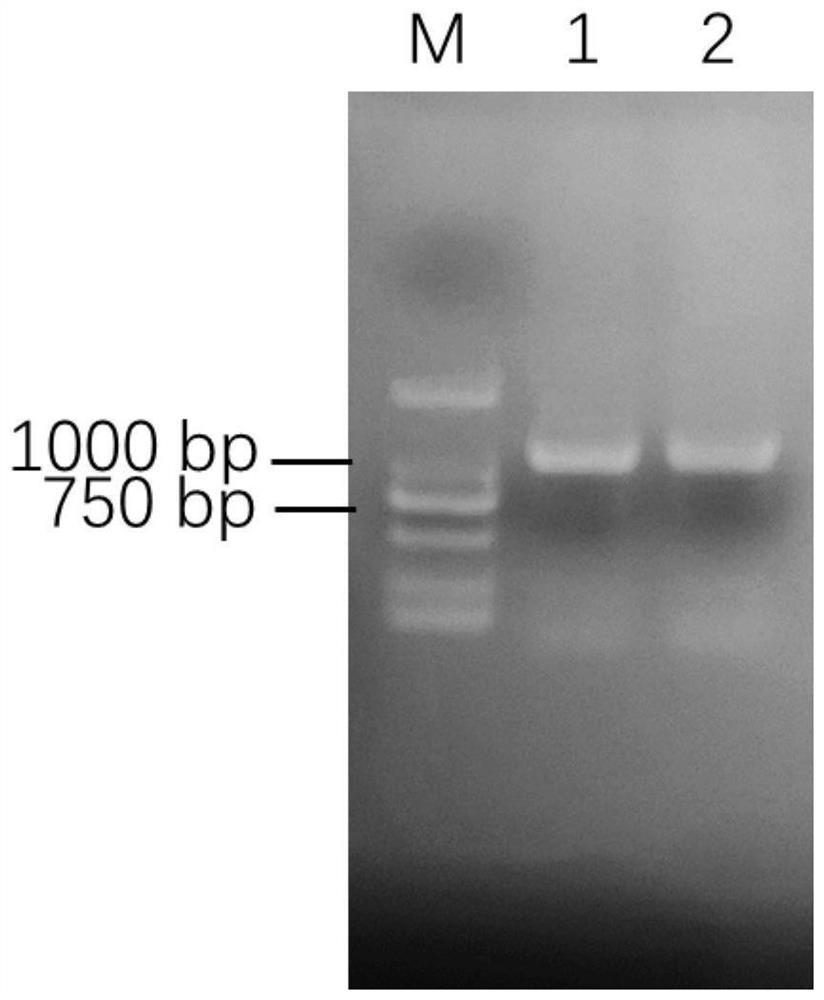
[0069]Example 3 Acquisition of the gene encoding the PheNAP8 transcription factor of Phyllostachys pubescens
[0070] The material used in this example is moso bamboo leaves, which are stored at -80°C after quick-freezing in liquid nitrogen.
[0071] 1) Extraction of total RNA from leaves of Phyllostachys pubescens
[0072] Carry out the extraction of total RNA and the synthesis of first-strand cDNA according to the method of embodiment 1
[0073] 3) RT-PCR amplification of the PheNAP8 gene sequence
[0074] The full-length primers were designed according to the Phyllostachys pubescens genome database, which are: NAP1-F: 5'-ATGATGATGTCGAACCCGG-3' (SEQ ID NO.7) and NAP1-R: 5'-TCAGTTCATCCCCATGTTTGAAT-3' (SEQ ID NO.8). The reverse transcription product was used as a template, and NAP1-F and NAP1-R were used as primers for PCR amplification. PCR products were subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis ( image 3 ), recover the target product, connect with pGEMT-easy, transform E...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com